以下部分展示了一个 MIP 问题示例,并展示如何解决此问题。具体问题如下:
尽可能增加 x + 10y,但需遵循以下限制条件:
x + 7y≤ 17.5- 0 ≤
x≤ 3.5 - 0 ≤
y x,y个整数
由于约束条件是线性的,因此这只是一个线性优化问题,其中解决方案必须是整数。下图显示了问题的可行区域中整数点。
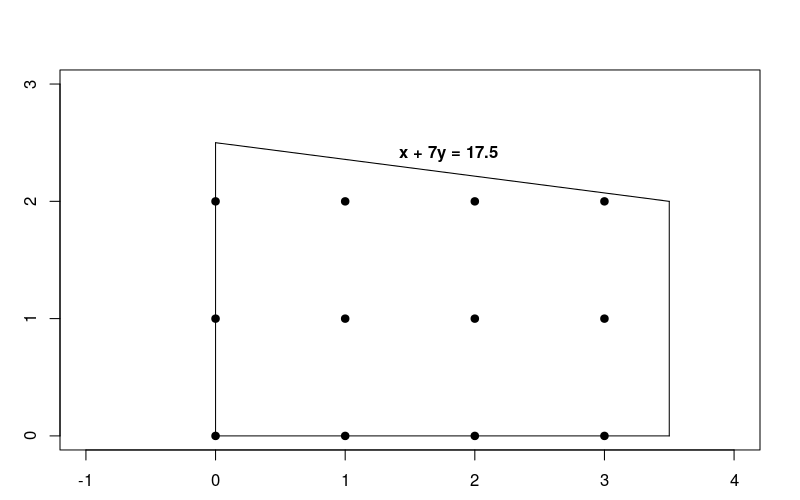
请注意,此问题与解决 LP 问题中介绍的线性优化问题非常相似,但在本例中,我们要求解是整数。
解决 MIP 问题的基本步骤
要解决 MIP 问题,您的程序应包含以下步骤:
- 导入线性求解器封装容器,
- 声明 MIP 求解器,
- 定义变量
- 定义约束条件,
- 定义目标,
- 调用 MIP 求解器,
- 展示解决方案
使用 MPSolver 的解决方案
以下部分介绍了使用 MPSolver 封装容器和 MIP 求解器解决该问题的程序。
默认的 OR-Tools MIP 求解器为 SCIP。
导入线性求解器封装容器
导入(或包含)OR-Tools 线性求解器封装容器(MIP 求解器和线性求解器的接口),如下所示。
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
C++
#include <memory> #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
声明 MIP 求解器
以下代码声明了用于求解问题的 MIP 求解器。此示例使用第三方求解器 SCIP。
Python
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT")
if not solver:
return
C++
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
Java
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP");
if (solver == null) {
System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP");
return;
}
C#
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
定义变量
以下代码定义了问题中的变量。
Python
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x")
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
C#
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
该程序使用 MakeIntVar 方法(或变体,具体取决于编码语言)创建采用非负整数值的变量 x 和 y。
定义限制条件
以下代码定义了该问题的约束条件。
Python
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
C++
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5. MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0"); c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c0->SetCoefficient(y, 7); // x <= 3.5. MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1"); c1->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c1->SetCoefficient(y, 0); LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
Java
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c1.setCoefficient(y, 0);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
C#
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5);
// x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
设定目标
以下代码定义了问题的 objective function。
Python
# Maximize x + 10 * y. solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
C++
// Maximize x + 10 * y. MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 10); objective->SetMaximization();
Java
// Maximize x + 10 * y. MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(x, 1); objective.setCoefficient(y, 10); objective.setMaximization();
C#
// Maximize x + 10 * y. solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y);
调用求解器
以下代码会调用求解器。
Python
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
C++
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
Java
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
C#
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
显示解决方案
以下代码将显示解决方案。
Python
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
C++
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; LOG(INFO) << "Objective value = " << objective->Value(); LOG(INFO) << "x = " << x->solution_value(); LOG(INFO) << "y = " << y->solution_value();
Java
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
C#
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
以下是该问题的解决方法。
Number of variables = 2 Number of constraints = 2 Solution: Objective value = 23 x = 3 y = 2
目标函数的最佳值为 23,出现在点 x = 3 和 y = 2 处。
完成计划
以下是完整的计划。
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def main():
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT")
if not solver:
return
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x")
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
# Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
print("\nAdvanced usage:")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.wall_time():d} milliseconds")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.iterations():d} iterations")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.nodes():d} branch-and-bound nodes")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <memory>
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void SimpleMipProgram() {
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
const double infinity = solver->infinity();
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c0->SetCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c1->SetCoefficient(y, 0);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective();
objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
objective->SetCoefficient(y, 10);
objective->SetMaximization();
