スケジューリングに関するよくある問題の一つにジョブショップがあります。 複数のマシンで処理されます
各ジョブは一連のタスクで構成されており、特定のタスクで実行する必要がある
各タスクを特定のマシンで処理する必要があります
たとえば、次のような単一の消費財の製造を仕事とします。
自動車
問題は、マシン上でのタスクのスケジュールを設定して、
スケジュールの length - すべてのジョブが完了するまでにかかる時間。
ジョブショップの問題にはいくつかの制約があります。
- そのジョブの前のタスクが開始されるまで、そのジョブのタスクは開始できません 完了していません。
- マシンは一度に 1 つのタスクしか処理できません。
- タスクは、開始したら完了するまで実行する必要があります。
問題の例
以下は、ジョブショップの問題の簡単な例です。ここでは、各タスクに 一組の数字(m, p)で計算。ここで、m はタスクを実行するマシンの番号 p はタスクの処理時間です。つまり、 示されます(ジョブとマシンの番号は 0 から始まります)。
- ジョブ 0 = [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)]
- ジョブ 1 = [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)]
- ジョブ 2 = [(1, 4), (2, 3)]
この例では、ジョブ 0 に 3 つのタスクがあります。1 つ目の(0, 3)は 3 時間単位でマシン 0 に実行させます2 つ目の (1, 2) は、 2 時間単位でマシン 1 を実行します。タスクは全部で 8 つあります。
問題の解決策
ジョブショップ問題の解決策は、ジョブごとに開始時刻を割り当て
これは、上記の制約を満たすタスクです。
次の図に、この問題の解決策の 1 つを示します。
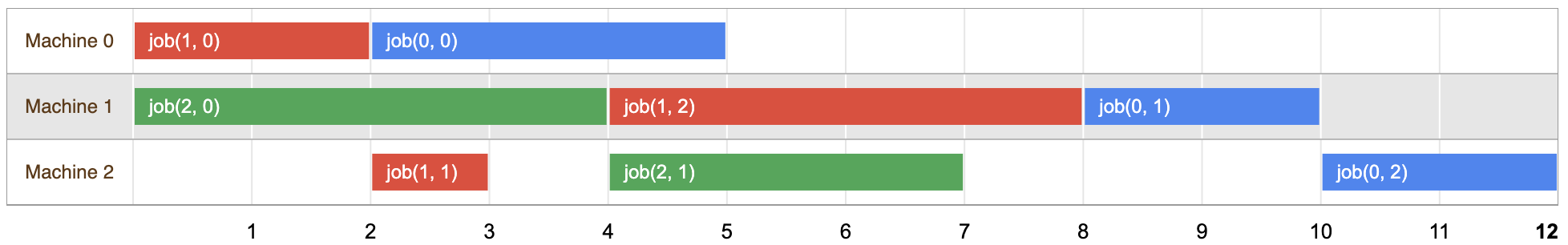
各ジョブのタスクが重複しない時間にスケジュールされていることを確認できます 問題が与えられた順序で並べます
このソリューションの長さは 12 時間で、3 つのジョブすべてが 確認します。 ただし、以下で説明するように、これは 解決できます。
問題の変数と制約
このセクションでは、変数と制約を
困難です。
まず、ジョブ i のシーケンスの j 番目のタスクを task(i, j) とします。対象
たとえば、task(0, 2) はジョブ 0 の 2 番目のタスクを示します。これは、
ペア (1, 2)。
次に、ti, j を task(i, j) の開始時間として定義します。「
ti, j はジョブショップ問題の変数です。検出
次の条件を満たす変数の値を定めることが含まれる
必要があります。
ジョブショップの問題には次の 2 種類の制約があります。
- 優先順位の制約 - いずれかの条件に合致する
実行する場合、最初のタスクをその前に完了する必要があります。
開始できます。たとえば、
task(0, 2)とtask(0, 3)は次のようになります。 実行させたいとしますtask(0, 2)の処理時間は 2 であるため、この時間はtask(0, 3)は、タスク 2 の開始時間から少なくとも 2 時間後である必要があります。 (おそらくタスク 2 はドアの塗装で、塗装が終わるまでに 2 時間かかります)。 dry.)その結果、次の制約が発生します。 <ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">- </ph>
t0, 2 + 2 <=t0, 3
- 重複制限なし - 重複の制限は、
同時に 2 つのタスクを処理することはできません
たとえば、task(0, 2) と task(2, 1) は両方ともマシン 1 で処理されます。
処理時間はそれぞれ 2 と 4 であるため、次のいずれかになります。
次の制約を満たす必要があります。
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">
- </ph>
t0, 2 + 2 <=t2, 1(task(0, 2)がスケジュールされている場合)task(2, 1)の前)またはt2, 1 + 4 <=t0, 2(task(2, 1)がスケジュールされている場合)task(0, 2)まで)。
問題の目標
ジョブショップの問題の目的は、メイクスパン(つまり、 ジョブの最も早い開始時刻から最も遅い終了時刻までの時間の長さ。
プログラム ソリューション
以降のセクションでは、この問題を解決するプログラムの主な要素について説明します。 ジョブショップの問題です
ライブラリのインポート
次のコードは、必要なライブラリをインポートします。
Python
import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h"
Java
import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream;
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
データを定義する
次に、プログラムは問題のデータを定義します。
Python
jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job)
C++
using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } }
Java
class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
C#
var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
モデルを宣言する
次のコードは、問題のモデルを宣言しています。
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel();
変数を定義する
次のコードは、問題に含まれる変数を定義します。
Python
# Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var)
C++
struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } }
Java
class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } }
C#
Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } }
ジョブとタスクごとに、プログラムはモデルの
NewIntVar/new_int_var/newIntVar メソッドを使用して変数を作成します。
start_var: タスクの開始時刻。end_var: タスクの終了時間。
start_var と end_var の上限は horizon です。
時間を表します。
horizon は、すべてのタスクを完了するのに十分な大きさです。理由は次のとおりです。
重複しない時間間隔(最適ではない時間)でタスクをスケジュールした場合、
スケジュールの合計時間は horizon です。したがって、
最適解の期間は horizon 以下にしてください。
次に、プログラムは NewIntervalVar/new_interval_var/newIntervalVar を使用します。
メソッドを使用して間隔変数を作成します。その値は可変時間です。
interval - タスクのこのメソッドへの入力は次のとおりです。
- タスクの開始時刻。
- タスクの時間間隔。
- タスクの終了時間。
- 区間変数の名前。
どの解でも、end_var から start_var を引いた値は duration と等しくする必要があります。
制約を定義する
次のコードは、問題の制約を定義しています。
Python
# Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end )
C++
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } }
Java
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } }
C#
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } }
プログラムはモデルの AddNoOverlap/add_no_overlap/addNoOverlap メソッドを使用します。
重複なしの制約を作成できます。これにより、特定のタスクの
重複しないようにする必要があります
次に、プログラムは優先順位の制約を追加します。これにより、 重複を排除できます。各ジョブと 線形制約が追加されて、終了時点が 時刻。
目標を定義する
次のコードは、問題の目的を定義します。
Python
# Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var)
C++
// Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var);
Java
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar);
C#
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar);
このコードは、目的変数を作成し、それが目標変数の最大値になるように 終了です
ソルバーを呼び出す
次のコードはソルバーを呼び出します。
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model)
C++
const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build());
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model);
C#
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}");
結果を表示する
次のコードは、結果(最適なスケジュールとタスクを含む)を表示します。 できます。
Python
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.")
C++
if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; }
Java
if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); }
C#
if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); }
最適なスケジュールを以下に示します。
Optimal Schedule Length: 11
Machine 0: job_0_0 job_1_0
[0,3] [3,5]
Machine 1: job_2_0 job_0_1 job_1_2
[0,4] [4,6] [7,11]
Machine 2: job_1_1 job_0_2 job_2_1
[5,6] [6,8] [8,11]

マシン 1 を調べている読者は、job_1_2 がなぜスケジュールされていたのか疑問に思うかもしれません。 6 ではなく 7 の時間に振り分けることになります。どちらも有効なソリューションだが、目的は メイクスパンを最小限に抑えることです。job_1_2 を先に移動してもメイクスパンは短縮されません なので、ソルバーの視点から見ると 2 つの解は等しくなります。
プログラム全体
最後に、ジョブショップ問題のプログラム全体を示します。
Python
"""Minimal jobshop example.""" import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model def main() -> None: """Minimal jobshop problem.""" # Data. jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job) # Create the model. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var) # Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end ) # Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var) # Creates the solver and solve. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model) if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.") # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" - conflicts: {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" - branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" - wall time: {solver.wall_time}s") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
C++
// Nurse scheduling problem with shift requests. #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void MinimalJobshopSat() { using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } } // Creates the model. CpModelBuilder cp_model; struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var); const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build()); if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; } // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main() { operations_research::sat::MinimalJobshopSat(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** Minimal Jobshop problem. */ public class MinimalJobshopSat { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model); if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); } // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.printf(" conflicts: %d%n", solver.numConflicts()); System.out.printf(" branches : %d%n", solver.numBranches()); System.out.printf(" wall time: %f s%n", solver.wallTime()); } private MinimalJobshopSat() {} }
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class ScheduleRequestsSat { private class AssignedTask : IComparable { public int jobID; public int taskID; public int start; public int duration; public AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } public int CompareTo(object obj) { if (obj == null) return 1; AssignedTask otherTask = obj as AssignedTask; if (otherTask != null) { if (this.start != otherTask.start) return this.start.CompareTo(otherTask.start); else return this.duration.CompareTo(otherTask.duration); } else throw new ArgumentException("Object is not a Temperature"); } } public static void Main(String[] args) { var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar); // Solve CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}"); if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); } Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts: {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()}s"); } }
