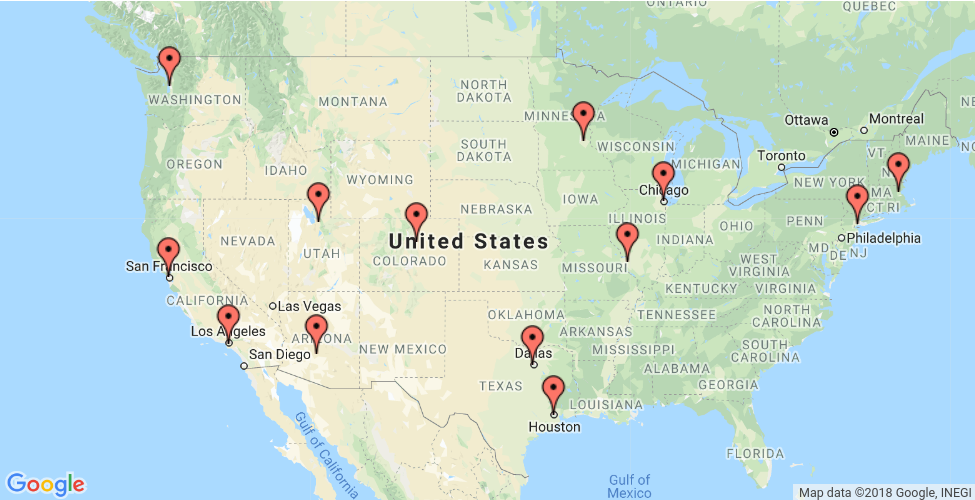
يقدم هذا القسم مثالاً يوضح كيفية حل مشكلة مندوب مبيعات السفر للمواقع الجغرافية المعروضة على الخريطة أدناه.
تقدم الأقسام التالية برامج بلغة Python وC++ وجافا وC# تعمل على حل مقدّم خدمة الرموز المميّزة باستخدام أدوات OR
إنشاء البيانات
ينشئ الرمز أدناه بيانات المشكلة.
لغة Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
لغة Java
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
مصفوفة المسافة عبارة عن مصفوفة يكون فيها i، j عبارة عن المسافة من الموقع i إلى الموقع j بالميل، حيث تتطابق فهارس الصفيف مع المواقع بالترتيب التالي:
0. New York - 1. Los Angeles - 2. Chicago - 3. Minneapolis - 4. Denver - 5. Dallas
- 6. Seattle - 7. Boston - 8. San Francisco - 9. St. Louis - 10. Houston - 11. Phoenix - 12. Salt Lake City
تشمل البيانات أيضًا ما يلي:
- عدد المركبات المتسببة في المشكلة، وهو 1 لأن هذا مقدّم خدمة الرموز المميزة (لمشكلة في توجيه المركبة (VRP)، يمكن أن يكون عدد المركبات أكبر من 1.)
- المستودع: موقع البدء والانتهاء للمسار. في هذه الحالة، المستودع هو 0، وهو ما يمثل مدينة نيويورك.
طرق أخرى لإنشاء مصفوفة المسافة
في هذا المثال، يتم تعريف مصفوفة المسافة بوضوح في البرنامج. من الممكن أيضًا استخدام دالة لحساب المسافات بين المواقع: على سبيل المثال، صيغة الإقليدية للمسافة بين النقاط في المستوى. ومع ذلك، لا يزال من الأفضل إجراء حساب مسبق للمسافات بين المواقع وحفظها في مصفوفة، بدلاً من حسابها في وقت التشغيل. راجع مثال: حفر لوحة الدارة الكهربائية للحصول على مثال يُنشئ مصفوفة المسافة بهذه الطريقة.
ويمكنك بدلاً من ذلك استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لمصفوفة المسافات في "خرائط Google" لإنشاء مصفوفة المسافة (أو وقت السفر) ديناميكيًا لمشكلة في التوجيه.
إنشاء نموذج التوجيه
يعمل الرمز التالي في القسم الرئيسي من البرامج على إنشاء
مدير الفهرس (manager) ونموذج التوجيه (routing). وتحوّل الطريقة
manager.IndexToNode الفهارس الداخلية للحلّل (التي يمكنك
تجاهلها بأمان) إلى أرقام المواقع الجغرافية. تتطابق أرقام المواقع مع فهارس مصفوفة المسافة.
لغة Python
data = create_data_model()
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
C++
DataModel data;
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
RoutingModel routing(manager);
لغة Java
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
C#
DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
الإدخالات في RoutingIndexManager هي:
- عدد صفوف مصفوفة المسافة، وهو عدد المواقع الجغرافية (بما في ذلك المستودع).
- عدد المركبات التي حدثت فيها المشكلة.
- العقدة المقابلة للمستودع.
إنشاء معاودة الاتصال بالمسافة
لاستخدام أداة تعيين المسار، يجب إنشاء معاودة اتصال للمسافات (أو النقل العام): دالة تأخذ أي زوج من المواقع الجغرافية وتعرض المسافة بينها. وأسهل طريقة لتنفيذ ذلك هي استخدام مصفوفة المسافة.
تنشئ الدالة التالية معاودة الاتصال وتسجّلها مع برنامج التعيين باسم
transit_callback_index.
لغة Python
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
C++
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
Java
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
C#
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
The callback accepts two indices, from_index and to_index, and returns the
corresponding entry of the distance matrix.
Set the cost of travel
The arc cost evaluator tells the solver how to calculate the cost of travel between any two locations — in other words, the cost of the edge (or arc) joining them in the graph for the problem. The following code sets the arc cost evaluator.
Python
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
لغة Java
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
في هذا المثال، مُقيِّم تكلفة القوس هو transit_callback_index، وهو المرجع الداخلي للحلّ لمعاودة الاتصال عن بُعد. وهذا يعني أن تكلفة السفر بين أي موقعين هي مجرد المسافة بينهما.
ومع ذلك، بصفة عامة، قد تتضمن التكاليف عوامل أخرى أيضًا.
يمكنك أيضًا تحديد عدّة مقدّري تكلفة قوس يعتمدون على المركبة التي تتنقل بين المواقع الجغرافية، باستخدام الطريقة routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfVehicle().
على سبيل المثال، إذا كانت سرعات المركبات مختلفة، يمكنك تحديد تكلفة السفر بين المواقع الجغرافية بحيث تكون المسافة مقسومةً على سرعة المركبة، أي وقت الرحلة.
تعيين معلمات البحث
تعيّن الشفرة التالية معلمات البحث الافتراضية وطريقة استرشادية للعثور على الحل الأول:
لغة Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
لغة Java
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
C#
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
يضبط الرمز استراتيجية الحلّ الأولى على PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC، ما يؤدي إلى إنشاء مسار أولي للأداة عن طريق إضافة حواف أقلّ وزنًا بشكل متكرّر ولا تؤدي إلى عقدة تمت زيارتها سابقًا (بخلاف المستودع). للتعرّف على الخيارات الأخرى، يمكنك الاطّلاع على
استراتيجية الحلّ الأولى.
إضافة طابعة الحل
يتم عرض الدالة التي تعرض الحل الذي تعرضه أداة الحل أدناه. تستخرج الدالة المسار من الحل وتطبعه إلى وحدة التحكم.
لغة Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
لغة Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
تعرض الدالة المسار الأمثل ومسافته على النحو الموضّح في
ObjectiveValue().
حل الحل وطباعته
وأخيرًا، يمكنك الاتصال بأداة الحل وطباعة الحل:
لغة Python
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
C++
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
لغة Java
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters); printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
C#
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
يؤدي هذا إلى عرض الحل وعرض المسار الأمثل.
تشغيل البرامج
عند تشغيل البرامج، يتم عرض الناتج التالي.
Objective: 7293 miles Route for vehicle 0: 0 -> 7 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 12 -> 6 -> 8 -> 1 -> 11 -> 10 -> 5 -> 9 -> 0
في هذا المثال، هناك مسار واحد فقط لأنه مقدّم خدمة الرموز المميزة. ولكن في المشكلات العامة لتوجيه المركبات، يحتوي الحل على مسارات متعددة.
