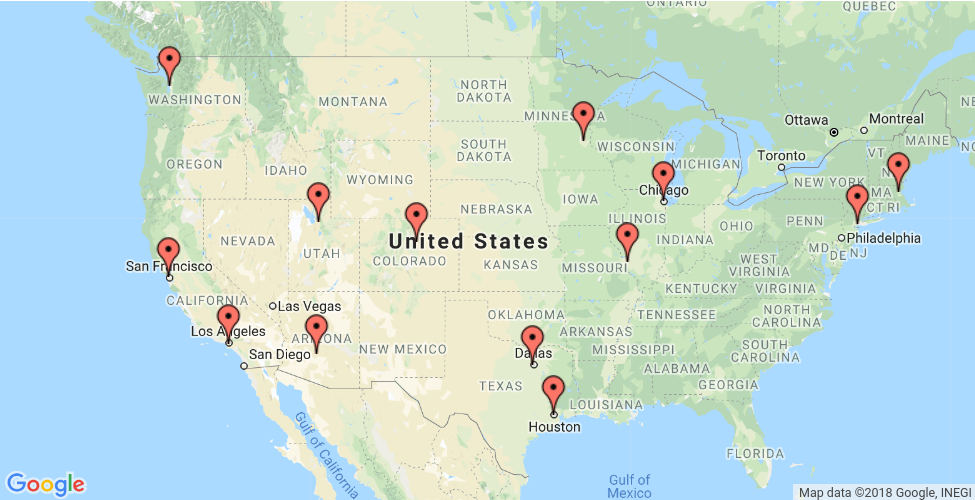
ส่วนนี้จะแสดงตัวอย่างที่แสดงวิธีการแก้ไขปัญหาพนักงานขาย (TSP) ของการท่องเที่ยวสําหรับสถานที่ที่แสดงบนแผนที่ด้านล่าง
ส่วนต่อไปนี้จะแสดงโปรแกรมใน Python, C++, Java และ C# ที่แก้ปัญหา TSP โดยใช้เครื่องมือ
สร้างข้อมูล
โค้ดด้านล่างจะสร้างข้อมูลสําหรับปัญหา
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
เมทริกซ์ระยะทางคืออาร์เรย์ที่มีรายการ i, j คือระยะทางจากตําแหน่ง i ไปยังตําแหน่ง j ในหน่วยไมล์ โดยที่ดัชนีอาร์เรย์สอดคล้องกับตําแหน่งตามลําดับต่อไปนี้
0. New York - 1. Los Angeles - 2. Chicago - 3. Minneapolis - 4. Denver - 5. Dallas
- 6. Seattle - 7. Boston - 8. San Francisco - 9. St. Louis - 10. Houston - 11. Phoenix - 12. Salt Lake City
ข้อมูลดังกล่าวยังรวมถึง
- จํานวนยานพาหนะที่มีปัญหา ซึ่งก็คือ 1 รายการเนื่องจากเป็น TSP (สําหรับปัญหาเกี่ยวกับการกําหนดเส้นทางยานพาหนะ (VRP) จํานวนยานพาหนะอาจมากกว่า 1 คัน)
- สถานีรถไฟ: ตําแหน่งเริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดสําหรับเส้นทาง ในกรณีนี้ สถานีคือ 0 ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับนิวยอร์ก
วิธีอื่นๆ ในการสร้างเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง
ในตัวอย่างนี้ เมทริกซ์ระยะทางได้รับการกําหนดอย่างชัดเจนในโปรแกรม นอกจากนี้ คุณยังใช้ฟังก์ชันในการคํานวณระยะทางระหว่างสถานที่ได้ด้วย เช่น สูตรยูคลิดสําหรับระยะทางระหว่างจุดในเครื่องบิน อย่างไรก็ตาม ระบบจะยังคงคํานวณระยะทางทั้งหมดระหว่างตําแหน่งต่างๆ ไว้ล่วงหน้าและจัดเก็บไว้ในเมทริกซ์ แทนที่จะคํานวณตามรันไทม์ ดูตัวอย่าง: การเจาะแผงวงจร สําหรับตัวอย่างที่สร้างเมทริกซ์ระยะทางด้วยวิธีนี้
อีกทางเลือกหนึ่งคือการใช้ Googleเมทริกซ์ระยะทางของ Google Maps เพื่อสร้างเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง (หรือเวลาเดินทาง) สําหรับปัญหาการกําหนดเส้นทางแบบไดนามิก
สร้างรูปแบบการกําหนดเส้นทาง
โค้ดต่อไปนี้ในส่วนหลักของโปรแกรมจะสร้างตัวจัดการดัชนี (manager) และรูปแบบการกําหนดเส้นทาง (routing) วิธีการ
manager.IndexToNode จะแปลงดัชนีภายในของเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์ (ซึ่งคุณจะละเว้นได้อย่างปลอดภัย) เป็นตัวเลขของสถานที่ หมายเลขสถานที่ตั้งจะสอดคล้องกับดัชนีสําหรับเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง
Python
data = create_data_model()
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
C++
DataModel data;
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
RoutingModel routing(manager);
Java
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
C#
DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
อินพุตไปยัง RoutingIndexManager คือ
- จํานวนแถวของเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง ซึ่งเป็นจํานวนสถานที่ (รวมถึงสถานีรถไฟ)
- จํานวนยานพาหนะที่เกิดปัญหา
- โหนดที่ตรงกับคลัง
สร้างโค้ดเรียกกลับระยะทาง
หากต้องการใช้เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิต คุณต้องสร้างการเรียกกลับ (หรือแผนการเดินทาง): ฟังก์ชันที่ใช้คู่ตําแหน่งและแสดงผลระยะทางระหว่างรายการเหล่านั้น วิธีที่ง่ายที่สุดคือการใช้เมทริกซ์ระยะทาง
