تقدم الأقسام التالية مثالاً على مشكلة MIP وتعرض كيفية حلها. إليك المشكلة:
يمكنك زيادة x + 10y إلى أقصى حد مع مراعاة القيود التالية:
x + 7y≤ 17.5- 0 ≤
x≤ 3.5 - 0 ≤
y x،yعدد صحيح
ونظرًا لأن القيود تكون خطية، فهذه مجرد مشكلة تحسين خطية تشترط أن تكون الحلول فيها أعدادًا صحيحة. يُظهر الرسم البياني أدناه نقاط العدد الصحيح في المنطقة الممكنة للمشكلة.
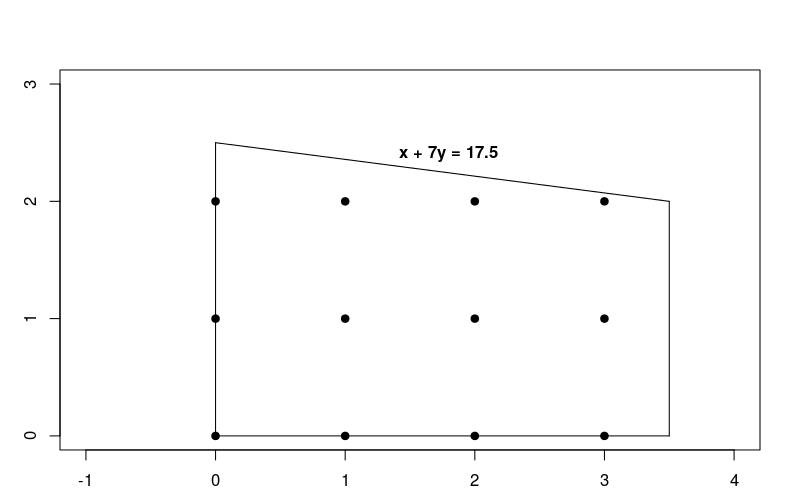
لاحظ أن هذه المسألة تتشابه إلى حد كبير مع مشكلة التحسين الخطي الموضحة في حل مشكلة LP، ولكن في هذه الحالة يجب أن تكون الحلول عبارة عن أعداد صحيحة.
الخطوات الأساسية لحل مشكلة MIP
لحل مشكلة MIP، يجب أن يتضمن برنامجك الخطوات التالية:
- عليك استيراد برنامج تضمين أداة الحلّ الخطي
- توضيح أداة حلّ MIP
- وتحديد المتغيرات،
- وتحديد القيود
- وتحديد الهدف
- يمكنك استدعاء أداة حل MIP
- عرض الحل
الحلّ باستخدام MPSolver
يعرض القسم التالي برنامجًا يحلّ المسألة باستخدام برنامج تضمين MPSolver وأداة حل MIP.
أداة حلّ MIP التلقائية لـ OR-Tools هي SCIP.
استيراد برنامج تضمين أداة حلّ المساواة بين نقاط الاتصال
عليك استيراد (أو تضمين) برنامج تضمين أداة حل المساواة بين نقاط الاتصال (OR-Tools)، وهو واجهة لأدوات حلّ المشاكل الخطية وأدوات حلّ المشاكل الخطية، كما هو موضّح أدناه.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
C++
#include <memory> #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
توضيح أداة حلّ MIP
تعلن التعليمة البرمجية التالية عن أداة حل MIP للمشكلة. يستخدم هذا المثال أداة الحلّ التابعة لجهة خارجية SCIP.
Python
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT")
if not solver:
return
C++
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
Java
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP");
if (solver == null) {
System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP");
return;
}
C#
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
تحديد المتغيّرات
تحدد التعليمة البرمجية التالية المتغيرات في المشكلة.
Python
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x")
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
C#
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
يستخدِم البرنامج طريقة MakeIntVar (أو إحدى الصيغ استنادًا إلى لغة الترميز) لإنشاء المتغيّرَين x وy اللذَين يستخدمان أعدادًا صحيحة غير سالبة.
تحديد القيود
تحدد التعليمة البرمجية التالية القيود الخاصة بالمشكلة.
Python
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
C++
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5. MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0"); c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c0->SetCoefficient(y, 7); // x <= 3.5. MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1"); c1->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c1->SetCoefficient(y, 0); LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
Java
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c1.setCoefficient(y, 0);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
C#
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5);
// x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
تحديد الهدف
يحدّد الرمز التالي السمة objective function للمشكلة.
Python
# Maximize x + 10 * y. solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
C++
// Maximize x + 10 * y. MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 10); objective->SetMaximization();
Java
// Maximize x + 10 * y. MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(x, 1); objective.setCoefficient(y, 10); objective.setMaximization();
C#
// Maximize x + 10 * y. solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y);
الاتصال بأداة الحلّ
يستدعي الرمز التالي أداة الحلّ.
Python
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
C++
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
Java
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
C#
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
عرض الحلّ
تعرض التعليمة البرمجية التالية الحل.
Python
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
C++
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; LOG(INFO) << "Objective value = " << objective->Value(); LOG(INFO) << "x = " << x->solution_value(); LOG(INFO) << "y = " << y->solution_value();
Java
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
C#
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
إليك حل المشكلة.
Number of variables = 2 Number of constraints = 2 Solution: Objective value = 23 x = 3 y = 2
القيمة المثلى لدالة الهدف هي 23، وتحدث عند النقطة
x = 3، y = 2.