حفظ المسارات إلى قائمة أو مصفوفة
بدلاً من طباعة الحل مباشرة، يمكنك حفظ المسار (أو المسارات، لـ VRP) في قائمة أو مصفوفة. ويشتمل هذا على ميزة جعل المسارات متاحة في حالة ما إذا كنت تريد إجراء شيء ما عليها لاحقًا. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك تشغيل البرنامج عدة مرات باستخدام معلمات مختلفة وحفظ المسارات في الحلول المعروضة في ملف للمقارنة.
تحفظ الدوال التالية المسارات في الحل إلى أي برنامج VRP (ربما مع عدة مركبات) كقائمة (Python) أو مصفوفة (C++).
لغة Python
def get_routes(solution, routing, manager):
"""Get vehicle routes from a solution and store them in an array."""
# Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array whose
# i,j entry is the jth location visited by vehicle i along its route.
routes = []
for route_nbr in range(routing.vehicles()):
index = routing.Start(route_nbr)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
routes.append(route)
return routes
C++
std::vector<std::vector<int>> GetRoutes(const Assignment& solution,
const RoutingModel& routing,
const RoutingIndexManager& manager) {
// Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array, whose
// i, j entry is the node for the jth visit of vehicle i.
std::vector<std::vector<int>> routes(manager.num_vehicles());
// Get routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < manager.num_vehicles(); ++vehicle_id) {
int64_t index = routing.Start(vehicle_id);
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
}
}
return routes;
}
يمكنك استخدام هذه الدوال للحصول على المسارات في أي من أمثلة VRP في قسم التوجيه.
تعرض الشفرة التالية المسارات.
لغة Python
routes = get_routes(solution, routing, manager)
# Display the routes.
for i, route in enumerate(routes):
print('Route', i, route)
C++
const std::vector⟨std::vector⟨int⟩⟩
routes = GetRoutes(*solution,
routing,
manager);
// Display the routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < routes.size(); ++vehicle_id) {
LOG(INFO) << "Route " << vehicle_id;
for (int j = 1; j < routes[vehicle_id].size(); ++j) {
LOG(INFO) << routes[vehicle_id][j];
}
}
بالنسبة إلى المثال الحالي، تعرض هذه الشفرة المسار التالي:
Route 0 [0, 7, 2, 3, 4, 12, 6, 8, 1, 11, 10, 5, 9, 0]
وكتمرين، عدِّل الرمز أعلاه لتنسيق الناتج بنفس طريقة طابعة الحل للبرنامج.
إكمال البرامج
يتم عرض برامج مقدّم خدمة الرموز المميّزة أدناه.
لغة Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) between cities."""
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
لغة Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP using distance matrix. */
public class TspCities {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCities.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP using distance matrix.
/// </summary>
public class TspCities
{
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
مثال: حفر لوحة الدوائر الكهربائية
يتضمن المثال التالي حفر ثقوب في لوحة دارجة باستخدام مثقاب تلقائي. تكمن المشكلة في العثور على أقصر مسار للمثقب الذي يجب اتخاذه على اللوحة من أجل حفر جميع الثقوب المطلوبة. هذا المثال مأخوذ من مكتبة TSPLIB لمشكلات مقدّم خدمة الرموز المميزة.
في ما يلي رسم بياني للنقاط المبعثرة للمواقع الجغرافية للثقوب:
تقدم الأقسام التالية البرامج التي تجد حلاً جيدًا لمشكلة لوحة الدائرة، باستخدام معلمات البحث الافتراضية للحل. وسنعرض بعد ذلك كيفية إيجاد حل أفضل من خلال تغيير إستراتيجية البحث.
إنشاء البيانات
تتكون بيانات المشكلة من 280 نقطة في الطائرة، موضحة في المخطط المبعثر أعلاه. ينشئ البرنامج البيانات في مصفوفة من الأزواج المطلوبة المرتبطة بالنقاط في المستوى، كما هو موضح أدناه.
لغة Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
لغة Java
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
حساب مصفوفة المسافة
تحسب الدالة أدناه المسافة الإقليدية بين أي نقطتين في البيانات وتخزّنها في مصفوفة. ونظرًا لأن محلل التوجيه يعمل على الأعداد الصحيحة، تعمل الدالة على تقريب المسافات المحسوبة إلى الأعداد الصحيحة. ولا يؤثر التقريب على الحل في هذا المثال، ولكن قد يحدث في حالات أخرى. راجع تحجيم مصفوفة المسافة للحصول على طريقة لتجنب مشكلات التقريب التقريبية.
لغة Python
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
C++
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
لغة Java
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
إضافة معاودة الاتصال بالمسافة
وتكون الشفرة التي تنشئ معاودة الاتصال عن بُعد هي نفسها تقريبًا الشفرة في المثال السابق. ومع ذلك، يستدعي البرنامج في هذه الحالة الدالة التي تحسب مصفوفة المسافة قبل إضافة رد الاتصال.
لغة Python
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
لغة Java
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
طابعة الحل
تطبع الدالة التالية الحل إلى وحدة التحكم. للحفاظ على المخرجات أصغر حجمًا، تعرض الدالة مؤشرات المواقع في المسار فقط.
لغة Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
لغة Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
الوظيفة الرئيسية
الدالة الأساسية هي في الأساس الوظيفة الموجودة في المثال السابق، ولكنها تتضمن أيضًا استدعاء الدالة التي تنشئ مصفوفة المسافة.
تشغيل البرنامج
يتم عرض البرامج الكاملة في القسم التالي. وعند تشغيل البرنامج، يتم عرض المسار التالي:
Total distance: 2790 Route of vehicle 0: 0 -> 1 -> 279 -> 2 -> 278 -> 277 -> 247 -> 248 -> 249 -> 246 -> 244 -> 243 -> 242 -> 241 -> 240 -> 239 -> 238 -> 237 -> 236 -> 235 -> 234 -> 233 -> 232 -> 231 -> 230 -> 245 -> 250 -> 229 -> 228 -> 227 -> 226 -> 225 -> 224 -> 223 -> 222 -> 221 -> 220 -> 219 -> 218 -> 217 -> 216 -> 215 -> 214 -> 213 -> 212 -> 211 -> 210 -> 209 -> 208 -> 251 -> 254 -> 255 -> 257 -> 256 -> 253 -> 252 -> 207 -> 206 -> 205 -> 204 -> 203 -> 202 -> 142 -> 141 -> 146 -> 147 -> 140 -> 139 -> 265 -> 136 -> 137 -> 138 -> 148 -> 149 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 178 -> 179 -> 180 -> 181 -> 182 -> 183 -> 184 -> 186 -> 185 -> 192 -> 196 -> 197 -> 198 -> 144 -> 145 -> 143 -> 199 -> 201 -> 200 -> 195 -> 194 -> 193 -> 191 -> 190 -> 189 -> 188 -> 187 -> 163 -> 164 -> 165 -> 166 -> 167 -> 168 -> 169 -> 171 -> 170 -> 172 -> 105 -> 106 -> 104 -> 103 -> 107 -> 109 -> 110 -> 113 -> 114 -> 116 -> 117 -> 61 -> 62 -> 63 -> 65 -> 64 -> 84 -> 85 -> 115 -> 112 -> 86 -> 83 -> 82 -> 87 -> 111 -> 108 -> 89 -> 90 -> 91 -> 102 -> 101 -> 100 -> 99 -> 98 -> 97 -> 96 -> 95 -> 94 -> 93 -> 92 -> 79 -> 88 -> 81 -> 80 -> 78 -> 77 -> 76 -> 74 -> 75 -> 73 -> 72 -> 71 -> 70 -> 69 -> 66 -> 68 -> 67 -> 57 -> 56 -> 55 -> 54 -> 53 -> 52 -> 51 -> 50 -> 49 -> 48 -> 47 -> 46 -> 45 -> 44 -> 43 -> 58 -> 60 -> 59 -> 42 -> 41 -> 40 -> 39 -> 38 -> 37 -> 36 -> 35 -> 34 -> 33 -> 32 -> 31 -> 30 -> 29 -> 124 -> 123 -> 122 -> 121 -> 120 -> 119 -> 118 -> 156 -> 157 -> 158 -> 173 -> 162 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 150 -> 151 -> 155 -> 152 -> 154 -> 153 -> 128 -> 129 -> 130 -> 131 -> 18 -> 19 -> 20 -> 127 -> 126 -> 125 -> 28 -> 27 -> 26 -> 25 -> 21 -> 24 -> 22 -> 23 -> 13 -> 12 -> 14 -> 11 -> 10 -> 9 -> 7 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 275 -> 274 -> 273 -> 272 -> 271 -> 270 -> 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 132 -> 133 -> 269 -> 268 -> 134 -> 135 -> 267 -> 266 -> 264 -> 263 -> 262 -> 261 -> 260 -> 258 -> 259 -> 276 -> 3 -> 4 -> 0
في ما يلي رسم بياني للمسار المقابل:
تبحث مكتبة OR أدوات الجولة أعلاه بسرعة كبيرة: في أقل من ثانية على جهاز كمبيوتر عادي. إجمالي مدة الجولة أعلاه 2790.
إكمال البرامج
في ما يلي البرامج الكاملة لمثال لوحة الدوائر الكهربائية.
لغة Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) on a circuit board."""
import math
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["locations"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.locations.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
لغة Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP. */
public class TspCircuitBoard {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCircuitBoard.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.locations.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP.
/// A description of the problem can be found here:
/// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesperson_problem.
/// </summary>
public class TspCircuitBoard
{
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.Locations.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Define cost of each arc.
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
تغيير إستراتيجية البحث
لا تُرجع أداة حل التوجيه دائمًا الحل الأمثل إلى مقدّم خدمة الرموز المميّزة، لأن مشاكل التوجيه لا يمكن حلها. على سبيل المثال، الحل الذي تم عرضه في المثال السابق ليس هو المسار الأمثل.
وللعثور على حل أفضل، يمكنك استخدام استراتيجية بحث أكثر تقدّمًا، يُطلق عليها اسم البحث المحلي الموجَّه، ويُمكِّن هذه الأداة من الهروب من الحد الأدنى المحلي ، وهو حل أقصر من جميع المسارات القريبة، ولكنه ليس الحد الأدنى العالمي. بعد الابتعاد عن الحد الأدنى المحلي، يتابع برنامج الحل البحث.
توضح الأمثلة أدناه كيفية تعيين بحث محلي موجَّه لمثال على لوحة الدوائر.
لغة Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
search_parameters.log_search = True
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_local_search_metaheuristic(
LocalSearchMetaheuristic::GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH);
searchParameters.mutable_time_limit()->set_seconds(30);
search_parameters.set_log_search(true);
لغة Java
أضِف عبارة "استيراد" التالية في بداية البرنامج:import com.google.protobuf.Duration;ثم اضبط معلمات البحث على النحو التالي:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.setLocalSearchMetaheuristic(LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Value.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
.setTimeLimit(Duration.newBuilder().setSeconds(30).build())
.setLogSearch(true)
.build();
C#
أضِف السطر التالي في بداية البرنامج:using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes; // Durationثم اضبط معلمات البحث على النحو التالي:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
searchParameters.LocalSearchMetaheuristic = LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Types.Value.GuidedLocalSearch;
searchParameters.TimeLimit = new Duration { Seconds = 30 };
searchParameters.LogSearch = true;
للحصول على إستراتيجيات بحث محلي أخرى، راجع خيارات البحث المحلي.
تتيح الأمثلة أعلاه أيضًا إمكانية تسجيل الدخول إلى البحث. على الرغم من أن تسجيل الدخول غير مطلوب، يمكن أن يكون مفيدًا لتصحيح الأخطاء.
عند تشغيل البرنامج بعد إجراء التغييرات الموضحة أعلاه، ستحصل على الحل التالي، وهو أقصر من الحل الموضح في القسم السابق.
Objective: 2672 Route: 0 -> 3 -> 276 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 -> 14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 23 -> 22 -> 24 -> 21 -> 25 -> 26 -> 27 -> 28 -> 125 -> 126 -> 127 -> 20 -> 19 -> 130 -> 129 -> 128 -> 153 -> 154 -> 152 -> 155 -> 151 -> 150 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 180 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 158 -> 157 -> 156 -> 118 -> 119 -> 120 -> 121 -> 122 -> 123 -> 124 -> 29 -> 30 -> 31 -> 32 -> 33 -> 34 -> 35 -> 36 -> 37 -> 38 -> 39 -> 40 -> 41 -> 42 -> 59 -> 60 -> 58 -> 43 -> 44 -> 45 -> 46 -> 47 -> 48 -> 49 -> 50 -> 51 -> 52 -> 53 -> 54 -> 55 -> 56 -> 57 -> 67 -> 68 -> 66 -> 69 -> 70 -> 71 -> 72 -> 73 -> 75 -> 74 -> 76 -> 77 -> 78 -> 80 -> 81 -> 88 -> 79 -> 92 -> 93 -> 94 -> 95 -> 96 -> 97 -> 98 -> 99 -> 100 -> 101 -> 102 -> 91 -> 90 -> 89 -> 108 -> 111 -> 87 -> 82 -> 83 -> 86 -> 112 -> 115 -> 85 -> 84 -> 64 -> 65 -> 63 -> 62 -> 61 -> 117 -> 116 -> 114 -> 113 -> 110 -> 109 -> 107 -> 103 -> 104 -> 105 -> 106 -> 173 -> 172 -> 171 -> 170 -> 169 -> 168 -> 167 -> 166 -> 165 -> 164 -> 163 -> 162 -> 187 -> 188 -> 189 -> 190 -> 191 -> 192 -> 185 -> 186 -> 184 -> 183 -> 182 -> 181 -> 179 -> 178 -> 149 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 266 -> 267 -> 135 -> 134 -> 268 -> 269 -> 133 -> 132 -> 131 -> 18 -> 17 -> 16 -> 15 -> 270 -> 271 -> 272 -> 273 -> 274 -> 275 -> 259 -> 258 -> 260 -> 261 -> 262 -> 263 -> 264 -> 265 -> 139 -> 140 -> 147 -> 146 -> 141 -> 142 -> 145 -> 144 -> 198 -> 197 -> 196 -> 193 -> 194 -> 195 -> 200 -> 201 -> 199 -> 143 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 206 -> 207 -> 252 -> 253 -> 256 -> 257 -> 255 -> 254 -> 251 -> 208 -> 209 -> 210 -> 211 -> 212 -> 213 -> 214 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 218 -> 219 -> 220 -> 221 -> 222 -> 223 -> 224 -> 225 -> 226 -> 227 -> 232 -> 233 -> 234 -> 235 -> 236 -> 237 -> 230 -> 231 -> 228 -> 229 -> 250 -> 245 -> 238 -> 239 -> 240 -> 241 -> 242 -> 243 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 248 -> 247 -> 277 -> 278 -> 2 -> 279 -> 1 -> 0
لمزيد من خيارات البحث، راجع خيارات التوجيه.
يمكن الآن لأفضل الخوارزميات حل روتيني لمثيلات SPS مع عشرات الآلاف من العقد. (السجلّ وقت الكتابة هو مثال pla85900 في TSPLIB، وهو تطبيق VLSI يحتوي على 85900 عقدة. بالنسبة إلى حالات معينة تشتمل على الملايين من العُقد، تم اكتشاف أن هذه الحلول مضمونة أن تكون ضمن 1% من الجولة المثالية.)
تغيير حجم مصفوفة المسافة
نظرًا لأن أداة حل التوجيه تعمل على الأعداد الصحيحة، إذا كانت مصفوفة المسافة تتضمن إدخالات ليست أعدادًا صحيحة، يجب عليك تقريب المسافات إلى أعداد صحيحة. إذا كانت بعض المسافات صغيرة، فقد يؤثر التقريب على الحل.
ولتجنب أي مشكلة في التقريب، يمكنك scale مصفوفة المسافة: ضرب
جميع إدخالات المصفوفة في عدد كبير - لنفترض 100. ويؤدي هذا إلى ضرب طول أي مسار في عامل 100، ولكنه لا يغير الحل. والميزة تتمثل في أنه عند تقريب إدخالات المصفوفة، فإن مقدار التقريب
(الذي يبلغ 0.5 على الأكثر) صغير جدًا مقارنة بالمسافات، لذلك لن يؤثر في الحل بشكلٍ كبير.
في حالة تغيير مصفوفة المسافة، ستحتاج أيضًا إلى تغيير طابعة المحلول لتقسيم أطوال المسار التي تم تغيير حجمها على عامل القياس، بحيث تعرض المسافات غير المقيسَة للمسارات.
