이 문서에서는 Actions on Google과 맞춤 대화 사용자 인터페이스를 정의하는 처리 서비스 간에 통신하기 위한 웹훅 형식을 설명합니다.
Actions on Google과 처리가 Actions on Google 웹훅 형식을 통해 통신하는 방식을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.
- Actions on Google과의 대화에 참여하기 위해 처리에서 Actions on Google의 HTTP 요청에 응답할 수 있는 웹훅을 구현합니다.
- 사용자가 작업을 호출하면 처리는 사용자의 요청을 설명하는 JSON 페이로드가 포함된
HTTP POST를 수신합니다. - 그러면 처리는 요청 페이로드에서 매개변수를 읽고, 적절한 JSON 형식의 응답을 생성하고, 이 응답으로 어시스턴트에 응답을 전송합니다.
요청 유형
다음 표에는 웹훅이 어시스턴트에서 수신할 수 있는 요청 유형이 요약되어 있습니다.
| 유형 | 설명 | JSON 예 |
|---|---|---|
| 호출 요청 | 처리와 대화를 시작하거나 딥 링크 작업을 트리거하는 사용자 발화 (예: '개인 요리사에게 저녁 식사 레시피 찾아 줘')
|
|
| 대화 요청 | 처리와의 대화가 시작된 후 동일 세션에서의 사용자 발화입니다. 대화 웹훅 형식에서 이는 처리에서 이전 차례에 요청한 actions.intent.TEXT 인텐트에 해당하는 사용자의 원시 텍스트 응답입니다. |
|
| 도우미 결과 | 웹훅이 대화의 일부 (예: actions.intent.OPTION, actions.intent.PERMISSION)를 처리하기 위해 이전 대화 차례에서 도우미 인텐트를 요청한 경우 어시스턴트가 처리에 전송한 요청입니다. |
대화 요청 및 응답
