Un problema comune di pianificazione è quello delle offerte di lavoro, in cui vengono assegnati più lavori vengono elaborati su più computer.
Ogni job consiste in una sequenza di attività, che devono essere eseguite in un
e ogni attività deve essere elaborata su una macchina specifica.
Ad esempio, il lavoro potrebbe essere la produzione di un singolo articolo di consumo,
un'automobile.
Il problema è pianificare le attività sulle macchine in modo da ridurre al minimo
length della pianificazione: il tempo necessario per il completamento di tutti i job.
Esistono diversi vincoli per il problema dell'officina:
- Non è possibile avviare attività per un job finché l'attività precedente per quel job non è completata.
- Una macchina può lavorare a un'unica attività alla volta.
- Una volta avviata, un'attività deve essere eseguita fino al completamento.
Problema di esempio
Di seguito è riportato un semplice esempio di problema relativo all'officina, in cui ogni attività è etichettata da una coppia di numeri (m, p), dove m è il numero della macchina per cui deve essere elaborata su e p è il tempo di elaborazione dell'attività: per la quantità di tempo richiesta. (La numerazione di job e macchine inizia da 0.)
- job 0 = [(0; 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)]
- job 1 = [(0; 2), (2; 1), (1, 4)]
- lavoro 2 = [(1, 4), (2, 3)]
Nell'esempio, il job 0 ha tre attività. Il primo, (0, 3), deve essere elaborato sulla macchina 0 in 3 unità di tempo. Il secondo, (1, 2), deve essere elaborato macchina 1 in 2 unità di tempo e così via. In tutto, ci sono otto attività.
Una soluzione al problema
Una soluzione al problema dell'officina è l'assegnazione di un'ora di inizio per ogni
che soddisfa i vincoli indicati sopra.
Il diagramma seguente mostra una possibile soluzione al problema:
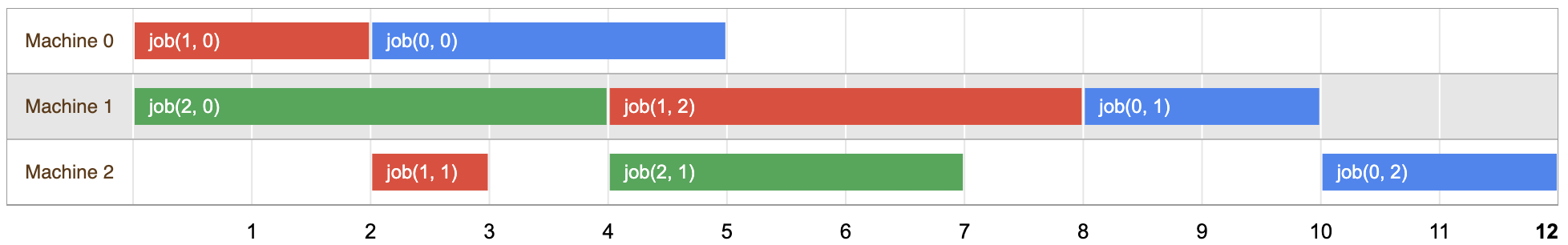
Puoi controllare che le attività per ogni lavoro siano pianificate in un orario non sovrapposto intervalli, nell'ordine indicato dal problema.
La lunghezza di questa soluzione è 12, che è la prima volta in cui tutti e tre i job sono completate. Tuttavia, come vedrai di seguito, questa non è la soluzione ottimale per risolvere il problema.
Variabili e vincoli per il problema
Questa sezione descrive come impostare le variabili e i vincoli per
problema.
Innanzitutto, consenti a task(i, j) di indicare la j-esima attività nella sequenza per il job i. Per
ad esempio task(0, 2) indica la seconda attività per il job 0, che corrisponde
la coppia (1, 2) nella descrizione del problema.
Ora definisci ti, j come ora di inizio per task(i, j). La
ti, j sono le variabili nel problema dell'offerta di lavoro. Trova un
soluzione comporta la determinazione dei valori per queste variabili che soddisfano i
requisito del problema.
Esistono due tipi di vincoli per il problema relativo alle offerte di lavoro:
- Vincoli di precedenza: derivano dalla condizione che per qualsiasi
due attività consecutive nello stesso job, la prima deve essere completata prima
per avviare il deployment. Ad esempio,
task(0, 2)etask(0, 3)sono di attività consecutive per il job 0. Poiché il tempo di elaborazione ditask(0, 2)è 2, l'ora di inizio per Il valoretask(0, 3)deve essere successivo di almeno 2 unità di tempo all'ora di inizio per l'attività 2. (Forse l'attività 2 è dipingere una porta e servono due ore prima che il colore dry.) Di conseguenza, ottieni il seguente vincolo:t0, 2 + 2 <=t0, 3
- Nessun vincolo di sovrapposizione: deriva dalla limitazione che una
non può lavorare su due attività contemporaneamente.
Ad esempio, l'attività(0, 2) e l'attività(2, 1) vengono entrambe elaborate sulla macchina 1.
Poiché i loro tempi di elaborazione sono rispettivamente 2 e 4, uno dei seguenti
i vincoli devono contenere:
t0, 2 + 2 <=t2, 1 (setask(0, 2)è pianificato prima del giornotask(2, 1)) ot2, 1 + 4 <=t0, 2 (setask(2, 1)è pianificato prima del giornotask(0, 2)).