ฟังก์ชันต่อไปนี้จะสร้างโค้ดเรียกกลับและลงทะเบียนกับเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์เป็น transit_callback_index
Python
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
C++
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
Java
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
C#
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
The callback accepts two indices, from_index and to_index, and returns the
corresponding entry of the distance matrix.
Set the cost of travel
The arc cost evaluator tells the solver how to calculate the cost of travel between any two locations — in other words, the cost of the edge (or arc) joining them in the graph for the problem. The following code sets the arc cost evaluator.
Python
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
ในตัวอย่างนี้ ผู้ประเมินต้นทุนของเส้นโค้งคือ transit_callback_index ซึ่งเป็นการอ้างอิงภายในของเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์การเรียกกลับของระยะทาง ซึ่งหมายความว่าต้นทุนการเดินทางระหว่างสถานที่ 2 แห่งเป็นเพียงระยะทางระหว่างสถานที่ 2 แห่ง
แต่โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ค่าใช้จ่ายอาจขึ้นอยู่กับปัจจัยอื่นๆ ด้วย
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังกําหนดผู้ประเมินต้นทุนทางโค้งหลายรายการได้ โดยขึ้นอยู่กับยานพาหนะที่เดินทางระหว่างสถานที่ต่างๆ โดยใช้เมธอด routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfVehicle()
เช่น หากยานพาหนะมีความเร็วแตกต่างกัน คุณอาจกําหนดค่าใช้จ่ายในการเดินทางระหว่างสถานที่ให้เป็นระยะทางหารด้วยความเร็วของยานพาหนะ กล่าวคือ เวลาเดินทาง
ตั้งค่าพารามิเตอร์การค้นหา
โค้ดต่อไปนี้จะกําหนดพารามิเตอร์การค้นหาเริ่มต้นและเมธอดที่เป็นตัวของเขาในการค้นหาโซลูชันแรก
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
Java
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
C#
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
โค้ดนี้ตั้งกลยุทธ์การแก้ปัญหาแรกเป็น PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC ซึ่งจะสร้างเส้นทางเริ่มต้นสําหรับเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์ด้วยเพิ่มขอบที่มีน้ําหนักน้อยซ้ําๆ ซึ่งไม่ได้นําไปสู่โหนดที่เคยเข้าชม (นอกเหนือจาก Depot) ดูตัวเลือกอื่นๆ ได้ที่กลยุทธ์โซลูชันแรก
เพิ่มเครื่องพิมพ์โซลูชัน
ฟังก์ชันที่แสดงโซลูชันที่เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์แสดงผลด้านล่าง ฟังก์ชันจะดึงเส้นทางจากโซลูชันและพิมพ์ไปยังคอนโซล
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
ฟังก์ชันจะแสดงเส้นทางที่ดีที่สุดและระยะทางที่กําหนดโดย ObjectiveValue()
แก้โจทย์และพิมพ์โซลูชัน
สุดท้าย คุณสามารถเรียกใช้เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์และพิมพ์โซลูชันได้
Python
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
C++
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
Java
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters); printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
C#
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
การดําเนินการนี้จะแสดงโซลูชันและแสดงเส้นทางที่ดีที่สุด
เรียกใช้โปรแกรม
เมื่อคุณเรียกใช้โปรแกรม โปรแกรมจะแสดงเอาต์พุตต่อไปนี้
Objective: 7293 miles Route for vehicle 0: 0 -> 7 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 12 -> 6 -> 8 -> 1 -> 11 -> 10 -> 5 -> 9 -> 0
ในตัวอย่างนี้มีเส้นทางเดียวเท่านั้นเพราะเป็น TSP แต่ปัญหาการกําหนดเส้นทางทั่วไปสําหรับยานพาหนะ โซลูชันมีเส้นทางหลายเส้นทาง
บันทึกเส้นทางลงในรายการหรืออาร์เรย์
แต่คุณจะบันทึกเส้นทาง (หรือเส้นทางสําหรับ VRP) ไปยังรายการหรืออาร์เรย์ได้ เพื่อเป็นทางเลือกในการพิมพ์โซลูชันโดยตรง คุณจะได้รับประโยชน์จากการแสดงเส้นทางเผื่อในกรณีที่อยากทําสิ่งเหล่านี้ในภายหลัง เช่น คุณสามารถเรียกใช้โปรแกรมได้หลายครั้งด้วยพารามิเตอร์ต่างๆ และบันทึกเส้นทางในโซลูชันที่แสดงผลไว้ในไฟล์เพื่อเปรียบเทียบ
ฟังก์ชันต่อไปนี้จะบันทึกเส้นทางในโซลูชันไปยัง VRP (อาจมีหลายยานพาหนะ) เป็นรายการ (Python) หรืออาร์เรย์ (C++)
Python
def get_routes(solution, routing, manager):
"""Get vehicle routes from a solution and store them in an array."""
# Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array whose
# i,j entry is the jth location visited by vehicle i along its route.
routes = []
for route_nbr in range(routing.vehicles()):
index = routing.Start(route_nbr)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
routes.append(route)
return routes
C++
std::vector<std::vector<int>> GetRoutes(const Assignment& solution,
const RoutingModel& routing,
const RoutingIndexManager& manager) {
// Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array, whose
// i, j entry is the node for the jth visit of vehicle i.
std::vector<std::vector<int>> routes(manager.num_vehicles());
// Get routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < manager.num_vehicles(); ++vehicle_id) {
int64_t index = routing.Start(vehicle_id);
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
}
}
return routes;
}
คุณใช้ฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้เพื่อดูเส้นทางในตัวอย่าง VRP ใดก็ได้ในส่วนการกําหนดเส้นทาง
โค้ดต่อไปนี้จะแสดงเส้นทาง
Python
routes = get_routes(solution, routing, manager)
# Display the routes.
for i, route in enumerate(routes):
print('Route', i, route)
C++
const std::vector⟨std::vector⟨int⟩⟩
routes = GetRoutes(*solution,
routing,
manager);
// Display the routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < routes.size(); ++vehicle_id) {
LOG(INFO) << "Route " << vehicle_id;
for (int j = 1; j < routes[vehicle_id].size(); ++j) {
LOG(INFO) << routes[vehicle_id][j];
}
}
สําหรับตัวอย่างปัจจุบัน โค้ดนี้จะแสดงเส้นทางต่อไปนี้
Route 0 [0, 7, 2, 3, 4, 12, 6, 8, 1, 11, 10, 5, 9, 0]
ในรูปแบบการออกกําลังกาย ให้แก้ไขโค้ดด้านบนเพื่อจัดรูปแบบเอาต์พุตในลักษณะเดียวกันกับเครื่องพิมพ์โซลูชันสําหรับโปรแกรม
สิ้นสุดโปรแกรม
โปรแกรม TSP ที่สมบูรณ์จะแสดงด้านล่าง
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) between cities."""
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP using distance matrix. */
public class TspCities {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCities.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP using distance matrix.
/// </summary>
public class TspCities
{
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
ตัวอย่าง: การเจาะแผงวงจร
ตัวอย่างถัดไปเกี่ยวกับการเจาะรูในแผงวงจรที่มีการเจาะอัตโนมัติ ปัญหาคือการหาเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดสําหรับสลักบนกระดานเพื่อเจาะรูที่จําเป็นทั้งหมด ตัวอย่างนี้นํามาจาก TSPLIB ซึ่งเป็นไลบรารีของปัญหา TSP
แผนภูมิกระจายของสถานที่ตั้งที่มีช่องโหว่มีดังนี้
ส่วนต่อไปนี้นําเสนอโปรแกรมที่หาวิธีแก้ไขปัญหาของวงจรวงจรโดยใช้พารามิเตอร์การค้นหาเริ่มต้นของเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิต หลังจากนั้น เราจะแสดงวิธีหาโซลูชันที่ดีขึ้นโดยเปลี่ยนกลยุทธ์การค้นหา
สร้างข้อมูล
ข้อมูลสําหรับปัญหาประกอบด้วย 280 จุดในเครื่องบิน โดยแสดงในแผนภูมิกระจายด้านบน โปรแกรมสร้างข้อมูลในอาร์เรย์ของคู่ลําดับที่สอดคล้องกับจุดในเครื่องบิน ตามที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
คํานวณเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง
ฟังก์ชันด้านล่างจะคํานวณระยะทาง Euclidean ระหว่าง 2 จุดในข้อมูลและจัดเก็บไว้ในอาร์เรย์ เนื่องจากเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิตทํางานโดยใช้จํานวนเต็ม ฟังก์ชันจะปัดเศษระยะทางที่คํานวณแล้วเป็นจํานวนเต็ม การปัดเศษจะไม่ส่งผลต่อโซลูชันในตัวอย่างนี้ แต่ในกรณีอื่นๆ โปรดดูการปรับขนาดเมทริกซ์ระยะทางเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการปัดเศษที่อาจเกิดขึ้น
Python
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
C++
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
Java
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
เพิ่มการติดต่อกลับทางไกล
โค้ดที่สร้างโค้ดเรียกกลับระยะทางเกือบจะเหมือนกับในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ แต่ในกรณีนี้ โปรแกรมจะเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่คํานวณเมทริกซ์ระยะทางก่อนที่จะเพิ่มโค้ดเรียกกลับ
Python
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
เครื่องพิมพ์โซลูชัน
ฟังก์ชันต่อไปนี้จะพิมพ์โซลูชันไปยังคอนโซล ฟังก์ชันจะแสดงเพียงดัชนีตําแหน่งในการกําหนดเส้นทางเพื่อให้เอาต์พุตมีขนาดกะทัดรัดมากขึ้น
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
ฟังก์ชันหลักเหมือนกับฟังก์ชันในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ แต่ยังมีการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่สร้างเมทริกซ์ระยะทางด้วย
การเรียกใช้โปรแกรม
โปรแกรมที่สมบูรณ์จะแสดงในส่วนถัดไป เมื่อคุณเรียกใช้โปรแกรม โปรแกรมจะแสดงเส้นทางต่อไปนี้
Total distance: 2790 Route of vehicle 0: 0 -> 1 -> 279 -> 2 -> 278 -> 277 -> 247 -> 248 -> 249 -> 246 -> 244 -> 243 -> 242 -> 241 -> 240 -> 239 -> 238 -> 237 -> 236 -> 235 -> 234 -> 233 -> 232 -> 231 -> 230 -> 245 -> 250 -> 229 -> 228 -> 227 -> 226 -> 225 -> 224 -> 223 -> 222 -> 221 -> 220 -> 219 -> 218 -> 217 -> 216 -> 215 -> 214 -> 213 -> 212 -> 211 -> 210 -> 209 -> 208 -> 251 -> 254 -> 255 -> 257 -> 256 -> 253 -> 252 -> 207 -> 206 -> 205 -> 204 -> 203 -> 202 -> 142 -> 141 -> 146 -> 147 -> 140 -> 139 -> 265 -> 136 -> 137 -> 138 -> 148 -> 149 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 178 -> 179 -> 180 -> 181 -> 182 -> 183 -> 184 -> 186 -> 185 -> 192 -> 196 -> 197 -> 198 -> 144 -> 145 -> 143 -> 199 -> 201 -> 200 -> 195 -> 194 -> 193 -> 191 -> 190 -> 189 -> 188 -> 187 -> 163 -> 164 -> 165 -> 166 -> 167 -> 168 -> 169 -> 171 -> 170 -> 172 -> 105 -> 106 -> 104 -> 103 -> 107 -> 109 -> 110 -> 113 -> 114 -> 116 -> 117 -> 61 -> 62 -> 63 -> 65 -> 64 -> 84 -> 85 -> 115 -> 112 -> 86 -> 83 -> 82 -> 87 -> 111 -> 108 -> 89 -> 90 -> 91 -> 102 -> 101 -> 100 -> 99 -> 98 -> 97 -> 96 -> 95 -> 94 -> 93 -> 92 -> 79 -> 88 -> 81 -> 80 -> 78 -> 77 -> 76 -> 74 -> 75 -> 73 -> 72 -> 71 -> 70 -> 69 -> 66 -> 68 -> 67 -> 57 -> 56 -> 55 -> 54 -> 53 -> 52 -> 51 -> 50 -> 49 -> 48 -> 47 -> 46 -> 45 -> 44 -> 43 -> 58 -> 60 -> 59 -> 42 -> 41 -> 40 -> 39 -> 38 -> 37 -> 36 -> 35 -> 34 -> 33 -> 32 -> 31 -> 30 -> 29 -> 124 -> 123 -> 122 -> 121 -> 120 -> 119 -> 118 -> 156 -> 157 -> 158 -> 173 -> 162 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 150 -> 151 -> 155 -> 152 -> 154 -> 153 -> 128 -> 129 -> 130 -> 131 -> 18 -> 19 -> 20 -> 127 -> 126 -> 125 -> 28 -> 27 -> 26 -> 25 -> 21 -> 24 -> 22 -> 23 -> 13 -> 12 -> 14 -> 11 -> 10 -> 9 -> 7 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 275 -> 274 -> 273 -> 272 -> 271 -> 270 -> 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 132 -> 133 -> 269 -> 268 -> 134 -> 135 -> 267 -> 266 -> 264 -> 263 -> 262 -> 261 -> 260 -> 258 -> 259 -> 276 -> 3 -> 4 -> 0
นี่คือกราฟของเส้นทางที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ส่วนไลบรารี OR เครื่องมือจะค้นหาทัวร์ชมข้างต้นได้อย่างรวดเร็วมากในเวลาไม่ถึง 1 วินาทีในคอมพิวเตอร์ทั่วไป ความยาวรวมของทัวร์ด้านบนคือ 2,790
สิ้นสุดโปรแกรม
ตัวอย่างโปรแกรมแผงวงจรที่สมบูรณ์มีดังนี้
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) on a circuit board."""
import math
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["locations"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.locations.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP. */
public class TspCircuitBoard {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCircuitBoard.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.locations.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP.
/// A description of the problem can be found here:
/// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesperson_problem.
/// </summary>
public class TspCircuitBoard
{
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.Locations.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Define cost of each arc.
