Introduzione
I codici a barre ruotati hanno lo stesso aspetto dei normali codici a barre, ma cambiano periodicamente solitamente ogni minuto e il terminale/lettore è programmato per accettare il più recente. Questa misura di sicurezza riduce i rischi associati a screenshot del codice a barre, in particolare furto o furto di biglietti non autorizzati rivendibili. La rotazione dei codici a barre può anche fungere da riserva per i dispositivi che non possono sfruttare Smart Tap per il mancato supporto della tecnologia NFC (assenza di hardware oppure disattivato).
Riferimento API
Per i dettagli tecnici sui codici a barre rotanti, vedere
Tipo di RotatingBarcode.
Payload di esempio
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
Meccanismi di riserva
Sul dispositivo dell'utente viene utilizzato un solo meccanismo di utilizzo alla volta, in base alla configurazione della tessera e alle funzionalità del dispositivo. In ordine di priorità, vengono utilizzati i seguenti tipi di utilizzo:
-
Smart Tap: se è specificato un payload smart-tap e se il dispositivo supporta
NFC/HCE
- Tieni presente che questo valore può essere ignorato dall'utente facendo clic su "Mostra codice", che forzerà la visualizzazione del codice a barre rotante/statico.
- Rotazione del codice a barre: se viene specificato un payload di rotazione del codice a barre
- Codice a barre statico: se viene specificato un payload del codice a barre
La specifica di più payload di riscatto può garantire il supporto di tutti gli utenti, ma potrebbe avere implicazioni per la sicurezza. In particolare, l'uso di un codice a barre statico di riserva per un codice a barre rotante annulla la maggior parte dei vantaggi in termini di sicurezza codici a barre rotanti. Un codice a barre di riserva statico verrà mostrato solo nelle visualizzazioni web o su client che non supportano la rotazione dei codici a barre. A partire da oggi, prevediamo tutti i client Google Wallet per supportare la rotazione dei codici a barre.
Salva flusso
L'API Google Wallet offre diversi flussi, tra cui:
- Creare i corsi con le carte regalo in anticipo o in un momento in cui non hai fretta
- Invio degli oggetti completi nel JWT o salvataggio degli oggetti prima per poi farvi riferimento per ID nel tuo JWT
- Aggiornamento degli oggetti dopo il salvataggio
Il campo rotatingBarcode proposto è compatibile con tutti questi flussi, tuttavia, per migliorare la sicurezza, consigliamo quanto segue:
-
Chiama l'API
object:insertper inserire la tessera nella server di Google Wallet e configura il pulsante Aggiungi a Google Wallet per fare riferimento all'oggetto specifico per ID nel tuo JWT. Ciò garantisce che il JWT risultante non include il codice segreto del codice a barre rotante. - Usa una chiave segreta OTP che abbia come ambito una singola tessera
- La chiave, a meno che non venga aggiornata, dovrebbe essere valida per tutta la durata della tessera. Non prevediamo che questa chiave venga aggiornata con alcuna frequenza durante il normale funzionamento.
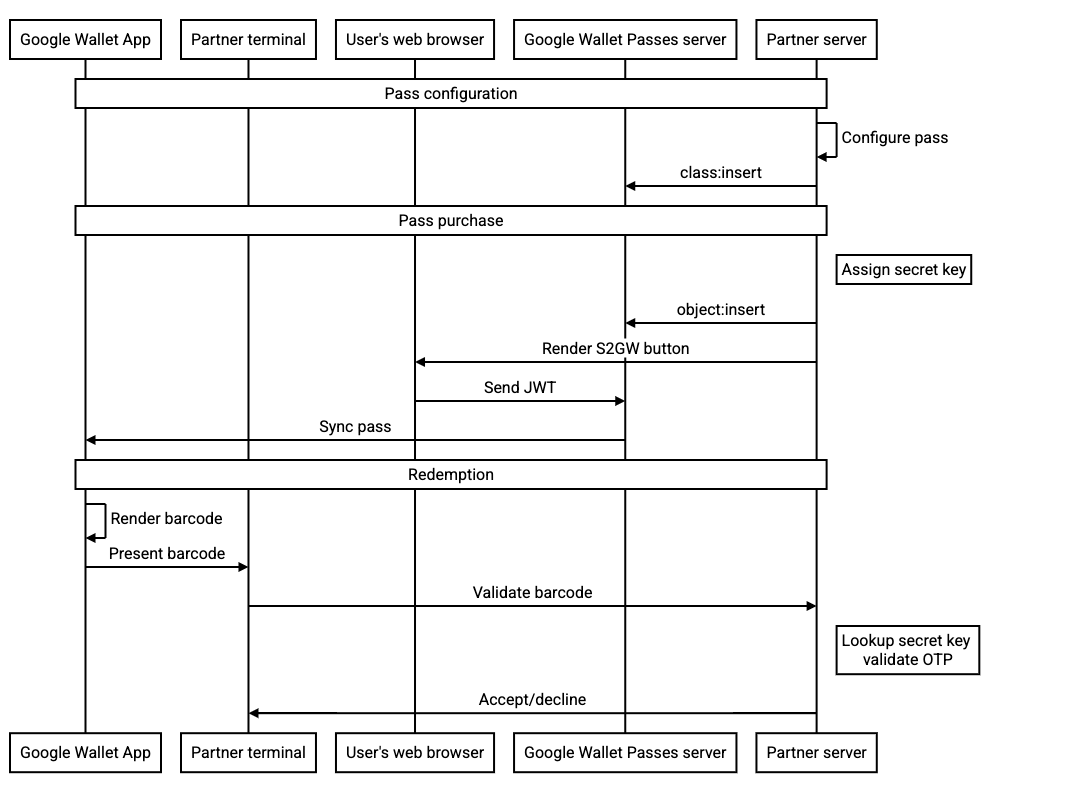
Il seguente diagramma di sequenza illustra il flusso tra i vari attori per un'integrazione tipica: