网络钩子是合作伙伴指定的网址,RBM 平台会在该网址上发布消息和事件。此网址充当接收包含事件相关数据的 HTTPS POST 请求的端点。这意味着,系统会通过 HTTPS 安全地将数据发送到您的应用。
网络钩子网址可能如下所示:https://[your company name].com/api/rbm-events。配置好网络钩子后,您就可以开始接收消息和事件了。
合作伙伴网络钩子和代理网络钩子
您可以在合作伙伴级别或代理级别配置网络钩子。
- 您的合作伙伴 webhook 会应用于您维护的每个客服人员。如果您的客服人员具有类似的行为,或者您只有一位客服人员,请使用合作伙伴 Webhook。
- 代理 Webhook 适用于各个代理。如果您运营多个具有不同行为的代理,可以为每个代理设置不同的 webhook。
如果您同时配置了合作伙伴网络钩子和代理网络钩子,则代理网络钩子对其特定代理具有优先级,而合作伙伴网络钩子适用于没有自己网络钩子的任何代理。
配置代理 webhook
您会在合作伙伴的 webhook 中收到发送给代理的消息。如果您希望特定代理的消息到达其他 webhook,请设置代理 webhook。
- 打开 Business Communications 开发者控制台,然后使用您的 RBM 合作伙伴 Google 账号登录。
- 点击您的代理。
- 点击集成。
- 对于网络钩子,点击配置。
- 在网络钩子端点网址部分,输入以“https://”开头的 webhook 网址。
- 记下您的
clientToken值。您需要使用它来验证您收到的消息是否来自 Google。 将 webhook 配置为接受具有指定
clientToken参数的POST请求,并发送包含secret参数的纯文本值作为响应正文的200 OK响应。例如,如果您的 webhook 收到具有以下正文内容的
POST请求{ "clientToken":"SJENCPGJESMGUFPY", "secret":"1234567890" }然后,您的 webhook 应确认
clientToken值,如果clientToken正确无误,则返回200 OK响应,并将1234567890作为响应正文:// clientToken from Configure const myClientToken = "SJENCPGJESMGUFPY"; // Example endpoint app.post("/rbm-webhook", (req, res) => { const msg = req.body; if (msg.clientToken === myClientToken) { res.status(200).send(msg.secret); return; } res.send(400); });在 Play 管理中心内,点击验证。RBM 验证您的 webhook 后,对话框将关闭。
验证收到的消息
由于 webhook 可以接收来自任何发件人的邮件,因此您应先验证 Google 是否发送了传入邮件,然后再处理邮件内容。
如需验证您收到的消息是否由 Google 发送,请按以下步骤操作:
- 提取邮件的
X-Goog-Signature标头。这是消息正文载荷经过哈希处理且采用 base64 编码的副本。 - 对请求的
message.body元素中的 RBM 载荷进行 Base-64 解码。 - 使用 webhook 的客户端令牌(您在设置 webhook 时指定的令牌)作为密钥,为 base-64 解码的消息载荷的字节创建 SHA512 HMAC,并对结果进行 base64 编码。
- 将
X-Goog-Signature哈希与您创建的哈希进行比较。- 如果哈希值匹配,则表示您已确认消息是由 Google 发送的。
如果哈希值不匹配,请使用已知有效的消息检查您的哈希处理流程。
如果您的哈希处理流程正常运行,但您收到了一条您认为是欺诈性邮件,请与我们联系。
Node.js
if ((requestBody.hasOwnProperty('message')) && (requestBody.message.hasOwnProperty('data'))) { // Validate the received hash to ensure the message came from Google RBM let userEventString = Buffer.from(requestBody.message.data, 'base64'); let hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha512', CLIENT_TOKEN); let data = hmac.update(userEventString); let genHash = data.digest('base64'); let headerHash = req.header('X-Goog-Signature'); if (headerHash === genHash) { let userEvent = JSON.parse(userEventString); console.log('userEventString: ' + userEventString); handleMessage(userEvent); } else { console.log('hash mismatch - ignoring message'); } } res.sendStatus(200);
消息处理
如果通过 webhook 返回的不是 200 OK,则会被视为传送失败。
开发者必须注意,以较高的速率发送消息会以较高的速率生成 webhook 通知,因此必须设计代码,确保其能够以预期的速率使用通知。开发者务必要考虑可能导致失败响应的情况,包括来自其网站容器的 500 响应、超时或上游失败。需要考虑的事项包括:
- 确保您的 DDoS 防护配置能够处理预期的 webhook 通知速率。
- 确保数据库连接池等资源不会耗尽,并产生超时或
500响应。
开发者应确保以异步方式处理 RBM 事件,并且不会阻止该 webhook 返回 200 OK。
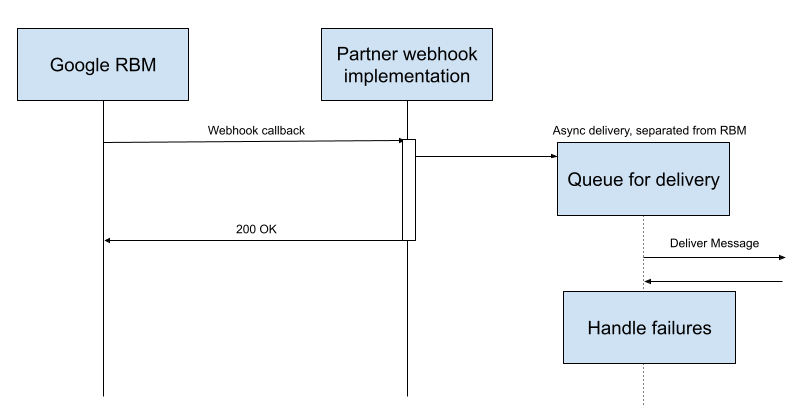
请务必不要在 webhook 本身中处理 RBM 事件。处理过程中的任何错误或延迟都可能会影响 webhook 返回代码:
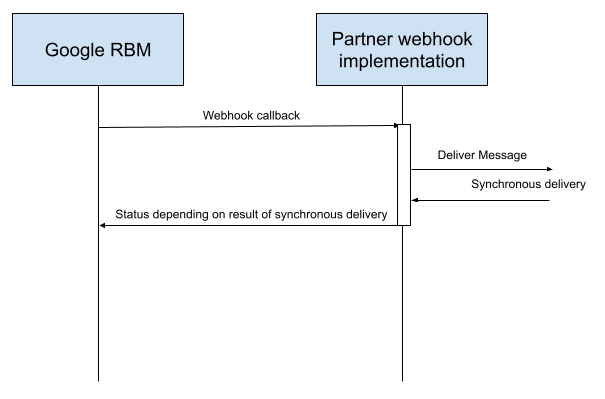
递送失败时的行为
当 RBM 从网络钩子调用收到 200 OK 以外的响应时,会使用退避和重试机制。RBM 会增加重试之间的等待时间,最长可达 600 秒。系统会继续重试 7 天,之后便会丢弃该邮件。
代理级 webhook 的影响
RBM 会将合作伙伴的消息加入一个队列。如果合作伙伴使用的是代理级 webhook,请务必注意,一个 webhook 的失败会影响向其他 webhook 传送内容。在消息失败的后退期内,系统会调用其他代理的 Webhook。不过,由于失败的消息会加入队列以进行重试,因此总体投放率会下降,其他代理也会受到影响。
开发者必须了解这种模式并相应地编写代码,尽可能接受消息并将其加入队列以进行处理,以最大限度地减少返回失败的可能性。
