As seções abaixo apresentam um exemplo de problema de MIP e mostram como resolvê-lo. Este é o problema:
Maximize x + 10y sujeito às seguintes restrições:
x + 7y≤ 17,5- 0 ≤
x≤ 3,5 - 0 ≤
y x,ynúmeros inteiros
Como as restrições são lineares, esse é apenas um problema de otimização linear em que as soluções precisam ser números inteiros. O gráfico abaixo mostra os pontos inteiros na região viável para o problema.
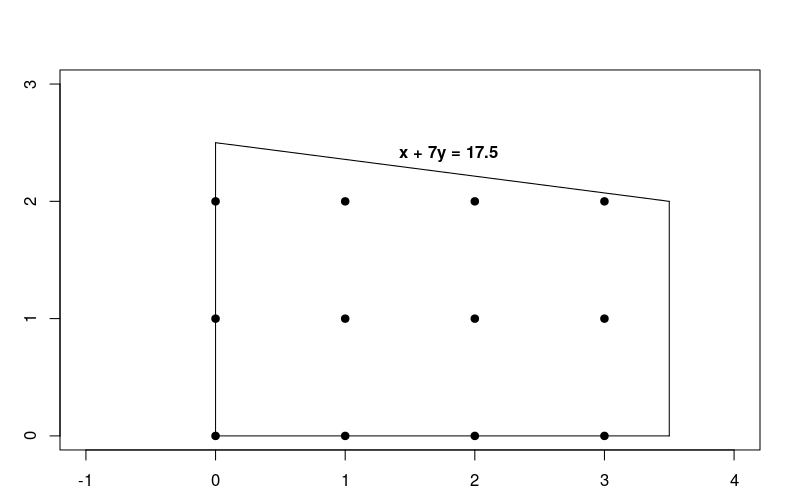
Observe que esse problema é muito semelhante ao de otimização linear descrito em Resolver um problema de LP, mas nesse caso exigimos que as soluções sejam números inteiros.
Etapas básicas para resolver um problema de MIP
Para resolver um problema de MIP, seu programa deve incluir as seguintes etapas:
- Importe o wrapper do solucionador linear
- declarar o solucionador MIP,
- definir as variáveis,
- definir as restrições,
- definir o objetivo,
- chamar o solucionador MIP e
- mostrar a solução
Solução usando o MPSolver
Na seção a seguir, apresentamos um programa que resolve o problema usando o wrapper MPSolver e um solucionador MIP.
O solucionador MIP padrão das ferramentas OR é SCIP.
Importar o wrapper do solucionador linear
Importe ou inclua o wrapper de solucionador linear OR-Tools, uma interface para solucionadores de MIP e solucionadores lineares, conforme mostrado abaixo.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
C++
#include <memory> #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
Declarar o solucionador MIP
O código a seguir declara o solucionador MIP para o problema. Este exemplo usa o solucionador SCIP de terceiros.
Python
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT")
if not solver:
return
C++
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
Java
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP");
if (solver == null) {
System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP");
return;
}
C#
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
Definir as variáveis
O código a seguir define as variáveis do problema.
Python
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x")
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
C#
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
O programa usa o método MakeIntVar (ou uma variante, dependendo da linguagem de
codificação) para criar as variáveis x e y que assumem valores inteiros
não negativos.
Definir as restrições
O código a seguir define as restrições para o problema.
Python
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
C++
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5. MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0"); c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c0->SetCoefficient(y, 7); // x <= 3.5. MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1"); c1->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c1->SetCoefficient(y, 0); LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
Java
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c1.setCoefficient(y, 0);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
C#
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5);
// x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
Definir o objetivo
O código a seguir define o objective function do problema.
Python
# Maximize x + 10 * y. solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
C++
// Maximize x + 10 * y. MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 10); objective->SetMaximization();
Java
// Maximize x + 10 * y. MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(x, 1); objective.setCoefficient(y, 10); objective.setMaximization();
C#
// Maximize x + 10 * y. solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y);
Chamar o solucionador
O código a seguir chama o solucionador.
Python
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
C++
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
Java
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
C#
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
Mostrar a solução
O código a seguir exibe a solução.
Python
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
C++
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; LOG(INFO) << "Objective value = " << objective->Value(); LOG(INFO) << "x = " << x->solution_value(); LOG(INFO) << "y = " << y->solution_value();
Java
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
C#
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Aqui está a solução para o problema.
Number of variables = 2 Number of constraints = 2 Solution: Objective value = 23 x = 3 y = 2
O valor ideal da função de objetivo é 23, que ocorre no ponto
x = 3, y = 2.
Programas completos
Aqui estão os programas completos.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def main():
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT")
if not solver:
return
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x")
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
# Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
print("\nAdvanced usage:")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.wall_time():d} milliseconds")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.iterations():d} iterations")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.nodes():d} branch-and-bound nodes")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <memory>
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void SimpleMipProgram() {
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend.
