In diesem Abschnitt wird ein Beispiel für die Lösung des Problems des Handlungsreisenden (Traveling Sales Problem, TSP) für die Standorte auf der Karte unten dargestellt.
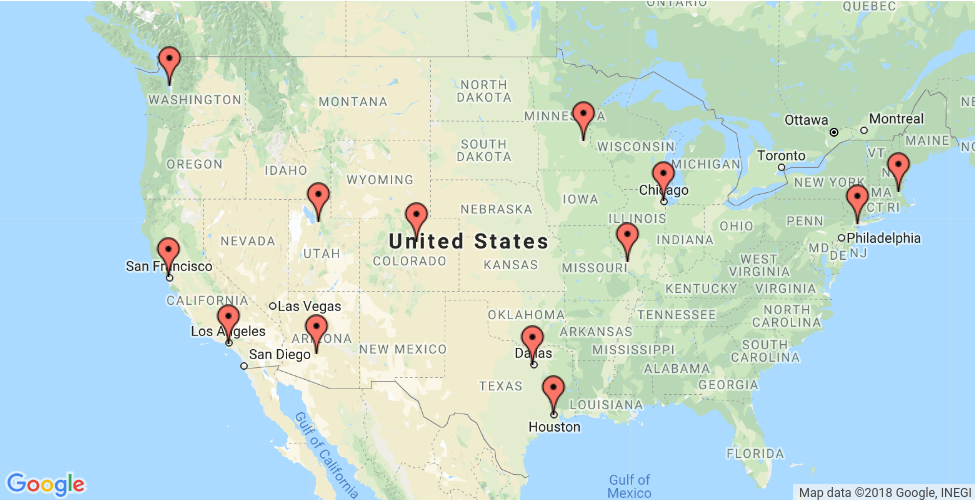
In den folgenden Abschnitten werden Programme in Python, C++, Java und C# vorgestellt, die den TSP mit OR-Tools lösen.
Daten erstellen
Mit dem folgenden Code werden die Daten für das Problem erstellt.
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
Die Entfernungsmatrix ist ein Array, dessen i, j-Eintrag die Entfernung vom Standort i zum Standort j in Meilen angibt, wobei die Array-Indizes der Position in der folgenden Reihenfolge entsprechen:
0. New York - 1. Los Angeles - 2. Chicago - 3. Minneapolis - 4. Denver - 5. Dallas
- 6. Seattle - 7. Boston - 8. San Francisco - 9. St. Louis - 10. Houston - 11. Phoenix - 12. Salt Lake City
Die Daten umfassen außerdem:
- Die Anzahl der Fahrzeuge, bei denen das Problem auftritt. Das ist 1, weil es sich um einen TSP handelt. (Bei einem Fahrzeugroutenproblem (VRP) kann die Anzahl der Fahrzeuge größer als 1 sein.)
- depot: Start- und Endpunkt der Route In diesem Fall ist das Depot 0, was New York entspricht.
Weitere Möglichkeiten zum Erstellen einer Entfernungsmatrix
In diesem Beispiel wird die Entfernungsmatrix im Programm explizit definiert. Es ist auch möglich, eine Funktion zu verwenden, um Entfernungen zwischen Orten zu berechnen, z. B. die euklidische Formel für die Entfernung zwischen Punkten in der Ebene. Es ist jedoch immer noch effizienter, alle Entfernungen zwischen Standorten im Voraus zu berechnen und in einer Matrix zu speichern, anstatt sie zur Laufzeit zu berechnen. Ein Beispiel zum Erstellen der Distanzmatrix finden Sie unter Beispiel: Leiterplatte bohren.
Eine weitere Alternative ist die Verwendung der Google Maps Distance Matrix API zur dynamischen Erstellung einer Entfernungs- bzw. Reisematrix für Routen.
Routingmodell erstellen
Mit dem folgenden Code im Hauptbereich der Programme werden der Indexmanager (manager) und das Routingmodell (routing) erstellt. Die Methode manager.IndexToNode konvertiert die internen Indizes des Matherechners (die Sie ignorieren können) in die Zahlen für Standorte. Standortzahlen entsprechen den Indexen für die Entfernungsmatrix.