일반적인 Actions on Google 상호작용 시나리오에서 사용자는 작업을 호출하는 문구를 말합니다. 응답을 제공하기 위해 Actions on Google은 사용자가 호출한 작업과 일치하는 처리를 찾아 요청을 전송합니다.
Actions on Google은 처리가 사용자의 호출에 적합하다고 판단하면 사용자의 요청 정보와 함께 JSON 페이로드가 포함된 HTTP 요청을 처리 엔드포인트로 전송하여 대화 세션을 시작합니다. 처리는 요청을 파싱하고 JSON 페이로드가 포함된 응답을 반환합니다. 그러면 Actions on Google이 사용자를 위해 페이로드를 렌더링된 음성 및 멀티미디어 출력으로 변환합니다.
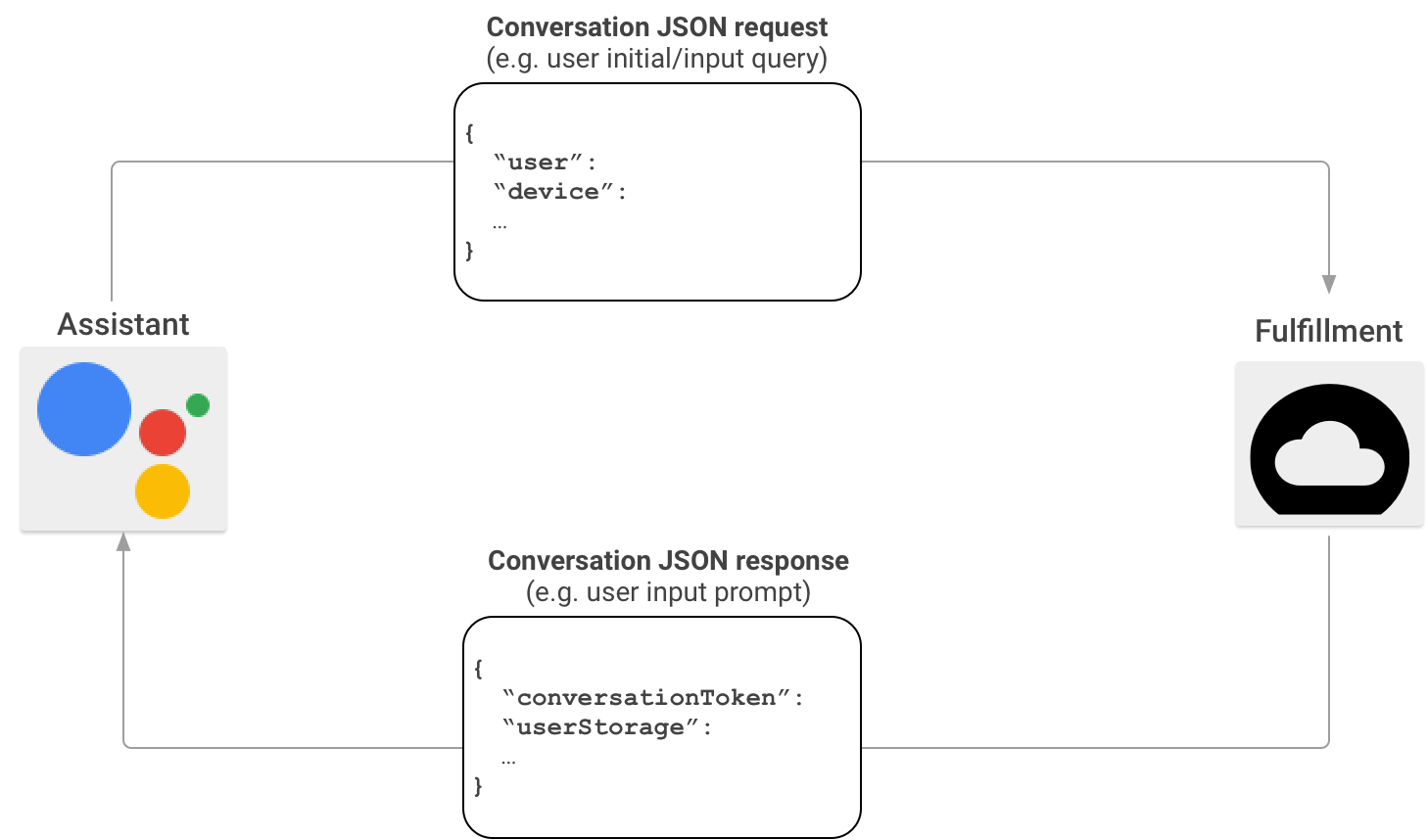
Actions on Google에서 Actions SDK를 통해 처리를 호출할 때 JSON 페이로드 형식에 대한 자세한 내용은 대화 웹훅 형식을 참조하세요.
Dialogflow 요청 및 응답
작업을 만들 때 선택적으로 Dialogflow를 사용하여 대화 인터페이스 빌드 작업을 간소화할 수 있습니다. 이 시나리오에서 Dialogflow는 Actions on Google과 처리 간의 프록시 역할을 합니다. Actions on Google은 HTTP/JSON 요청을 처리 엔드포인트로 직접 전송하는 대신 Dialogflow로 전송합니다.
Dialogflow는 원래 요청에 포함된 JSON 페이로드를 Dialogflow 웹훅 형식으로 래핑하고 결과 요청을 Dialogflow 처리로 전달합니다.
반대로, fulfillment가 Dialogflow에 응답을 전송할 때 응답의 JSON 페이로드는 Dialogflow 웹훅 형식을 준수해야 합니다. 처리는 Dialogflow JSON 요청에서 매개변수를 파싱하고 Dialogflow 웹훅 형식으로 응답을 생성합니다. 그러면 Dialogflow는 처리의 응답을 어시스턴트가 이해할 수 있는 응답 메시지로 변환합니다.