Obiettivo del problema
L'obiettivo del problema dell'officina è ridurre al minimo la makespan: periodo di tempo dalla prima ora di inizio dei job all'ultima ora di fine.
Una soluzione per il programma
Le seguenti sezioni descrivono gli elementi principali di un programma che risolve il problema problema in officina.
Importa le librerie
Il codice seguente importa la libreria richiesta.
Python
import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h"
Java
import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream;
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
Definisci i dati
Quindi, il programma definisce i dati relativi al problema.
Python
jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job)
C++
using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } }
Java
class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
C#
var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
Dichiara il modello
Il seguente codice dichiara il modello per il problema.
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel();
Definisci le variabili
Il seguente codice definisce le variabili nel problema.
Python
# Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var)
C++
struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } }
Java
class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } }
C#
Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } }
Per ogni job e attività, il programma utilizza il metodo
NewIntVar/new_int_var/newIntVar metodo per creare le variabili:
start_var: ora di inizio dell'attività.end_var: ora di fine dell'attività.
Il limite superiore per start_var e end_var è horizon, la somma dei valori
tempi di elaborazione per tutte le attività in tutti i job.
horizon è sufficientemente grande per completare tutte le attività per il seguente motivo:
se pianifichi le attività a intervalli di tempo non sovrapposti (un approccio non ottimale
soluzione), la durata totale della pianificazione è esattamente horizon. Quindi,
la durata della soluzione ottimale non può essere superiore a horizon.
Inoltre, il programma utilizza NewIntervalVar/new_interval_var/newIntervalVar
per creare una variabile intervallo, il cui valore è un tempo variabile
per l'attività. Gli input per questo metodo sono:
- L'ora di inizio dell'attività.
- La durata dell'intervallo di tempo per l'attività.
- L'ora di fine dell'attività.
- Il nome della variabile intervallo.
In qualsiasi soluzione, end_var meno start_var deve essere uguale a duration.
Definisci i vincoli
Il seguente codice definisce i vincoli per il problema.
Python
# Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end )
C++
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } }
Java
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } }
C#
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } }
Il programma utilizza il metodo AddNoOverlap/add_no_overlap/addNoOverlap del modello
per creare vincoli di non sovrapposizione, che impediscono alle attività
che la stessa macchina si sovrapponga nel tempo.
In seguito, il programma aggiunge i vincoli di precedenza, le attività consecutive per lo stesso job non si sovrappongano nel tempo. Per ogni job a ogni attività del job, viene aggiunto un vincolo lineare per specificare di un'attività prima dell'ora di inizio della successiva nel job.
Definisci l'obiettivo
Il seguente codice definisce l'obiettivo del problema.
Python
# Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var)
C++
// Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var);
Java
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar);
C#
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar);
Questo codice crea una variabile obiettivo e la vincola a essere il massimo la fine di tutti i job.
Richiama il risolutore
Il seguente codice chiama il risolutore.
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model)
C++
const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build());
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model);
C#
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}");
Visualizza i risultati
Il codice seguente mostra i risultati, tra cui la pianificazione e l'attività ottimali intervalli.
Python
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.")
C++
if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; }
Java
if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); }
C#
if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); }
La pianificazione ottimale è mostrata di seguito:
Optimal Schedule Length: 11
Machine 0: job_0_0 job_1_0
[0,3] [3,5]
Machine 1: job_2_0 job_0_1 job_1_2
[0,4] [4,6] [7,11]
Machine 2: job_1_1 job_0_2 job_2_1
[5,6] [6,8] [8,11]

I lettori con occhi d'aquila che esaminano la macchina 1 potrebbero chiedersi perché il job_1_2 sia stato programmato alle tempo 7 anziché 6. Entrambe sono soluzioni valide, ma ricorda: lo scopo è ridurre al minimo il trucco. Spostare job_1_2 prima non ridurrebbe il valore span , quindi le due soluzioni sono uguali dal punto di vista del risolutore.
Intero programma
Infine, ecco l'intero programma per il problema relativo alle officine.
Python
"""Minimal jobshop example.""" import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model def main() -> None: """Minimal jobshop problem.""" # Data. jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job) # Create the model. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var) # Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end ) # Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var) # Creates the solver and solve. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model) if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.") # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" - conflicts: {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" - branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" - wall time: {solver.wall_time}s") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
C++
// Nurse scheduling problem with shift requests. #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void MinimalJobshopSat() { using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } } // Creates the model. CpModelBuilder cp_model; struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var); const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build()); if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; } // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main() { operations_research::sat::MinimalJobshopSat(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** Minimal Jobshop problem. */ public class MinimalJobshopSat { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model); if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); } // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.printf(" conflicts: %d%n", solver.numConflicts()); System.out.printf(" branches : %d%n", solver.numBranches()); System.out.printf(" wall time: %f s%n", solver.wallTime()); } private MinimalJobshopSat() {} }
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class ScheduleRequestsSat { private class AssignedTask : IComparable { public int jobID; public int taskID; public int start; public int duration; public AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } public int CompareTo(object obj) { if (obj == null) return 1; AssignedTask otherTask = obj as AssignedTask; if (otherTask != null) { if (this.start != otherTask.start) return this.start.CompareTo(otherTask.start); else return this.duration.CompareTo(otherTask.duration); } else throw new ArgumentException("Object is not a Temperature"); } } public static void Main(String[] args) { var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar); // Solve CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}"); if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); } Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts: {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()}s"); } }
