Mapa choropleth to rodzaj mapy tematycznej, na której obszary administracyjne są pokolorowane lub zacienione zgodnie z wartością danych. Funkcja fabryki stylów umożliwia stylizowanie mapy na podstawie danych, w których każdy obszar administracyjny jest powiązany z zakresem wartości liczbowych. Przykładowa mapa poniżej przedstawia mapę tematyczną stanów USA.
W tym przykładzie dane składają się z identyfikatora miejsca stanu. Funkcja fabryczna style warunkowo koloruje każdy stan na podstawie zahaszowanej wartości identyfikatora miejsca dla tego stanu.
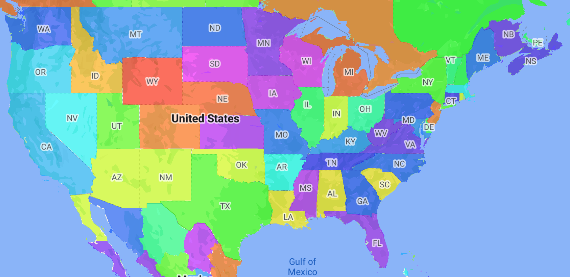
Jeśli nie masz jeszcze identyfikatora mapy i stylu mapy, wykonaj czynności opisane w sekcji Pierwsze kroki. Pamiętaj, aby włączyć warstwę funkcji Administrative Area Level 1 (Region administracyjny poziomu 1).
Uzyskaj odniesienie do warstwy obiektów Obszar administracyjny – poziom 1 po zainicjowaniu mapy. W przypadku Stanów Zjednoczonych te poziomy administracyjne odpowiadają poszczególnym stanom.
Java
private FeatureLayer areaLevel1Layer;
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { areaLevel1Layer = map.getFeatureLayer(new FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build());
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer(); }Kotlin
private var areaLevel1Layer: FeatureLayer? = null
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Get the ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 feature layer. areaLevel1Layer = googleMap.getFeatureLayer(FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build())
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer() }Utwórz funkcję fabryki stylów i zastosuj ją do warstwy funkcji Obszar administracyjny – poziom 1. W tym przykładzie funkcja jest stosowana do wielokąta reprezentującego każdy stan w Stanach Zjednoczonych.
Java
private void styleAreaLevel1Layer() { FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> { if (feature instanceof PlaceFeature) { PlaceFeature placeFeature = (PlaceFeature) feature;
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. int hueColor = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300; if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300; }
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, new float[] {hueColor, 1, 1})) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }Kotlin
private fun styleAreaLevel1Layer() { val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature -> if (feature is PlaceFeature) { val placeFeature: PlaceFeature = feature as PlaceFeature
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. var hueColor: Int = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300 if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300 } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, floatArrayOf(hueColor.toFloat(), 1f, 1f))) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }

