शेड्यूल करने से जुड़ी एक आम समस्या नौकरी की दुकान है, जिसमें कई नौकरियां होती हैं कई मशीनों पर प्रोसेस होती हैं.
हर एक जॉब में कई टास्क होते हैं, जिन्हें दिए गए तरीके से पूरा किया जाना चाहिए.
ऑर्डर करने के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाता है और हर टास्क को एक खास मशीन पर प्रोसेस किया जाना चाहिए.
उदाहरण के लिए, नौकरी किसी एक उपभोक्ता आइटम का निर्माण हो सकता है, जैसे
एक ऑटोमोबाइल.
समस्या यह है कि मशीन पर टास्क शेड्यूल किए जाएं, ताकि कम से कम
शेड्यूल का length—सभी जॉब को पूरा होने में लगने वाला समय.
जॉब शॉप से जुड़ी समस्या के लिए कई पाबंदियां हैं:
- किसी जॉब के लिए कोई टास्क तब तक शुरू नहीं किया जा सकता, जब तक कि उस जॉब के लिए पिछला टास्क न हो पूरा हुआ.
- मशीन एक बार में सिर्फ़ एक ही टास्क पर काम कर सकती है.
- एक बार शुरू किए जाने के बाद, टास्क पूरा होने तक होता है.
उदाहरण के तौर पर दी गई समस्या
नीचे नौकरी की दुकान से जुड़ी समस्या का एक आसान उदाहरण दिया गया है, जिसमें हर टास्क को लेबल किया गया है नंबर के जोड़े (m, p) का इस्तेमाल करें, जहां m, टास्क की संख्या है पर प्रोसेस होना चाहिए और p टास्क का प्रोसेस होने में लगने वाला समय है — कम समय लगता है. (नौकरियों और मशीनों की संख्या 0 से शुरू होती है.)
- नौकरी 0 = [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)]
- नौकरी 1 = [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)]
- नौकरी 2 = [(1, 4), (2, 3)]
उदाहरण में, नौकरी 0 में तीन टास्क हैं. पहला, (0, 3), प्रोसेस होना चाहिए समय की 3 यूनिट में मशीन 0 पर. दूसरा, (1, 2), समय की 2 यूनिट में 1 मशीन वगैरह. कुल मिलाकर आठ टास्क हैं.
समस्या का समाधान
जॉब शॉप की समस्या का समाधान, हर एक व्यक्ति के लिए शुरुआत का समय तय करना है
यह टास्क, ऊपर दी गई शर्तों को पूरा करता है.
नीचे दिया गया डायग्राम, समस्या का एक संभावित समाधान दिखाता है:
अभी तक किसी भी व्यक्ति ने चेक इन नहीं किया है
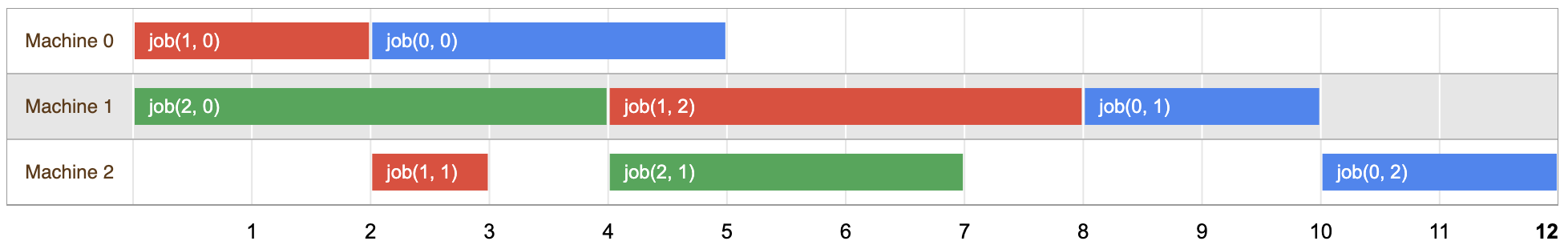
यह देखा जा सकता है कि हर टास्क के लिए टास्क, ओवरलैप न होने वाले समय पर शेड्यूल किए गए हैं या नहीं अंतरालों को, समस्या के क्रम में रखा जाता है.
इस सलूशन की अवधि 12 है. यह पहली बार है, जब तीनों जॉब पूर्ण हैं. हालांकि, जैसा कि आप नीचे देखेंगे, यह उस समस्या को हल कर सकें.
समस्या के लिए वैरिएबल और कंस्ट्रेंट
इस सेक्शन में, वैरिएबल और कंस्ट्रेंट को
समस्या.
सबसे पहले, task(i, j) को जॉब i के क्रम में मौजूद jth टास्क को बताने दें. इसके लिए
उदाहरण के लिए, task(0, 2) नौकरी 0 के लिए दूसरे टास्क को दिखाता है, जो इससे जुड़ा है
समस्या की जानकारी में, (1, 2) जोड़े.
इसके बाद, task(i, j) का शुरू होने का समय ti, j के तौर पर सेट करें. कॉन्टेंट बनाने
ti, j जॉब शॉप से जुड़ी समस्या का मुख्य वैरिएबल है. किसी
समाधान में इन वैरिएबल के लिए मान तय करना होता है, जो
की ज़रूरत.
जॉब शॉप से जुड़ी समस्या के लिए दो तरह की पाबंदियां होती हैं:
- प्राथमिकता प्रतिबंध — ये इस शर्त से पैदा होते हैं कि किसी
एक ही जॉब में लगातार दो टास्क करते हैं, तो पहला टास्क होने से पहले
दूसरा शुरू किया जा सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए,
task(0, 2)औरtask(0, 3)नौकरी के लिए लगातार होने वाले टास्क.task(0, 2)को प्रोसेस होने में लगने वाला समय 2 है. इसलिए, शुरू होने का समय दूसरे टास्क के लिए, शुरू होने के समय के बाद कीtask(0, 3)यूनिट में कम से कम दो यूनिट होनी चाहिए. (शायद टास्क 2 किसी दरवाज़े को पेंट करना है और पेंट करने में दो घंटे लगते हैं dry.) इस वजह से, आपको यह कंस्ट्रेंट मिलता है:t0, 2 + 2 <=t0, 3
- कोई ओवरलैप सीमा नहीं — ये इस वजह से पैदा होती हैं,
मशीन एक साथ दो काम नहीं कर सकती.
उदाहरण के लिए, टास्क(0, 2) और टास्क(2, 1), दोनों मशीन 1 पर प्रोसेस किए जाते हैं.
प्रोसेस होने में लगने वाला समय 2 और 4 है, इसलिए इनमें से कोई एक समय देखें
शर्तों में ये बातें शामिल होनी चाहिए:
t0, 2 + 2 <=t2, 1 (अगरtask(0, 2)शेड्यूल किया गया हैtask(2, 1)से पहले) याt2, 1 + 4 <=t0, 2 (अगरtask(2, 1)शेड्यूल किया गया हैtask(0, 2)से पहले).
समस्या का मकसद
जॉब शॉप से जुड़ी समस्या का मकसद मेकस्पैन को कम करना है: जॉब के शुरू होने के समय से लेकर हाल की आखिरी तारीख तक की अवधि.
प्रोग्राम का समाधान
नीचे दिए गए सेक्शन में उस प्रोग्राम के मुख्य एलिमेंट के बारे में बताया गया है जो समस्याओं को हल करता है जॉब शॉप से जुड़ी समस्या है.
लाइब्रेरी इंपोर्ट करें
यहां दिया गया कोड ज़रूरी लाइब्रेरी इंपोर्ट करता है.
Python
import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h"
Java
import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream;
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
डेटा तय करना
इसके बाद, प्रोग्राम, समस्या के लिए डेटा तय करता है.
Python
jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job)
C++
using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } }
Java
class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
C#
var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
मॉडल का एलान करना
यहां दिया गया कोड, समस्या के लिए मॉडल बताता है.
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel();
वैरिएबल तय करना
नीचे दिया गया कोड, समस्या में शामिल वैरिएबल के बारे में बताता है.
Python
# Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var)
C++
struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } }
Java
class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } }
C#
Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } }
हर टास्क और टास्क के लिए, प्रोग्राम में मॉडल की
वैरिएबल बनाने के लिए NewIntVar/new_int_var/newIntVar तरीका:
start_var: टास्क के शुरू होने का समय.end_var: टास्क के खत्म होने का समय.
start_var और end_var की ऊपरी सीमा horizon है, जो
सभी जॉब में सभी टास्क की प्रोसेसिंग में लगने वाला समय.
horizon इन वजहों से सभी टास्क को पूरा करने के लिए काफ़ी है:
अगर आपने टास्क को नॉन-ओवरलैपिंग टाइम इंटरवल में शेड्यूल किया है, तो यह
समाधान), शेड्यूल की कुल अवधि ठीक horizon है. इसलिए,
इष्टतम समाधान की अवधि horizon से ज़्यादा नहीं हो सकती.
इसके बाद, प्रोग्राम NewIntervalVar/new_interval_var/newIntervalVar का इस्तेमाल करता है
इंटरवल वैरिएबल बनाने का तरीका —जिसकी वैल्यू वैरिएबल समय है
इंटरवल — के हिसाब से देखें. इस तरीके के इनपुट हैं:
- टास्क के शुरू होने का समय.
- टास्क के लिए समयावधि.
- टास्क के खत्म होने का समय.
- इंटरवल वैरिएबल का नाम.
किसी भी हल में, end_var घटाकर start_var duration के बराबर होना चाहिए.
सीमाएं तय करना
यह कोड समस्या की सीमाओं के बारे में बताता है.
Python
# Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end )
C++
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } }
Java
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } }
C#
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } }
प्रोग्राम, मॉडल के AddNoOverlap/add_no_overlap/addNoOverlap तरीके का इस्तेमाल करता है
नो ओवरलैप कंस्ट्रेंट बनाने के लिए, जो
ओवरलैप कर रहा है.
इसके बाद, प्रोग्राम में प्राथमिकता वाले कंस्ट्रेंट को जोड़ दिया जाता है, जो एक ही जॉब में समय पर ओवरलैप होने वाले लगातार टास्क. हर नौकरी के लिए और जॉब में हर टास्क के लिए, एक लीनियर कंस्ट्रेंट जोड़ दिया जाता है, ताकि यह बताया जा सके कि आखिर में टास्क का समय, जॉब में अगले टास्क के शुरू होने के समय से पहले होने वाला है.
मकसद तय करना
नीचे दिया गया कोड, समस्या के मकसद के बारे में बताता है.
Python
# Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var)
C++
// Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var);
Java
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar);
C#
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar);
यह कोड एक मकसद वैरिएबल बनाता है और उसे इतना सीमित करता है कि सभी नौकरियों को खत्म करने के लिए किया जा सकता है.
सॉल्वर आज़माएं
यहां दिया गया कोड, सॉल्वर को कॉल करता है.
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model)
C++
const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build());
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model);
C#
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}");
नतीजे दिखाएं
यह कोड, सबसे सही शेड्यूल और टास्क के साथ नतीजे दिखाता है अंतराल.
Python
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.")
C++
if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; }
Java
if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); }
C#
if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); }
सबसे सही शेड्यूल नीचे दिखाया गया है:
Optimal Schedule Length: 11
Machine 0: job_0_0 job_1_0
[0,3] [3,5]
Machine 1: job_2_0 job_0_1 job_1_2
[0,4] [4,6] [7,11]
Machine 2: job_1_1 job_0_2 job_2_1
[5,6] [6,8] [8,11]

ईगल जैसी आंखों वाला उपयोगकर्ता, जो मशीन 1 की जांच कर रहा है, हो सकता है कि Job_1_2 को इसके शेड्यूल के तौर पर क्यों शेड्यूल किया गया है समय 6 के बजाय समय 7. दोनों ही समाधान मान्य हैं, लेकिन याद रखें: लक्ष्य तरीका है कि काम कम हो जाए. Job_1_2 को पहले ले जाने से मेकस्पैन कम नहीं होगा इसलिए, सॉल्वर के नज़रिए से दोनों सलूशन बराबर होते हैं.
पूरा प्रोग्राम
आख़िर में, जॉब शॉप से जुड़ी समस्या के लिए पूरा प्रोग्राम यहाँ दिया गया है.
Python
"""Minimal jobshop example.""" import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model def main() -> None: """Minimal jobshop problem.""" # Data. jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job) # Create the model. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var) # Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end ) # Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var) # Creates the solver and solve. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model) if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.") # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" - conflicts: {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" - branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" - wall time: {solver.wall_time}s") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
C++
// Nurse scheduling problem with shift requests. #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void MinimalJobshopSat() { using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } } // Creates the model. CpModelBuilder cp_model; struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var); const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build()); if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; } // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main() { operations_research::sat::MinimalJobshopSat(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** Minimal Jobshop problem. */ public class MinimalJobshopSat { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model); if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); } // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.printf(" conflicts: %d%n", solver.numConflicts()); System.out.printf(" branches : %d%n", solver.numBranches()); System.out.printf(" wall time: %f s%n", solver.wallTime()); } private MinimalJobshopSat() {} }
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class ScheduleRequestsSat { private class AssignedTask : IComparable { public int jobID; public int taskID; public int start; public int duration; public AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } public int CompareTo(object obj) { if (obj == null) return 1; AssignedTask otherTask = obj as AssignedTask; if (otherTask != null) { if (this.start != otherTask.start) return this.start.CompareTo(otherTask.start); else return this.duration.CompareTo(otherTask.duration); } else throw new ArgumentException("Object is not a Temperature"); } } public static void Main(String[] args) { var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar); // Solve CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}"); if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); } Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts: {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()}s"); } }