Python
data = create_data_model()
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
C++
DataModel data;
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
RoutingModel routing(manager);
Java
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
C#
DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
Die Eingaben für RoutingIndexManager sind:
- Die Anzahl der Zeilen der Entfernungsmatrix, also die Anzahl der Standorte (einschließlich des Depots).
- Die Anzahl der Fahrzeuge, bei denen das Problem aufgetreten ist.
- Der dem Depot entsprechende Knoten.
Callback für die Entfernung erstellen
Sie müssen einen Entfernungs- (oder Transit-)Callback erstellen, um den Routing-Lösler verwenden zu können. Dabei handelt es sich um eine Funktion, die für ein beliebiges Standortpaar die Entfernung zwischen ihnen zurücklegt. Am einfachsten ist dies mit der Entfernungsmatrix.
Die folgende Funktion erstellt den Callback und registriert ihn beim Resolver als transit_callback_index.
Python
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
C++
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
Java
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
C#
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
The callback accepts two indices, from_index and to_index, and returns the
corresponding entry of the distance matrix.
Set the cost of travel
The arc cost evaluator tells the solver how to calculate the cost of travel between any two locations — in other words, the cost of the edge (or arc) joining them in the graph for the problem. The following code sets the arc cost evaluator.
Python
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
In diesem Beispiel ist der Bogenkostenauswerter transit_callback_index, der interne Verweis des Matherechners auf den Entfernungs-Callback. Die Reisekosten zwischen zwei Standorten sind also nur die Entfernungen zwischen ihnen.
Im Allgemeinen können die Kosten jedoch auch andere Faktoren umfassen.
Mit der Methode routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfVehicle() können Sie auch mehrere Bewertungsbogenwerte angeben, die davon abhängen, welches Fahrzeug zwischen Standorten fährt.
Wenn die Fahrzeuge beispielsweise unterschiedliche Geschwindigkeiten haben, können Sie die Reisekosten als Standorte durch die Geschwindigkeit des Fahrzeugs, also die Fahrtzeit, berechnen.
Suchparameter festlegen
Mit dem folgenden Code werden die Standardsuchparameter und eine heuristische Methode zum Ermitteln der ersten Lösung festgelegt:
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
Java
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
C#
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
Der Code legt die erste Lösungsstrategie auf PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC fest, wodurch eine erste Route für den Matherechner erstellt wird, indem wiederholt Kanten mit der geringsten Gewichtung hinzugefügt werden, die nicht zu einem zuvor besuchten Knoten (mit Ausnahme des Depots) führen. Weitere Optionen finden Sie unter Erste Lösungsstrategie.
Lösungsdrucker hinzufügen
Im Folgenden sehen Sie die Funktion, die die vom Rechner zurückgegebene Lösung anzeigt. Die Funktion extrahiert die Route aus der Lösung und gibt sie an die Konsole aus.
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
Die Funktion zeigt die optimale Route und die Entfernung an, die durch ObjectiveValue() angegeben werden.
Lösung lösen und ausdrucken
Abschließend können Sie die Lösung aufrufen und die Lösung ausgeben:
Python
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
C++
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
Java
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters); printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
C#
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
Dadurch wird die Lösung zurückgegeben und die optimale Route angezeigt.
Programme ausführen
Wenn Sie die Programme ausführen, wird die folgende Ausgabe angezeigt.
Objective: 7293 miles Route for vehicle 0: 0 -> 7 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 12 -> 6 -> 8 -> 1 -> 11 -> 10 -> 5 -> 9 -> 0
In diesem Beispiel gibt es nur eine Route, da es sich um einen TSP handelt. Bei allgemeineren Problemen mit der Routenführung enthält die Lösung mehrere Routen.
Routen in einer Liste oder einem Array speichern
Alternativ zum direkten Drucken der Lösung können Sie die Route (oder Routen für eine VRP) in einer Liste oder einem Array speichern. Dies hat den Vorteil, dass die Routen für den Fall verfügbar gemacht werden, dass Sie sie später nutzen möchten. Sie können das Programm beispielsweise mehrmals mit verschiedenen Parametern ausführen und die Routen in den zurückgegebenen Lösungen zum Vergleich in einer Datei speichern.
Mit den folgenden Funktionen werden die Routen in der Lösung in einem beliebigen VRP (möglicherweise mit mehreren Fahrzeugen) als Liste (Python) oder Array (C++) gespeichert.
Python
def get_routes(solution, routing, manager):
"""Get vehicle routes from a solution and store them in an array."""
# Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array whose
# i,j entry is the jth location visited by vehicle i along its route.
routes = []
for route_nbr in range(routing.vehicles()):
index = routing.Start(route_nbr)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
routes.append(route)
return routes
C++
std::vector<std::vector<int>> GetRoutes(const Assignment& solution,
const RoutingModel& routing,
const RoutingIndexManager& manager) {
// Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array, whose
// i, j entry is the node for the jth visit of vehicle i.
std::vector<std::vector<int>> routes(manager.num_vehicles());
// Get routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < manager.num_vehicles(); ++vehicle_id) {
int64_t index = routing.Start(vehicle_id);
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
}
}
return routes;
}
Sie können diese Funktionen verwenden, um die Routen in einem der VRP-Beispiele im Abschnitt „Routing“ abzurufen.
Mit dem folgenden Code werden die Routen angezeigt.
Python
routes = get_routes(solution, routing, manager)
# Display the routes.
for i, route in enumerate(routes):
print('Route', i, route)
C++
const std::vector⟨std::vector⟨int⟩⟩
routes = GetRoutes(*solution,
routing,
manager);
// Display the routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < routes.size(); ++vehicle_id) {
LOG(INFO) << "Route " << vehicle_id;
for (int j = 1; j < routes[vehicle_id].size(); ++j) {
LOG(INFO) << routes[vehicle_id][j];
}
}
Für das aktuelle Beispiel gibt dieser Code die folgende Route zurück:
Route 0 [0, 7, 2, 3, 4, 12, 6, 8, 1, 11, 10, 5, 9, 0]
Ändern Sie den Code oben so, dass die Ausgabe auf dieselbe Weise wie der Lösungsdrucker für das Programm formatiert wird.
Programme abschließen
Die vollständigen TSP-Programme sind unten aufgeführt.
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) between cities."""
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP using distance matrix. */
public class TspCities {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCities.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP using distance matrix.
/// </summary>
public class TspCities
{
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
Beispiel: Leiterplatte bohren
Das nächste Beispiel umfasst das Bohren von Löchern in einer Leiterplatte mit automatischem Bohren. Das Problem besteht darin, die kürzeste Route für den Bohrvorgang auf dem Feld zu finden, um alle erforderlichen Löcher zu bohren. Das Beispiel stammt von TSPLIB, einer Bibliothek von TSP-Problemen.
Hier ist das Streudiagramm der Standorte für die Löcher:
In den folgenden Abschnitten werden Programme aufgeführt, die mit den Standardsuchparametern des Rechners eine gute Lösung für das Problem mit der Leiterplatte finden. Anschließend zeigen wir dir, wie du durch Ändern der Suchstrategie eine bessere Lösung finden kannst.
Daten erstellen
Die Daten für das Problem bestehen aus 280 Punkten in der Ebene (siehe Streudiagramm oben). Das Programm erstellt die Daten in einem Array von geordneten Paaren, die den Punkten in der Ebene entsprechen, wie unten dargestellt.
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
Distanzmatrix berechnen
Die folgende Funktion berechnet die euklidische Entfernung zwischen zwei beliebigen Punkten in den Daten und speichert sie in einem Array. Da der Routing-Lauflöser die Ganzzahlen verarbeitet, rundet die Funktion die berechneten Entfernungen auf Ganzzahlen auf. Die Rundung hat in diesem Beispiel keine Auswirkungen auf die Lösung. Wie Sie Probleme mit Rundungen vermeiden, erfahren Sie unter Entfernungsmatrix skalieren.