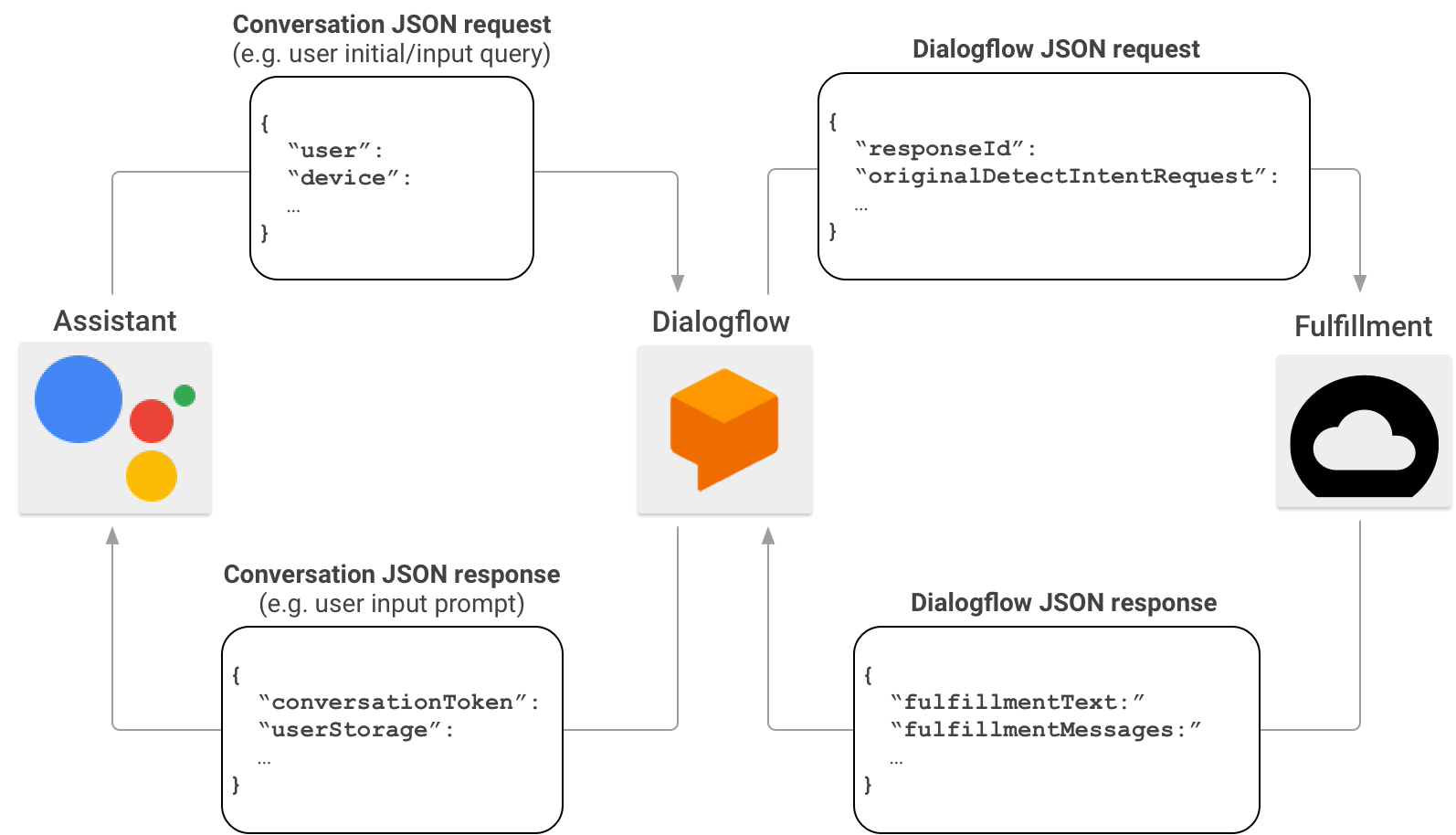
Actions on Google에서 Dialogflow를 통해 처리를 호출할 때 JSON 페이로드 형식에 대한 자세한 내용은 Dialogflow 웹훅 형식을 참조하세요.