इस पेज पर, प्रोग्राम के ज़रिए किसी डेटासेट को ऐक्सेस करने और उसकी स्टाइल तय करने का तरीका बताया गया है. साथ ही, इसमें पॉइंट, पॉलीगॉन, और पॉलीलाइन ज्यामिति के आधार पर डेटा फ़ीचर के स्टाइलिंग उदाहरण दिए गए हैं.
डेटासेट के लिए डेटा के हिसाब से स्टाइलिंग की सुविधा, डेटा की सुविधाओं को रेंडर करती है. यह सुविधा, डेटासेट बनाने के लिए इस्तेमाल की गई जियोस्पेशल डेटा फ़ाइल से मिले अक्षांश और देशांतर के कोऑर्डिनेट के आधार पर काम करती है.
पॉइंट डेटा की स्टाइलिंग का उदाहरण
इस उदाहरण में, पॉइंट ज्यामिति पर आधारित डेटा सुविधाओं को स्टाइल करने का तरीका दिखाया गया है.

डेटासेट के बारे में जानकारी
इस उदाहरण में इस्तेमाल किया गया डेटासेट, न्यूयॉर्क सिटी के सेंट्रल पार्क में साल 2018 में गिलहरियों पर किए गए सर्वे का नतीजा है. CSV डेटा फ़ाइल के इस उदाहरण में, x और y कॉलम का इस्तेमाल जगह की जानकारी के लिए किया गया है. इसमें LatLng कॉलम शामिल है, लेकिन इसका इस्तेमाल इस उदाहरण में नहीं किया गया है. ऐसा इसलिए है, क्योंकि डेटासेट सिर्फ़ WKT फ़ॉर्मैट के साथ काम करते हैं. हालांकि, ऐसा तब होता है, जब कॉलम का नाम WKT हो. जगह की जानकारी के लिए इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले फ़ॉर्मैट के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, CSV फ़ाइल से जुड़ी ज़रूरी शर्तें देखें.
गिलहरी की जनगणना वाले डेटासेट में, गिलहरियों के फ़रों के रंग और उनके व्यवहार से जुड़े अलग-अलग डेटा पॉइंट शामिल हैं. सभी डेटा पॉइंट देखने के लिए, हॉरिज़ॉन्टल स्क्रोल करना न भूलें.
| X | Y | UniqueSquirrelID | हैक्टेयर | Shift | तारीख | Hectare SquirrelNumber | उम्र | PrimaryFurColor | HighlightFurColor | CombinationofPrimaryandHighlightColor | Colornotes | जगह | AboveGroundSighter मेज़रमेंट | SpecificLocation | दौड़ना | जानवर का पीछा जारी है | क्लाइंबिंग | खाना | चारा ढूंढना | अन्य गतिविधियां | Kuks | Quaas | Moans | Tailflags | Tailtwitches | तरीके | उदासीन | Runsfrom | OtherInteractions | LatLng |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -73.9561344937861 | 40.7940823884086 | 37F-PM-1014-03 | 37F | PM | 10142018 | 3 | + | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | POINT (-73.9561344937861 40.7940823884086) | |||||||||
| -73.9688574691102 | 40.7837825208444 | 21B-AM-1019-04 | 21B | AM | 10192018 | 4 | + | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | POINT (-73.9688574691102 40.7837825208444) | |||||||||
| -73.9742811484852 | 40.775533619083 | 11B-PM-1014-08 | 11B | PM | 10142018 | 8 | स्लेटी | स्लेटी+ | Above Ground | 10 | गलत | सही | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | POINT (-73.97428114848522 40.775533619083) | ||||||
| -73.9596413903948 | 40.7903128889029 | 32E-PM-1017-14 | 32E | PM | 10172018 | 14 | वयस्क | स्लेटी | स्लेटी+ | किसी भी पते को मुख्य पते के तौर पर नहीं चुना गया है. हाइलाइट के तौर पर चुने गए आइटम को ग्रे रंग में दिखाया गया है. कार्यकारी अडजस्टमेंट किए गए. | गलत | गलत | गलत | सही | सही | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | सही | POINT (-73.9596413903948 40.7903128889029) | ||||||
| -73.9702676472613 | 40.7762126854894 | 13E-AM-1017-05 | 13E | AM | 10172018 | 5 | वयस्क | स्लेटी | दालचीनी | स्लेटी+दालचीनी | Above Ground | पेड़ के ठूंठ पर | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | सही | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | POINT (-73.9702676472613 40.7762126854894) | ||||
| -73.9683613516225 | 40.7725908847499 | 11H-AM-1010-03 | 11 घंटे | AM | 10102018 | 3 | वयस्क | दालचीनी | सफ़ेद | सिनेमन+सफ़ेद | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | सही | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | सही | गलत | सही | गलत | POINT (-73.9683613516225 40.7725908847499) | ||||||
| -73.9541201789795 | 40.7931811701082 | 36H-AM-1010-02 | 36 घंटे | AM | 10102018 | 2 | वयस्क | स्लेटी | स्लेटी+ | सिर्फ़ हैक्टेयर के बाहर | ग्राउंड प्लेन | FALSE | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | सही | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | गलत | POINT (-73.9541201789795 40.7931811701082) |
पॉइंट डेटा को स्टाइल करने की सुविधाएं
इस उदाहरण में दिए गए कोड में, हर पॉइंट के फ़िल कलर और स्ट्रोक कलर को स्टाइल करने के लिए, CombinationofPrimaryandHighlightColor एट्रिब्यूट का इस्तेमाल किया गया है. इस एट्रिब्यूट में, हर गिलहरी के लिए फ़रों के मुख्य और दूसरे रंग को शामिल किया गया है.
Kotlin
private fun styleDatasetsLayer() {
// Create the style factory function. val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature ->
// Set default colors to to yellow and point radius to 8. var fillColor = Color.YELLOW var strokeColor = Color.YELLOW var pointRadius = 8F // Check if the feature is an instance of DatasetFeature. if (feature is DatasetFeature) {
val furColors: MutableMap<String, String> = feature.getDatasetAttributes() // Determine CombinationofPrimaryandHighlightColor attribute. val furColor = furColors!!["CombinationofPrimaryandHighlightColor"] when (furColor) { "Black+" -> { fillColor = Color.BLACK strokeColor= Color.BLACK } "Cinnamon+" -> { fillColor = -0x750000 strokeColor= -0x750000 } "Cinnamon+Gray" -> { fillColor = -0x750000 strokeColor= -0x750000 pointRadius = 6F } "Cinnamon+White" -> { fillColor = -0x750000 strokeColor= Color.WHITE pointRadius = 6F } "Gray+" -> fillColor = Color.GRAY "Gray+Cinnamon" -> { fillColor = Color.GRAY strokeColor= -0x750000 pointRadius = 6F } "Gray+Cinnamon, White" -> { fillColor = Color.LTGRAY strokeColor= -0x750000 pointRadius = 6F } "Gray+White" -> { fillColor = Color.GRAY strokeColor= Color.WHITE pointRadius = 6F } } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() .fillColor(fillColor) .strokeColor(strokeColor) .pointRadius(pointRadius) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. datasetLayer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }
Java
private void styleDatasetsLayer() {
// Create the style factory function. FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> {
// Check if the feature is an instance of DatasetFeature. if (feature instanceof DatasetFeature) {
// Determine CombinationofPrimaryandHighlightColor attribute. Map<String, String> furColors = ((DatasetFeature) feature).getDatasetAttributes(); String furColor = furColors.get("CombinationofPrimaryandHighlightColor"); // Set default colors to to yellow and point radius to 8. int fillColor = Color.YELLOW; int strokeColor = Color.YELLOW; int pointRadius = 8; switch (furColor) { case "Black+": fillColor = Color.BLACK; strokeColor = Color.BLACK; break; case "Cinnamon+": fillColor = 0xff8b0000; strokeColor = 0xff8b0000; break; case "Cinnamon+Gray": fillColor = 0xff8b0000; strokeColor = Color.GRAY; pointRadius = 6; break; case "Cinnamon+White": fillColor = 0xff8b0000; strokeColor = Color.WHITE; pointRadius = 6; break; case "Gray+": fillColor = Color.GRAY; strokeColor = Color.GRAY; break; case "Gray+Cinnamon": fillColor = Color.GRAY; strokeColor = 0xff8b0000; pointRadius = 6; break; case "Gray+Cinnamon, White": fillColor = Color.LTGRAY; strokeColor = 0xff8b0000; pointRadius = 6; break; case "Gray+White": fillColor = Color.GRAY; strokeColor = Color.WHITE; pointRadius = 6; break; default: fillColor = Color.YELLOW; strokeColor = Color.YELLOW; pointRadius = 8; } return new FeatureStyle.Builder() .fillColor(fillColor) .strokeColor(strokeColor) .pointRadius(pointRadius) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. datasetLayer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }
पॉलीगॉन डेटा की स्टाइलिंग का उदाहरण
इस उदाहरण में, पॉलीगॉन ज्यामिति पर आधारित डेटा फ़ीचर को स्टाइल करने का तरीका दिखाया गया है.
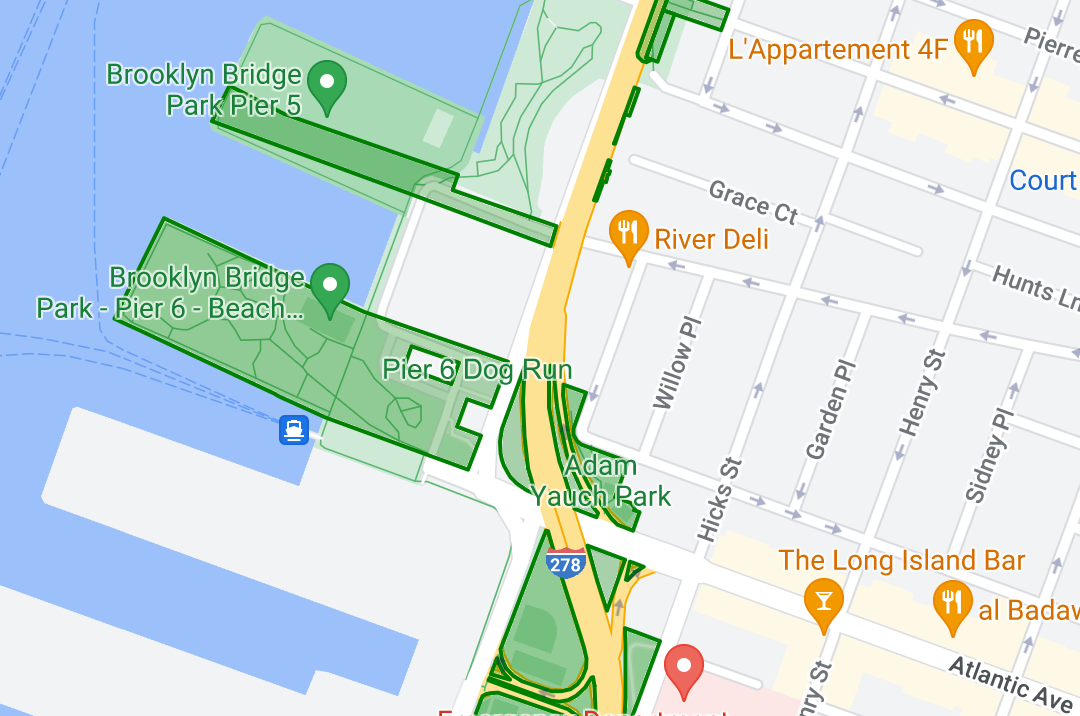
डेटासेट के बारे में जानकारी
इस उदाहरण में इस्तेमाल किए गए डेटासेट में, न्यूयॉर्क सिटी के पार्क दिखाए गए हैं. डेटासेट की GeoJSON फ़ाइल के इस उदाहरण में, एक फ़ीचर एंट्री दिखाई गई है.
{ "type": "Feature", "properties": { "jurisdiction": "DPR", "mapped": "False", "zipcode": "11356", "acres": "0.05", "location": "College Pl., College Pt. Blvd., bet. 11 Ave. and 12 Ave.", "nys_assembly": "27", "councildistrict": "19", "url": "http://www.nycgovparks.org/parks/Q042/", "typecategory": "Triangle/Plaza", "us_congress": "14", "eapply": "Poppenhusen Park", "parentid": "Q-07", "gispropnum": "Q042", "retired": "false", "communityboard": "407", "objectid": "6248", "globalid": "F4810079-CBB9-4BE7-BBFA-B3C0C35D5DE5", "name311": "Poppenhusen Park", "department": "Q-07", "pip_ratable": "true", "subcategory": "Sitting Area/Triangle/Mall", "precinct": "109", "permit": "true", "acquisitiondate": null, "omppropid": "Q042", "gisobjid": "100000301", "signname": "Poppenhusen Park", "address": null, "permitparent": "Q-07", "class": "PARK", "nys_senate": "11", "permitdistrict": "Q-07", "borough": "Q", "waterfront": "false" }, "geometry": { "type": "MultiPolygon", "coordinates": [ [ [ [ -73.84575702371716, 40.78796240884273 ], [ -73.84593393292693, 40.78796857347548 ], [ -73.84577256469657, 40.787651355629556 ], [ -73.84575702371716, 40.78796240884273 ] ] ] ] } },
पॉलीगॉन डेटा फ़ीचर की स्टाइल बदलना
इस उदाहरण में दिया गया कोड, "Undeveloped" या "Parkway" की typecategory से जुड़ी डेटा सुविधाओं पर खास रंग लागू करता है. साथ ही, अन्य सभी सुविधाओं को हरे रंग में दिखाता है.