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:";
LOG(INFO) << "Objective value = " << objective->Value();
LOG(INFO) << "x = " << x->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << "y = " << y->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << "\nAdvanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->wall_time() << " milliseconds";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->iterations() << " iterations";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->nodes()
<< " branch-and-bound nodes";
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
operations_research::SimpleMipProgram();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.linearsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/** Minimal Mixed Integer Programming example to showcase calling the solver. */
public final class SimpleMipProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP");
if (solver == null) {
System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP");
return;
}
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c1.setCoefficient(y, 0);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 1);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 10);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.nodes() + " branch-and-bound nodes");
}
private SimpleMipProgram() {}
}
C#
using System;
using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
public class SimpleMipProgram
{
static void Main()
{
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5);
// x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y);
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("\nAdvanced usage:");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.WallTime() + " milliseconds");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Iterations() + " iterations");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Nodes() + " branch-and-bound nodes");
}
}
比较线性和整数优化
我们将上述整数优化问题的解决方法与移除了整数约束的相应线性优化问题的解决方法进行比较。您可能会猜测,整数问题的解决方法是最接近线性解决方案的可行区域中的整数点,即点 x = 0、y = 2。但后面会介绍,事实并非如此
通过进行以下更改,您可以轻松修改上一部分中的程序来解决线性问题:
- 替换 MIP 求解器
使用 LP 求解器
Python
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend. solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT") if not solver: returnC++
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend. std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP")); if (!solver) { LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable."; return; }Java
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend. MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP"); if (solver == null) { System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP"); return; }C#
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend. Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP"); if (solver is null) { return; }Python
# Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP") if not solver: returnC++
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("GLOP"));Java
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP"); if (solver == null) { System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP"); return; }C#
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP"); if (solver is null) { return; } - 替换整数变量
连续变量
Python
infinity = solver.infinity() # x and y are integer non-negative variables. x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x") y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y") print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());C#
// x and y are integer non-negative variables. Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y"); Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());Python
infinity = solver.infinity() # Create the variables x and y. x = solver.NumVar(0.0, infinity, "x") y = solver.NumVar(0.0, infinity, "y") print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // Create the variables x and y. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Create the variables x and y. MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());C#
// Create the variables x and y. Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y"); Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
进行这些更改并再次运行程序后,您会获得以下输出:
Number of variables = 2 Number of constraints = 2 Objective value = 25.000000 x = 0.000000 y = 2.500000
线性问题的解法发生在 x = 0 点 y = 2.5,目标函数等于 25。下图显示了线性和整数问题的解法。
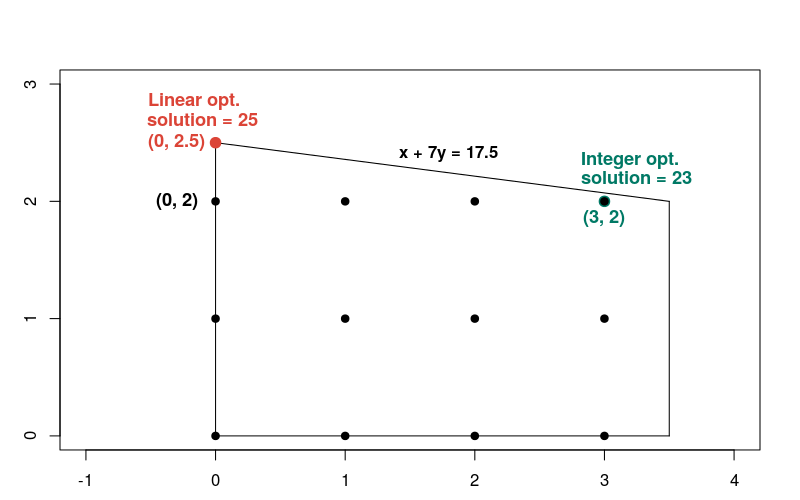
请注意,与可行区域中大多数其他整数点相比,整数解并不接近线性解。一般来说,线性优化问题和相应的整数优化问题的解决方法可能相差很大。因此,这两类问题需要采用不同的方法来解决。
