Page Summary
-
Get started with advanced markers by obtaining an API key, enabling the Maps JavaScript API, and creating a map ID.
-
Update your map initialization code to include loading the advanced markers library and providing a map ID when instantiating the map.
-
For testing purposes, use
DEMO_MAP_IDas the map ID or utilize the provided example code, but replace the example map IDs for production. -
Optionally, check map capabilities to ensure advanced markers are available or to implement a fallback if they are not supported.
Follow these steps to get set up with advanced markers.
Get an API key and enable the Maps JavaScript API
Before using advanced markers, you need a Cloud project with a billing account, and the Maps JavaScript API enabled. To learn more, see Set up your Google Cloud project.
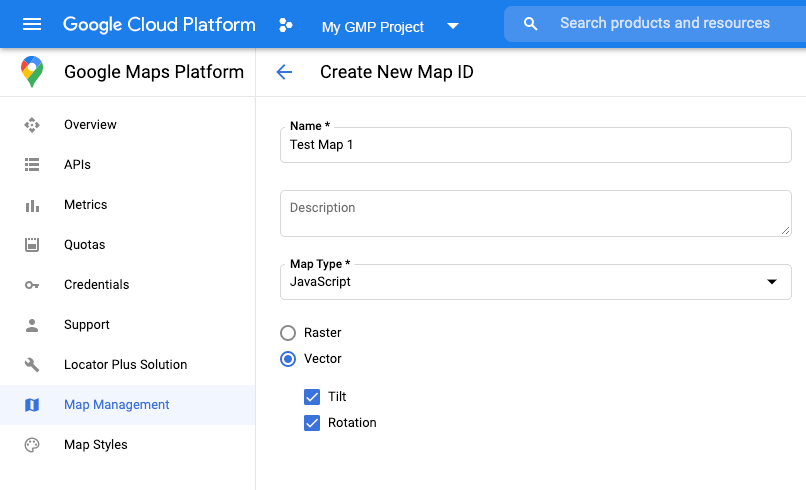
Create a map ID
To create a new map ID, follow the steps in Cloud customization. Set the Map type to JavaScript, and select either the Vector or Raster option.
Update your map initialization code
This requires the map ID you just created. It can be found on your Maps Management page.
Load the advanced markers library from within an
asyncfunction when needed:const { AdvancedMarkerElement } = await google.maps.importLibrary("marker") as google.maps.MarkerLibrary;
Provide a map ID when you instantiate the map using the
mapIdproperty. This can be a map ID that you provide, orDEMO_MAP_ID.const map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), { center: {lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644}, zoom: 8, mapId: 'YOUR_MAP_ID' });
Check map capabilities (optional)
Advanced markers requires a map ID. If the map ID is missing,
advanced markers cannot load. As a troubleshooting step,
you can add a mapcapabilities_changed listener to subscribe to map capability
changes. Using Map Capabilities is optional, and recommended only for testing
and troubleshooting purposes, or for runtime fallback purposes.
// Optional: subscribe to map capability changes. map.addListener('mapcapabilities_changed', () => { const mapCapabilities = map.getMapCapabilities(); if (!mapCapabilities.isAdvancedMarkersAvailable) { // Advanced markers are *not* available, add a fallback. } });