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
const double infinity = solver->infinity();
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c0->SetCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c1->SetCoefficient(y, 0);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective();
objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
objective->SetCoefficient(y, 10);
objective->SetMaximization();
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:";
LOG(INFO) << "Objective value = " << objective->Value();
LOG(INFO) << "x = " << x->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << "y = " << y->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << "\nAdvanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->wall_time() << " milliseconds";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->iterations() << " iterations";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << solver->nodes()
<< " branch-and-bound nodes";
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
operations_research::SimpleMipProgram();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.linearsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/** Minimal Mixed Integer Programming example to showcase calling the solver. */
public final class SimpleMipProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP");
if (solver == null) {
System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP");
return;
}
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 17.5, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 7);
// x <= 3.5.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 3.5, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c1.setCoefficient(y, 0);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 1);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 10);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.nodes() + " branch-and-bound nodes");
}
private SimpleMipProgram() {}
}
C#
using System;
using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
public class SimpleMipProgram
{
static void Main()
{
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend.
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
// x and y are integer non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
// x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5);
// x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
// Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y);
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("\nAdvanced usage:");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.WallTime() + " milliseconds");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Iterations() + " iterations");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Nodes() + " branch-and-bound nodes");
}
}
Comparando a otimização linear e de número inteiro
Vamos comparar a solução ao problema de otimização de números inteiros, mostrado acima,
com a solução para o problema de otimização linear correspondente, em que
as restrições de números inteiros são removidas. Você pode supor que a solução para o problema de números inteiros seria o ponto inteiro na região viável mais próxima da solução linear, ou seja, o ponto x = 0, y = 2. Mas, como você verá
a seguir, esse não é o caso.
Você pode modificar facilmente o programa na seção anterior para resolver o problema linear fazendo estas mudanças:
- Substitua o solucionador MIP
com o solucionador LP
Python
# Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend. solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("SAT") if not solver: returnC++
// Create the mip solver with the SCIP backend. std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP")); if (!solver) { LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable."; return; }Java
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend. MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("SCIP"); if (solver == null) { System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP"); return; }C#
// Create the linear solver with the SCIP backend. Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("SCIP"); if (solver is null) { return; }Python
# Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP") if not solver: returnC++
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("GLOP"));Java
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP"); if (solver == null) { System.out.println("Could not create solver SCIP"); return; }C#
// Create the linear solver with the GLOP backend. Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP"); if (solver is null) { return; } - Substituir as variáveis inteiras
com variáveis contínuas
Python
infinity = solver.infinity() # x and y are integer non-negative variables. x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "x") y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, "y") print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // x and y are integer non-negative variables. MPVariable x = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeIntVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());C#
// x and y are integer non-negative variables. Variable x = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeIntVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y"); Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());Python
infinity = solver.infinity() # Create the variables x and y. x = solver.NumVar(0.0, infinity, "x") y = solver.NumVar(0.0, infinity, "y") print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // Create the variables x and y. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Create the variables x and y. MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());C#
// Create the variables x and y. Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y"); Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
Depois de fazer essas alterações e executar o programa novamente, você receberá a seguinte saída:
Number of variables = 2 Number of constraints = 2 Objective value = 25.000000 x = 0.000000 y = 2.500000
A solução para o problema linear ocorre no ponto x = 0, y = 2.5, em que a função objetivo é igual a 25. Aqui está um gráfico que mostra as soluções
para os problemas de linear e inteiro.
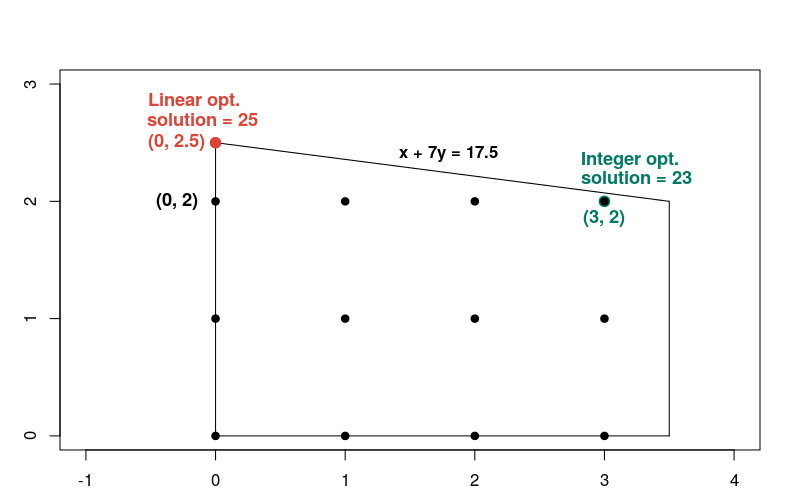
Observe que a solução de números inteiros não está próxima da solução linear, em comparação com a maioria dos outros pontos inteiros na região viável. Em geral, as soluções para um problema de otimização linear e os problemas de otimização de números inteiros correspondentes podem ser distantes. Por isso, os dois tipos de problemas exigem métodos diferentes para serem resolvidos.