Python
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
C++
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
Java
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
Callback für die Entfernung hinzufügen
Der Code, der den Callback für die Entfernung erstellt, ist fast identisch mit dem im vorherigen Beispiel. In diesem Fall ruft das Programm jedoch die Funktion auf, die die Entfernungsmatrix berechnet, bevor der Callback hinzugefügt wird.
Python
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
Lösungsdrucker
Die folgende Funktion gibt die Lösung in der Konsole aus. Damit die Ausgabe kompakter ist, zeigt die Funktion nur die Indexe der Standorte in der Route an.
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
Hauptfunktion
Die Hauptfunktion ist im Wesentlichen mit der im vorherigen Beispiel identisch, enthält jedoch auch einen Aufruf an die Funktion, die die Entfernungsmatrix erstellt.
Ausführen des Programms
Die vollständigen Programme finden Sie im nächsten Abschnitt. Wenn Sie das Programm ausführen, wird die folgende Route angezeigt:
Total distance: 2790 Route of vehicle 0: 0 -> 1 -> 279 -> 2 -> 278 -> 277 -> 247 -> 248 -> 249 -> 246 -> 244 -> 243 -> 242 -> 241 -> 240 -> 239 -> 238 -> 237 -> 236 -> 235 -> 234 -> 233 -> 232 -> 231 -> 230 -> 245 -> 250 -> 229 -> 228 -> 227 -> 226 -> 225 -> 224 -> 223 -> 222 -> 221 -> 220 -> 219 -> 218 -> 217 -> 216 -> 215 -> 214 -> 213 -> 212 -> 211 -> 210 -> 209 -> 208 -> 251 -> 254 -> 255 -> 257 -> 256 -> 253 -> 252 -> 207 -> 206 -> 205 -> 204 -> 203 -> 202 -> 142 -> 141 -> 146 -> 147 -> 140 -> 139 -> 265 -> 136 -> 137 -> 138 -> 148 -> 149 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 178 -> 179 -> 180 -> 181 -> 182 -> 183 -> 184 -> 186 -> 185 -> 192 -> 196 -> 197 -> 198 -> 144 -> 145 -> 143 -> 199 -> 201 -> 200 -> 195 -> 194 -> 193 -> 191 -> 190 -> 189 -> 188 -> 187 -> 163 -> 164 -> 165 -> 166 -> 167 -> 168 -> 169 -> 171 -> 170 -> 172 -> 105 -> 106 -> 104 -> 103 -> 107 -> 109 -> 110 -> 113 -> 114 -> 116 -> 117 -> 61 -> 62 -> 63 -> 65 -> 64 -> 84 -> 85 -> 115 -> 112 -> 86 -> 83 -> 82 -> 87 -> 111 -> 108 -> 89 -> 90 -> 91 -> 102 -> 101 -> 100 -> 99 -> 98 -> 97 -> 96 -> 95 -> 94 -> 93 -> 92 -> 79 -> 88 -> 81 -> 80 -> 78 -> 77 -> 76 -> 74 -> 75 -> 73 -> 72 -> 71 -> 70 -> 69 -> 66 -> 68 -> 67 -> 57 -> 56 -> 55 -> 54 -> 53 -> 52 -> 51 -> 50 -> 49 -> 48 -> 47 -> 46 -> 45 -> 44 -> 43 -> 58 -> 60 -> 59 -> 42 -> 41 -> 40 -> 39 -> 38 -> 37 -> 36 -> 35 -> 34 -> 33 -> 32 -> 31 -> 30 -> 29 -> 124 -> 123 -> 122 -> 121 -> 120 -> 119 -> 118 -> 156 -> 157 -> 158 -> 173 -> 162 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 150 -> 151 -> 155 -> 152 -> 154 -> 153 -> 128 -> 129 -> 130 -> 131 -> 18 -> 19 -> 20 -> 127 -> 126 -> 125 -> 28 -> 27 -> 26 -> 25 -> 21 -> 24 -> 22 -> 23 -> 13 -> 12 -> 14 -> 11 -> 10 -> 9 -> 7 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 275 -> 274 -> 273 -> 272 -> 271 -> 270 -> 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 132 -> 133 -> 269 -> 268 -> 134 -> 135 -> 267 -> 266 -> 264 -> 263 -> 262 -> 261 -> 260 -> 258 -> 259 -> 276 -> 3 -> 4 -> 0
Hier ist eine Grafik mit der entsprechenden Route:
Die OR-Tools-Bibliothek findet die obige Tour sehr schnell: auf einem typischen Computer in weniger als einer Sekunde. Die Gesamtlänge der obigen Tour beträgt 2.790.