Kotlin
private fun styleDatasetsLayer() {
// Create the style factory function. val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature ->
// Check if the feature is an instance of DatasetFeature. if (feature is DatasetFeature) { // Determine the value of the typecategory attribute. val typeCategories: MutableMap<String, String> = feature.getDatasetAttributes() val typeCategory = typeCategories!!["typecategory"] // Set default colors to green. var fillColor = 0x4000ff00 var strokeColor = 0xff00ff00 when (typeCategory) { "Undeveloped" -> { // Color undeveloped areas blue. fillColor = 0x400000ff strokeColor = 0x400000ff } "Parkway" -> { // Color parkway areas red. fillColor = 0x40ff0000 strokeColor = 0x40ff0000 } else -> { // Color all other areas green. fillColor = 0x4000ff00 strokeColor = 0xff00ff00 } } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() .fillColor(fillColor) .strokeColor(strokeColor) .strokeWidth(2F) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. datasetLayer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }
Java
private void styleDatasetsLayer() {
// Create the style factory function. FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> {
// Check if the feature is an instance of DatasetFeature. if (feature instanceof DatasetFeature) {
// Determine the value of the typecategory attribute. Map<String, String> typeCategories = ((DatasetFeature) feature).getDatasetAttributes(); String typeCategory = typeCategories.get("typecategory"); // Set default colors to green. int fillColor = 0x4000ff00; int strokeColor = 0xff00ff00; switch (typeCategory) { case "Undeveloped": // Color undeveloped areas blue. fillColor = 0x400000ff; strokeColor = 0xff0000ff; break; case "Parkway": // Color parkway areas red. fillColor = 0x40ff0000; strokeColor = 0xffff0000; break; default: // Color all other areas green. fillColor = 0x4000ff00; strokeColor = 0xff00ff00; } return new FeatureStyle.Builder() .fillColor(fillColor) .strokeColor(strokeColor) .strokeWidth(2) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. datasetLayer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }
पॉलीलाइन डेटा की स्टाइलिंग का उदाहरण
इस उदाहरण में, पॉलीलाइन ज्यामिति पर आधारित डेटा सुविधाओं को स्टाइल करने का तरीका दिखाया गया है.
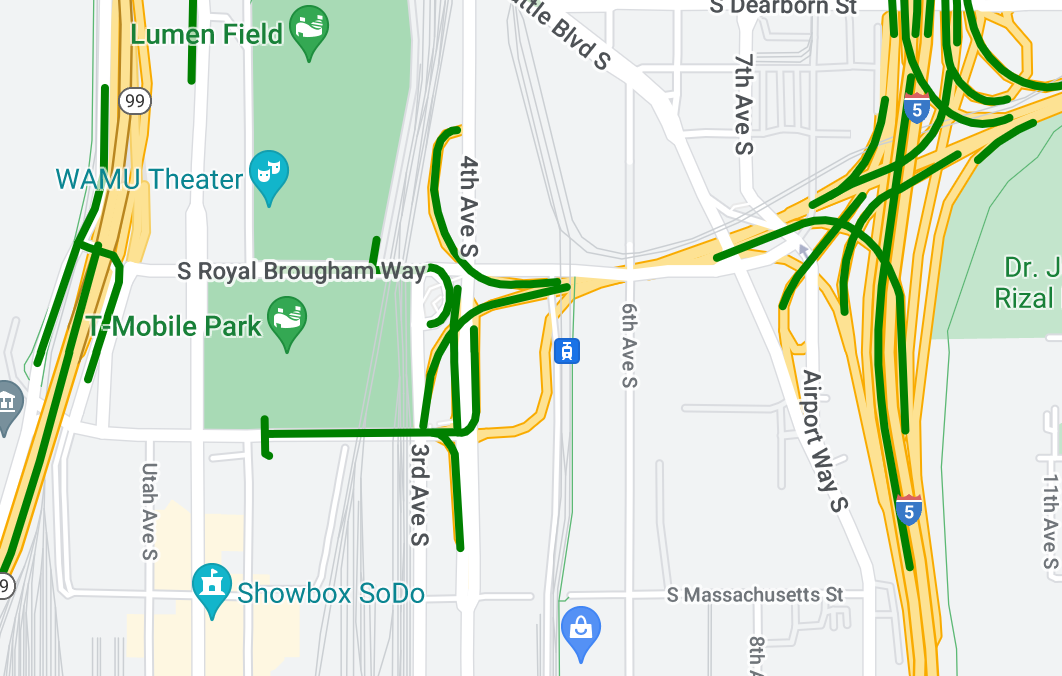
डेटासेट के बारे में जानकारी
इस उदाहरण में इस्तेमाल किए गए डेटासेट में, सिएटल इलाके के पुल दिखाए गए हैं. डेटासेट की GeoJSON फ़ाइल के इस उदाहरण में, एक फ़ीचर एंट्री दिखाई गई है.
