Es posible que recuerdes de los ejercicios de combinación de atributos en el módulo de datos categóricos que el siguiente problema de clasificación no es lineal:

"No lineal" significa que no se puede predecir con exactitud una etiqueta con una con el formato \(b + w_1x_1 + w_2x_2\). En otras palabras, la "superficie de decisión" no es una línea.
Sin embargo, si hacemos una combinación de atributos en los atributos $x_1$ y $x_2$, podemos luego representar la relación no lineal entre los dos atributos con un modelo lineal: $b + w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + w_3x_3$, donde $x_3$ es la combinación de atributos $x_1$ y $x_2$:
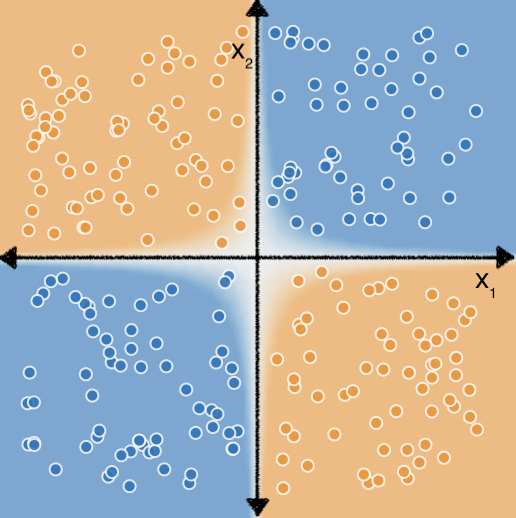
Ahora, considera el siguiente conjunto de datos:

Es posible que también lo recuerdes de los ejercicios de combinación de atributos. que determinar las combinaciones de atributos correctas para ajustar un modelo lineal a estos datos requería un poco más de esfuerzo y experimentación.
Pero ¿qué pasaría si no tuvieras que hacer toda esa experimentación por tu cuenta? Las redes neuronales son un conjunto de arquitecturas de modelos diseñadas para encontrar nonlinear patrones en los datos. Durante el entrenamiento de una red neuronal, el modelo aprende automáticamente las combinaciones de atributos óptimas que se deben realizar en los datos de entrada para minimizar la pérdida.
En las siguientes secciones, analizaremos con más detalle cómo funcionan las redes neuronales.