Programme abschließen
Hier sind die vollständigen Programme für das Platinenbeispiel:
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) on a circuit board."""
import math
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["locations"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.locations.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP. */
public class TspCircuitBoard {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCircuitBoard.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.locations.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP.
/// A description of the problem can be found here:
/// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesperson_problem.
/// </summary>
public class TspCircuitBoard
{
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.Locations.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Define cost of each arc.
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
Suchstrategie ändern
Die Routinglösung löst nicht immer die optimale Lösung an einen TSP zurück, da Routingprobleme rechenintensiv sind. Die im vorherigen Beispiel zurückgegebene Lösung ist beispielsweise nicht die optimale Route.
Für eine bessere Lösung können Sie eine erweiterte Suchstrategie mit dem Namen guided local search verwenden. Damit kann der Löserechner ein lokales lokales Minimum maskieren, das kürzer ist als alle nahe gelegenen Routen, aber nicht das globale Minimum ist. Nach dem Entfernen vom lokalen Minimum setzt der Rechner die Suche fort.
Die folgenden Beispiele zeigen, wie Sie eine geführte lokale Suche für die Leiterplatte einrichten.
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
search_parameters.log_search = True
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_local_search_metaheuristic(
LocalSearchMetaheuristic::GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH);
searchParameters.mutable_time_limit()->set_seconds(30);
search_parameters.set_log_search(true);
Java
Fügen Sie am Anfang des Programms die folgende „import“-Anweisung ein:import com.google.protobuf.Duration;Legen Sie dann die Suchparameter so fest:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.setLocalSearchMetaheuristic(LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Value.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
.setTimeLimit(Duration.newBuilder().setSeconds(30).build())
.setLogSearch(true)
.build();
C#
Fügen Sie am Anfang des Programms die folgende Zeile ein:using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes; // DurationLegen Sie dann die Suchparameter so fest:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
searchParameters.LocalSearchMetaheuristic = LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Types.Value.GuidedLocalSearch;
searchParameters.TimeLimit = new Duration { Seconds = 30 };
searchParameters.LogSearch = true;
Weitere Strategien für die lokale Suche finden Sie unter Lokale Suchoptionen.
Die obigen Beispiele ermöglichen auch das Logging für die Suche. Das Logging ist zwar nicht erforderlich, kann aber bei der Fehlerbehebung hilfreich sein.
Wenn Sie das Programm ausführen, nachdem Sie die oben beschriebenen Änderungen vorgenommen haben, erhalten Sie die folgende Lösung, die kürzer ist als die im vorherigen Abschnitt gezeigte Lösung.
Objective: 2672 Route: 0 -> 3 -> 276 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 -> 14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 23 -> 22 -> 24 -> 21 -> 25 -> 26 -> 27 -> 28 -> 125 -> 126 -> 127 -> 20 -> 19 -> 130 -> 129 -> 128 -> 153 -> 154 -> 152 -> 155 -> 151 -> 150 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 180 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 158 -> 157 -> 156 -> 118 -> 119 -> 120 -> 121 -> 122 -> 123 -> 124 -> 29 -> 30 -> 31 -> 32 -> 33 -> 34 -> 35 -> 36 -> 37 -> 38 -> 39 -> 40 -> 41 -> 42 -> 59 -> 60 -> 58 -> 43 -> 44 -> 45 -> 46 -> 47 -> 48 -> 49 -> 50 -> 51 -> 52 -> 53 -> 54 -> 55 -> 56 -> 57 -> 67 -> 68 -> 66 -> 69 -> 70 -> 71 -> 72 -> 73 -> 75 -> 74 -> 76 -> 77 -> 78 -> 80 -> 81 -> 88 -> 79 -> 92 -> 93 -> 94 -> 95 -> 96 -> 97 -> 98 -> 99 -> 100 -> 101 -> 102 -> 91 -> 90 -> 89 -> 108 -> 111 -> 87 -> 82 -> 83 -> 86 -> 112 -> 115 -> 85 -> 84 -> 64 -> 65 -> 63 -> 62 -> 61 -> 117 -> 116 -> 114 -> 113 -> 110 -> 109 -> 107 -> 103 -> 104 -> 105 -> 106 -> 173 -> 172 -> 171 -> 170 -> 169 -> 168 -> 167 -> 166 -> 165 -> 164 -> 163 -> 162 -> 187 -> 188 -> 189 -> 190 -> 191 -> 192 -> 185 -> 186 -> 184 -> 183 -> 182 -> 181 -> 179 -> 178 -> 149 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 266 -> 267 -> 135 -> 134 -> 268 -> 269 -> 133 -> 132 -> 131 -> 18 -> 17 -> 16 -> 15 -> 270 -> 271 -> 272 -> 273 -> 274 -> 275 -> 259 -> 258 -> 260 -> 261 -> 262 -> 263 -> 264 -> 265 -> 139 -> 140 -> 147 -> 146 -> 141 -> 142 -> 145 -> 144 -> 198 -> 197 -> 196 -> 193 -> 194 -> 195 -> 200 -> 201 -> 199 -> 143 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 206 -> 207 -> 252 -> 253 -> 256 -> 257 -> 255 -> 254 -> 251 -> 208 -> 209 -> 210 -> 211 -> 212 -> 213 -> 214 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 218 -> 219 -> 220 -> 221 -> 222 -> 223 -> 224 -> 225 -> 226 -> 227 -> 232 -> 233 -> 234 -> 235 -> 236 -> 237 -> 230 -> 231 -> 228 -> 229 -> 250 -> 245 -> 238 -> 239 -> 240 -> 241 -> 242 -> 243 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 248 -> 247 -> 277 -> 278 -> 2 -> 279 -> 1 -> 0
Weitere Suchoptionen finden Sie unter Routingoptionen.
Die besten Algorithmen können jetzt routinemäßig TSP-Instanzen mit Zehntausenden von Knoten lösen. Der Eintrag zum Zeitpunkt der Erstellung dieses Dokuments ist die pla85900-Instanz in TSPLIB, einer VLSI-Anwendung mit 85.900 Knoten. Für bestimmte Instanzen mit Millionen von Knoten sind Lösungen unserer Erfahrung nach innerhalb von 1% einer optimalen Tour garantiert.)
Entfernungsmatrix skalieren
Da der Routing-Laufrechner über Ganzzahlen arbeitet, müssen Sie die Abstände auf Ganzzahlen runden, wenn Ihre Entfernungsmatrix nicht ganzzahlige Einträge enthält. Bei kleinen Entfernungen kann sich die Rundung auf die Lösung auswirken.
Um Probleme beim Runden zu vermeiden, können Sie die Distance Matrix scale aufschlüsseln: Multiplizieren Sie alle Einträge der Matrix mit einer großen Zahl, z. B. 100. Dadurch wird die Länge einer Route mit dem Faktor 100 multipliziert, ohne dass sich die Lösung ändert. Der Vorteil besteht darin, dass beim Runden der Matrixeinträge der Rundungsbetrag (maximal 0,5) im Vergleich zu den Entfernungen sehr klein ist, sodass er keine großen Auswirkungen auf die Lösung hat.
Wenn Sie die Entfernungsmatrix skalieren, müssen Sie auch den Lösungsdrucker ändern, um die skalierten Routenlängen durch den Skalierungsfaktor zu teilen, sodass die nicht skalierten Entfernungen der Routen angezeigt werden.
