Raw Depth API มีข้อมูลความลึกสำหรับรูปภาพจากกล้องที่มีความแม่นยำสูงกว่าข้อมูล Depth API แบบเต็ม แต่ไม่ได้ครอบคลุมทุกพิกเซลเสมอไป รูปภาพความลึกแบบดิบ รวมถึงรูปภาพความเชื่อมั่นที่ตรงกันยังสามารถประมวลผลเพิ่มเติมได้ ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปใช้ได้เฉพาะข้อมูลความลึกที่มีความแม่นยำเพียงพอสำหรับกรณีการใช้งานแต่ละรายการ
ความเข้ากันได้ของอุปกรณ์
ความลึกของไฟล์ข้อมูล RAW พร้อมใช้งานในอุปกรณ์ทั้งหมดที่รองรับ Depth API ส่วน Raw Depth API จะเหมือนกับ Depth API แบบเต็ม ไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้เซ็นเซอร์ตรวจจับความลึกของฮาร์ดแวร์ที่รองรับ เช่น เซ็นเซอร์ตรวจจับช่วงเวลาแสดงโฆษณา (ToF) อย่างไรก็ตาม ทั้ง Raw Depth API และ Depth API เต็มรูปแบบจะใช้เซ็นเซอร์ของฮาร์ดแวร์ที่รองรับซึ่งอุปกรณ์อาจมี
Raw Depth API เทียบกับ Depth API แบบเต็ม
Raw Depth API ให้ค่าประมาณความลึกที่มีความแม่นยำสูงกว่า แต่รูปภาพความลึกแบบข้อมูลดิบอาจไม่รวมค่าประมาณความลึกของพิกเซลทั้งหมดในรูปภาพจากกล้อง ในทางตรงกันข้าม API ความลึกแบบเต็มจะให้ความลึกโดยประมาณสำหรับทุกพิกเซล แต่ข้อมูลความลึกต่อพิกเซลอาจมีความแม่นยำน้อยลงเนื่องจากการปรับให้ความลึกและการประมาณค่าความลึกสอดคล้องกัน รูปแบบและขนาดของรูปภาพความลึกเหมือนกันใน API ทั้ง 2 รายการ เฉพาะเนื้อหาที่ต่างออกไป
ตารางต่อไปนี้แสดงความแตกต่างระหว่าง Raw Depth API กับ Depth API แบบเต็มโดยใช้รูปภาพเก้าอี้และโต๊ะในห้องครัว
| API | การคืนสินค้า | รูปภาพจากกล้อง | รูปภาพความลึก | รูปภาพความเชื่อมั่น |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| API ความลึกของไฟล์ข้อมูล RAW |
|

|
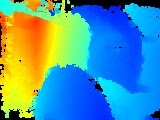
|

|
| API ความลึกเต็ม |
|

|
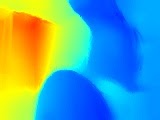
|
ไม่มี |
รูปภาพแสดงความมั่นใจ
ในรูปภาพความเชื่อมั่นที่แสดงผลโดย Raw Depth API ค่าความเชื่อมั่นที่มีสีอ่อนกว่าจะมีพิกเซลสีขาวแสดงถึงความเชื่อมั่นแบบเต็ม และพิกเซลสีดำแสดงถึงไม่มีความเชื่อมั่น โดยทั่วไป พื้นที่ในรูปภาพจากกล้องที่มีพื้นผิวมากกว่า เช่น ต้นไม้ จะมีความมั่นใจในความลึกของข้อมูลดิบสูงกว่าบริเวณที่ไม่มีพื้นผิว เช่น ผนังว่างเปล่า พื้นผิวที่ไม่มีพื้นผิวมักจะให้ค่าความเชื่อมั่นเป็น 0
หากอุปกรณ์เป้าหมายมีเซ็นเซอร์ความลึกของฮาร์ดแวร์ที่รองรับ ความมั่นใจว่าบริเวณต่างๆ ของภาพอยู่ใกล้กับกล้องมากพอก็จะมีแนวโน้มสูงขึ้น แม้จะวางบนพื้นผิวที่ไม่มีพื้นผิวก็ตาม
ต้นทุนการประมวลผล
ต้นทุนการประมวลผลของ Raw Depth API คิดเป็นประมาณครึ่งหนึ่งของต้นทุนการประมวลผลสำหรับ Depth API ทั้งหมด
กรณีการใช้งาน
เมื่อใช้ Raw Depth API คุณจะรับภาพที่มีความลึกซึ่งนำเสนอรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมของรูปทรงเรขาคณิตของวัตถุในฉากได้ ข้อมูลความลึกแบบดิบจะเป็นประโยชน์ในการสร้างประสบการณ์ AR ที่จำเป็นต้องมีความแม่นยำและรายละเอียดของความลึกเพิ่มขึ้นสำหรับงานทำความเข้าใจเรขาคณิต ตัวอย่างกรณีการใช้งานมีดังนี้
- การสร้าง 3 มิติใหม่
- การวัดผล
- การตรวจจับรูปร่าง
ข้อกำหนดเบื้องต้น
ตรวจสอบว่าคุณเข้าใจแนวคิด AR พื้นฐาน และวิธีกําหนดค่าเซสชัน ARCore ก่อนดำเนินการต่อ
เปิดใช้ความลึก
ในเซสชัน ARCore ใหม่ ให้ตรวจสอบว่าอุปกรณ์ของผู้ใช้รองรับความลึกหรือไม่ อุปกรณ์ที่เข้ากันได้กับ ARCore บางรุ่นอาจไม่รองรับ Depth API เนื่องจากข้อจำกัดด้านพลังงานในการประมวลผล เพื่อประหยัดทรัพยากร ระบบจะปิดใช้ความลึกใน ARCore ตามค่าเริ่มต้น เปิดใช้โหมดความลึกเพื่อให้แอปใช้ Depth API
Java
Config config = session.getConfig(); // Check whether the user's device supports Depth. if (session.isDepthModeSupported(Config.DepthMode.AUTOMATIC)) { // Enable depth mode. config.setDepthMode(Config.DepthMode.AUTOMATIC); } session.configure(config);
Kotlin
if (session.isDepthModeSupported(Config.DepthMode.AUTOMATIC)) { session.configure(session.config.apply { depthMode = Config.DepthMode.AUTOMATIC }) }
รับรูปภาพความลึกและความเชื่อมั่นแบบข้อมูลดิบล่าสุด
เรียกใช้ frame.acquireRawDepthImage16Bits() เพื่อรับรูปภาพความลึกซึ่งเป็นข้อมูลดิบล่าสุด พิกเซลรูปภาพบางส่วนที่แสดงผลผ่าน Raw Depth API จะมีข้อมูลความลึก และเฟรม ARCore บางเฟรมจะไม่มีรูปภาพความลึกแบบ RAW ใหม่ หากต้องการระบุว่ารูปภาพความลึกของข้อมูลดิบสำหรับเฟรมปัจจุบันเป็นรูปภาพใหม่ ให้เปรียบเทียบการประทับเวลากับการประทับเวลาของรูปภาพความลึกแบบ RAW ก่อนหน้า หากการประทับเวลาแตกต่างกัน รูปภาพความลึกแบบข้อมูลดิบจะอิงตามข้อมูลความลึกใหม่ มิเช่นนั้น รูปภาพความลึกจะเป็นเส้นโครงของข้อมูลความลึกก่อนหน้าซ้ำอีกครั้ง
โทรหา frame.acquireRawDepthConfidenceImage() เพื่อรับรูปภาพความเชื่อมั่น คุณใช้รูปภาพความเชื่อมั่นเพื่อตรวจสอบความแม่นยำของพิกเซลความลึกแบบ RAW แต่ละรายการได้ ระบบจะส่งรูปภาพแสดงความมั่นใจในรูปแบบ Y8 แต่ละพิกเซลเป็นจำนวนเต็ม 8 บิตที่ไม่มีเครื่องหมาย 0 หมายถึงความเชื่อมั่นน้อยที่สุด ขณะที่ 255 หมายถึงค่าสูงสุด
Java
// Use try-with-resources, so that images are released automatically. try ( // Depth image is in uint16, at GPU aspect ratio, in native orientation. Image rawDepth = frame.acquireRawDepthImage16Bits(); // Confidence image is in uint8, matching the depth image size. Image rawDepthConfidence = frame.acquireRawDepthConfidenceImage(); ) { // Compare timestamps to determine whether depth is is based on new // depth data, or is a reprojection based on device movement. boolean thisFrameHasNewDepthData = frame.getTimestamp() == rawDepth.getTimestamp(); if (thisFrameHasNewDepthData) { ByteBuffer depthData = rawDepth.getPlanes()[0].getBuffer(); ByteBuffer confidenceData = rawDepthConfidence.getPlanes()[0].getBuffer(); int width = rawDepth.getWidth(); int height = rawDepth.getHeight(); someReconstructionPipeline.integrateNewImage(depthData, confidenceData, width, height); } } catch (NotYetAvailableException e) { // Depth image is not (yet) available. }
Kotlin
try { // Depth image is in uint16, at GPU aspect ratio, in native orientation. frame.acquireRawDepthImage16Bits().use { rawDepth -> // Confidence image is in uint8, matching the depth image size. frame.acquireRawDepthConfidenceImage().use { rawDepthConfidence -> // Compare timestamps to determine whether depth is is based on new // depth data, or is a reprojection based on device movement. val thisFrameHasNewDepthData = frame.timestamp == rawDepth.timestamp if (thisFrameHasNewDepthData) { val depthData = rawDepth.planes[0].buffer val confidenceData = rawDepthConfidence.planes[0].buffer val width = rawDepth.width val height = rawDepth.height someReconstructionPipeline.integrateNewImage( depthData, confidenceData, width = width, height = height ) } } } } catch (e: NotYetAvailableException) { // Depth image is not (yet) available. }
สิ่งที่จะเกิดขึ้นหลังจากนี้
- ดูวิธีสร้างแอปของคุณเองด้วยความลึกแบบ Raw โดยไปที่ Codelab สำหรับความลึกแบบ Raw