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
การเปลี่ยนแปลงกลยุทธ์การค้นหา
เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิตไม่ได้แสดงผลโซลูชันที่ดีที่สุดไปยัง TSP เสมอไป เนื่องจากโจทย์การกําหนดเส้นทางนั้นไม่สามารถคํานวณแบบคํานวณได้ยาก ตัวอย่างเช่น วิธีแก้ไขในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ไม่ใช่เส้นทางที่เหมาะสม
หากต้องการวิธีแก้ไขที่ดีกว่า คุณสามารถใช้กลยุทธ์การค้นหาขั้นสูงที่เรียกว่าการค้นหาในพื้นที่แบบมีคําแนะนํา ซึ่งจะช่วยให้เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์ได้ใช้ค่าต่ําสุดในร้าน ซึ่งเป็นโซลูชันที่สั้นกว่าเส้นทางใกล้เคียงทั้งหมด แต่ไม่ใช่ค่าเฉลี่ยต่ําสุดทั่วโลก หลังจากออกจากตําแหน่งขั้นต่ําในเครื่องแล้ว เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์จะทําการค้นหาต่อไป
ตัวอย่างด้านล่างแสดงวิธีการตั้งค่าการค้นหาในเครื่องสําหรับตัวอย่างแผงวงจร
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
search_parameters.log_search = True
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_local_search_metaheuristic(
LocalSearchMetaheuristic::GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH);
searchParameters.mutable_time_limit()->set_seconds(30);
search_parameters.set_log_search(true);
Java
เพิ่มคําสั่ง "นําเข้า" ต่อไปนี้ที่จุดเริ่มต้นของโปรแกรมimport com.google.protobuf.Duration;แล้วตั้งค่าพารามิเตอร์การค้นหาดังนี้
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.setLocalSearchMetaheuristic(LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Value.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
.setTimeLimit(Duration.newBuilder().setSeconds(30).build())
.setLogSearch(true)
.build();
C#
เพิ่มบรรทัดต่อไปนี้ที่จุดเริ่มต้นของโปรแกรมusing Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes; // Durationแล้วตั้งค่าพารามิเตอร์การค้นหาดังนี้
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
searchParameters.LocalSearchMetaheuristic = LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Types.Value.GuidedLocalSearch;
searchParameters.TimeLimit = new Duration { Seconds = 30 };
searchParameters.LogSearch = true;
หากต้องการทราบกลยุทธ์การค้นหาอื่นๆ ในท้องถิ่น โปรดดูตัวเลือกการค้นหาในพื้นที่
ตัวอย่างข้างต้นยังเปิดใช้การบันทึกสําหรับการค้นหาด้วย แม้ว่าการบันทึกจะไม่จําเป็น แต่การแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องก็อาจเป็นประโยชน์
เมื่อเรียกใช้โปรแกรมหลังจากทําการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่แสดงด้านบน คุณจะได้รับโซลูชันต่อไปนี้ ซึ่งสั้นกว่าโซลูชันที่แสดงในส่วนก่อนหน้า
Objective: 2672 Route: 0 -> 3 -> 276 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 -> 14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 23 -> 22 -> 24 -> 21 -> 25 -> 26 -> 27 -> 28 -> 125 -> 126 -> 127 -> 20 -> 19 -> 130 -> 129 -> 128 -> 153 -> 154 -> 152 -> 155 -> 151 -> 150 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 180 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 158 -> 157 -> 156 -> 118 -> 119 -> 120 -> 121 -> 122 -> 123 -> 124 -> 29 -> 30 -> 31 -> 32 -> 33 -> 34 -> 35 -> 36 -> 37 -> 38 -> 39 -> 40 -> 41 -> 42 -> 59 -> 60 -> 58 -> 43 -> 44 -> 45 -> 46 -> 47 -> 48 -> 49 -> 50 -> 51 -> 52 -> 53 -> 54 -> 55 -> 56 -> 57 -> 67 -> 68 -> 66 -> 69 -> 70 -> 71 -> 72 -> 73 -> 75 -> 74 -> 76 -> 77 -> 78 -> 80 -> 81 -> 88 -> 79 -> 92 -> 93 -> 94 -> 95 -> 96 -> 97 -> 98 -> 99 -> 100 -> 101 -> 102 -> 91 -> 90 -> 89 -> 108 -> 111 -> 87 -> 82 -> 83 -> 86 -> 112 -> 115 -> 85 -> 84 -> 64 -> 65 -> 63 -> 62 -> 61 -> 117 -> 116 -> 114 -> 113 -> 110 -> 109 -> 107 -> 103 -> 104 -> 105 -> 106 -> 173 -> 172 -> 171 -> 170 -> 169 -> 168 -> 167 -> 166 -> 165 -> 164 -> 163 -> 162 -> 187 -> 188 -> 189 -> 190 -> 191 -> 192 -> 185 -> 186 -> 184 -> 183 -> 182 -> 181 -> 179 -> 178 -> 149 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 266 -> 267 -> 135 -> 134 -> 268 -> 269 -> 133 -> 132 -> 131 -> 18 -> 17 -> 16 -> 15 -> 270 -> 271 -> 272 -> 273 -> 274 -> 275 -> 259 -> 258 -> 260 -> 261 -> 262 -> 263 -> 264 -> 265 -> 139 -> 140 -> 147 -> 146 -> 141 -> 142 -> 145 -> 144 -> 198 -> 197 -> 196 -> 193 -> 194 -> 195 -> 200 -> 201 -> 199 -> 143 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 206 -> 207 -> 252 -> 253 -> 256 -> 257 -> 255 -> 254 -> 251 -> 208 -> 209 -> 210 -> 211 -> 212 -> 213 -> 214 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 218 -> 219 -> 220 -> 221 -> 222 -> 223 -> 224 -> 225 -> 226 -> 227 -> 232 -> 233 -> 234 -> 235 -> 236 -> 237 -> 230 -> 231 -> 228 -> 229 -> 250 -> 245 -> 238 -> 239 -> 240 -> 241 -> 242 -> 243 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 248 -> 247 -> 277 -> 278 -> 2 -> 279 -> 1 -> 0
โปรดดูตัวเลือกการค้นหาเพิ่มเติมที่หัวข้อตัวเลือกการกําหนดเส้นทาง
ตอนนี้อัลกอริทึมที่ดีที่สุดสามารถแก้ปัญหาอินสแตนซ์ TSP ที่มีโหนดหลายหมื่นรายการเป็นประจํา (ระเบียน ณ เวลาที่เขียนคืออินสแตนซ์ pla85900 ใน TSPLIB ซึ่งเป็นแอปพลิเคชัน VLSI ที่มี 85,900 โหนด ในบางกรณี โหนดหลายล้านรายการมีการแก้ปัญหาภายใน 1% ของทัวร์ที่เหมาะสมที่สุด)
การปรับขนาดเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง
เนื่องจากเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิตทํางานโดยใช้จํานวนเต็ม หากเมทริกซ์ระยะทางมีรายการที่ไม่ใช่จํานวนเต็ม คุณต้องปัดเศษระยะทางเป็นจํานวนเต็ม หากระยะทางไกลเกินไป การปัดเศษอาจมีผลต่อโซลูชัน
หากต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาการปัดเศษ คุณต้องscaleเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง: คูณรายการทั้งหมดของเมทริกซ์จํานวนมาก เช่น 100 โดยจะคูณความยาวของเส้นทางด้วยปัจจัย 100 แต่ไม่เปลี่ยนโซลูชัน ข้อดีตอนนี้คือเมื่อคุณปัดเศษรายการเมทริกซ์ จํานวนที่ปัดเศษ (ซึ่งเท่ากับ 0.5) จะมีน้อยมากเมื่อเทียบกับระยะทาง จึงไม่ส่งผลกับโซลูชันอย่างมาก
หากปรับขนาดเมทริกซ์ระยะทาง คุณยังจําเป็นต้องเปลี่ยนเครื่องพิมพ์ของโซลูชันเพื่อหารความยาวเส้นทางที่ปรับขนาดด้วยปัจจัยการปรับขนาด เพื่อให้แสดงระยะทางที่ปรับขนาดไม่ได้ของเส้นทาง