البرامج المكتملة
إليك البرامج الكاملة.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def main():
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT")
if not solver:
return
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x")
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
# Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
print("\nAdvanced usage:")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.wall_time():d} milliseconds")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.iterations():d} iterations")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.nodes():d} branch-and-bound nodes")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <memory>
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void SimpleMipProgram() {
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
const double infinity = solver->infinity();
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c0->SetCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c1->SetCoefficient(y, 0);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective();
objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
objective->SetCoefficient(y, 10);
objective->SetMaximization();
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:";
LOG(INFO) << "Objective value = " << objective->Value();
LOG(INFO) << "x = " << x->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << "y = " << y->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << "\nAdvanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->wall_time() << " milliseconds";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->iterations() << " iterations";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->nodes()
<< " branch-and-bound nodes";
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
operations_research::SimpleMipProgram();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.linearsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/** Minimal Mixed Integer Programming example to showcase calling the solver. */
public final class SimpleMipProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP");
if (solver == null) {
System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP");
return;
}
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c1.setCoefficient(y, 0);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 1);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 10);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.nodes() + " branch-and-bound nodes");
}
private SimpleMipProgram() {}
}
C#
using System;
using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
public class SimpleMipProgram
{
static void Main()
{
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5);
// x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y);
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("\nAdvanced usage:");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.WallTime() + " milliseconds");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Iterations() + " iterations");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Nodes() + " branch-and-bound nodes");
}
}
مقارنة التحسين الخطي والعدد الصحيح
لنقارن الحل بمشكلة تحسين العدد الصحيح، كما هو موضح أعلاه،
مع حل مشكلة التحسين الخطي المقابلة، والتي
تتمّ إزالة قيود الأعداد الصحيحة فيها. قد تعتقد أنّ حلّ مشكلة العدد الصحيح سيكون نقطة العدد الصحيح في المنطقة الممكنة الأقرب إلى الحل الخطي، أي النقطة x = 0، y = 2. ولكن كما سترى بعد ذلك،
هذا ليس هو الحال.
يمكنك تعديل البرنامج بسهولة في القسم السابق لحل مشكلة خطية من خلال إجراء التغييرات التالية:
- استبدال أداة حلّ MIP
باستخدام أداة حلّ LP
Python
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend. solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT") if not solver: returnC++
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend. std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP")); if (!solver) { LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable."; return; }Java
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend. MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP"); if (solver == null) { System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP"); return; }C#
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend. Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP"); if (solver is null) { return; }Python
# Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP") if not solver: returnC++
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("GLOP"));Java
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP"); if (solver == null) { System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP"); return; }C#
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP"); if (solver is null) { return; } - استبدال متغيرات الأعداد الصحيحة
بمتغيرات مستمرة
Python
infinity = solver.infinity() # x and y are integer non-negative variables. x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x") y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y") print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());C#
// x and y are integer non-negative variables. Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y"); Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());Python
infinity = solver.infinity() # Create the variables x and y. x = solver.NumVar(0.0, infinity, "x") y = solver.NumVar(0.0, infinity, "y") print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // Create the variables x and y. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Create the variables x and y. MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());C#
// Create the variables x and y. Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y"); Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
بعد إجراء هذه التغييرات وتشغيل البرنامج مرة أخرى، تحصل على الناتج التالي:
Number of variables = 2 Number of constraints = 2 Objective value = 25.000000 x = 0.000000 y = 2.500000
يقع حل المسألة الخطية عند النقطة x = 0، y = 2.5، حيث تساوي الدالة الهدف 25. إليكم رسم بياني يوضح حلول كل من
المسائل الخطية والأعداد الصحيحة.
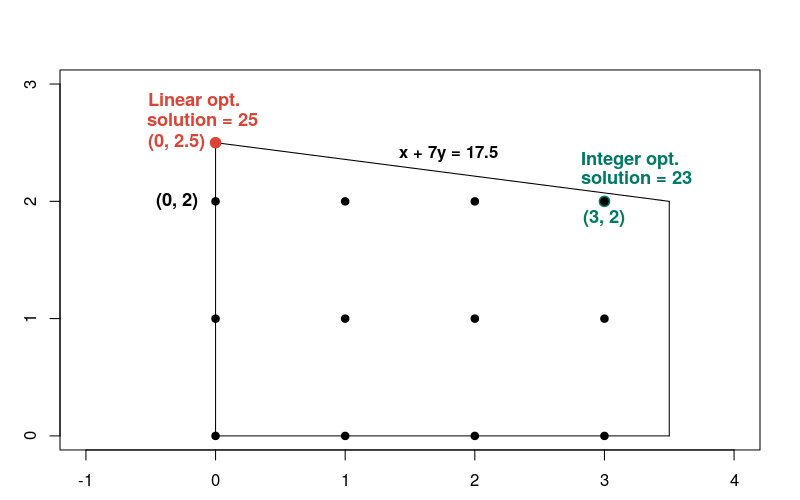
لاحظ أن حل العدد الصحيح ليس قريبًا من الحل الخطي، مقارنةً بمعظم نقاط الأعداد الصحيحة الأخرى في المنطقة الممكنة. بوجه عام، يمكن أن تكون الحلول لمشكلة التحسين الخطي ومشكلات تحسين الأعداد الصحيحة المقابلة مختلفة بشكل كبير. لهذا السبب، يتطلب نوعا المشكلات طرقًا مختلفة لحلهما.