{ "type": "Feature", "properties": { "OBJECTID": 1, "COMPTYPE": 66, "COMPKEY": 515774, "HANSEGKEY": 489781, "UNITID": "BRG-935", "UNITTYPE": " ", "BRGUNITID": "BRG-935", "UNITDESC_BRG": "YALE AVE BR REV LANE OC ", "UNITDESC_SEG": "HOWELL ST ON RP BETWEEN HOWELL ST AND I5 SB ", "INSTDATE": null, "EXPDATE": null, "STATUS": " ", "STATUSDT": null, "CONDITION": " ", "CONDDT": null, "OWN": " ", "LSTVERIFY": null, "MAINTBY": " ", "ADDBY": "GARCIAA", "ADDDTTM": "2010-01-21T00:00:00Z", "MODBY": null, "MODDTTM": null, "BR_NBR": 935, "BR_CODE": " 935", "BR_TYPE": "ST", "BR_NAME": "YALE AVE BR REV LANE OC", "BR_FACILITIES": "YALE AVE-SR 5 ON RAMP", "BR_FEATURES": "SR 5 REV LANE", "BR_RATING": 0, "BR_INSET": 1, "BR_GEO": "DT", "BR_OWNER": "DOT", "BR_OWNER_NAME": "State of Washington", "GEOBASID": 0, "XGEOBASID": 0, "GISSEGKEY": 489781, "EARTHQUAKE_RESPONSE_TEAM": " ", "SHAPE_Length": 220.11891836147655 }, "geometry": { "type": "LineString", "coordinates": [ [ -122.329201929090928, 47.616910448708538 ], [ -122.329206483407461, 47.616976719821004 ], [ -122.32921802149356, 47.617042137515213 ], [ -122.329236413912909, 47.617105967923777 ], [ -122.329261454336034, 47.617167494985758 ], [ -122.329292861855023, 47.617226028479571 ], [ -122.329330284134699, 47.617280911766009 ], [ -122.329373301365223, 47.617331529154569 ], [ -122.329421430971635, 47.617377312810319 ], [ -122.329474133027375, 47.617417749124023 ], [ -122.32953081631139, 47.617452384473893 ] ] } },
पॉलीलाइन डेटा की स्टाइल से जुड़ी सुविधाएं
नीचे दिए गए स्निपेट में, सभी डेटा सुविधाओं पर एक ही स्टाइल लागू की गई है.
Kotlin
private fun styleDatasetsLayer() {
// Create the style factory function. val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature ->
// Check if the feature is an instance of DatasetFeature. if (feature is DatasetFeature) {
return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Define a style with green stroke with a width of 4. .strokeColor(0xff00ff00.toInt()) .strokeWidth(4F) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. datasetLayer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }
Java
private void styleDatasetsLayer() {
// Create the style factory function. FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> {
// Check if the feature is an instance of DatasetFeature. if (feature instanceof DatasetFeature) {
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Define a style with green stroke with a width of 4. .strokeColor(0xff00ff00) .strokeWidth(4) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. datasetLayer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }
