Webhook 是合作夥伴指定的網址,用於 RBM 平台發布訊息和事件。這個網址會做為端點,用於接收含有事件資料的 HTTPS POST 要求。這表示資料會透過 HTTPS 安全傳送至應用程式。
Webhook 網址可能會像這樣:https://[your company name].com/api/rbm-events。設定 webhook 後,您就可以開始接收訊息和事件。
合作夥伴 Webhook 和服務專員 Webhook
你可以在合作夥伴層級或服務專員層級設定 Webhook。
- 您的合作夥伴 webhook 會套用到您維護的每個服務專員。如果您的服務項目有類似行為,或是您只有一個服務項目,請使用合作夥伴 webhook。
- 服務專員 Webhook 適用於個別服務專員。如果您有不同行為的多個服務代理,可以為每個服務代理設定不同的 webhook。
如果您同時設定了合作夥伴 Webhook 和代理程式 Webhook,代理程式 Webhook 會優先套用至其特定代理程式,而合作夥伴 Webhook 則會套用至任何沒有專屬 Webhook 的代理程式。
設定代理程式 Webhook
您會透過合作夥伴 Webhook 接收服務專員傳送的訊息。如果您希望特定服務專員的訊息傳送至其他 Webhook,請設定服務專員 Webhook。
- 開啟 Business Communications 開發人員控制台,然後使用 RBM 合作夥伴的 Google 帳戶登入。
- 按一下代理程式。
- 點選 [Integrations] (整合)。
- 在「Webhook」部分,按一下「設定」。
- 在「Webhook 端點網址」中,輸入開頭為「https://」的 Webhook 網址。
- 請記下
clientToken值。您需要這項資訊,才能驗證您收到的訊息是否來自 Google。 設定 Webhook 以便接受含有指定
clientToken參數的POST要求,並傳送200 OK回應,其中secret參數的純文字值做為回應主體。舉例來說,如果 webhook 收到以下內容的
POST要求{ "clientToken":"SJENCPGJESMGUFPY", "secret":"1234567890" }接著,Webhook 應確認
clientToken值,如果clientToken正確,則傳回200 OK回應,並以1234567890做為回應主體:// clientToken from Configure const myClientToken = "SJENCPGJESMGUFPY"; // Example endpoint app.post("/rbm-webhook", (req, res) => { const msg = req.body; if (msg.clientToken === myClientToken) { res.status(200).send(msg.secret); return; } res.send(400); });在開發人員控制台中,按一下「驗證」。RBM 驗證 webhook 後,對話方塊就會關閉。
驗證收到的訊息
由於 webhook 可接收來自任何寄件者的訊息,因此您應先確認 Google 傳送的訊息,再處理訊息內容。
如要確認你收到的訊息是由 Google 傳送,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 擷取訊息的
X-Goog-Signature標頭。這是訊息主體酬載的雜湊 Base64 編碼副本。 - 將要求
message.body元素中的 RBM 酬載解碼為 Base-64。 - 使用 webhook 的用戶端權杖 (您在設定 webhook 時指定的) 做為金鑰,為 base-64 解碼訊息酬載的位元組建立 SHA512 HMAC,然後將結果以 base64 編碼。
- 將
X-Goog-Signature雜湊與您建立的雜湊進行比較。- 如果雜湊相符,表示您已確認 Google 傳送了訊息。
如果雜湊不相符,請針對已知有效的訊息檢查雜湊處理程序。
如果您的雜湊處理程序運作正常,但您收到的訊息疑似為詐騙訊息,請與我們聯絡。
Node.js
if ((requestBody.hasOwnProperty('message')) && (requestBody.message.hasOwnProperty('data'))) { // Validate the received hash to ensure the message came from Google RBM let userEventString = Buffer.from(requestBody.message.data, 'base64'); let hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha512', CLIENT_TOKEN); let data = hmac.update(userEventString); let genHash = data.digest('base64'); let headerHash = req.header('X-Goog-Signature'); if (headerHash === genHash) { let userEvent = JSON.parse(userEventString); console.log('userEventString: ' + userEventString); handleMessage(userEvent); } else { console.log('hash mismatch - ignoring message'); } } res.sendStatus(200);
訊息處理
如果 webhook 傳回的內容不是 200 OK,就會視為傳送失敗。
開發人員必須留意,如果以高頻率傳送訊息,就會以高頻率產生 webhook 通知,因此必須設計程式碼,確保能夠以預期的頻率使用通知。開發人員必須考量可能導致失敗回應的情況,包括來自網路容器的 500 回應、逾時或上游失敗。需要考量的事項包括:
- 確認 DDoS 防護功能已設定為處理預期的 webhook 通知頻率。
- 確保資料庫連線池等資源不會耗盡,並產生逾時或
500回應。
開發人員應確保 RBM 事件的處理作業以非同步方式執行,且不會阻止 webhook 傳回 200 OK。
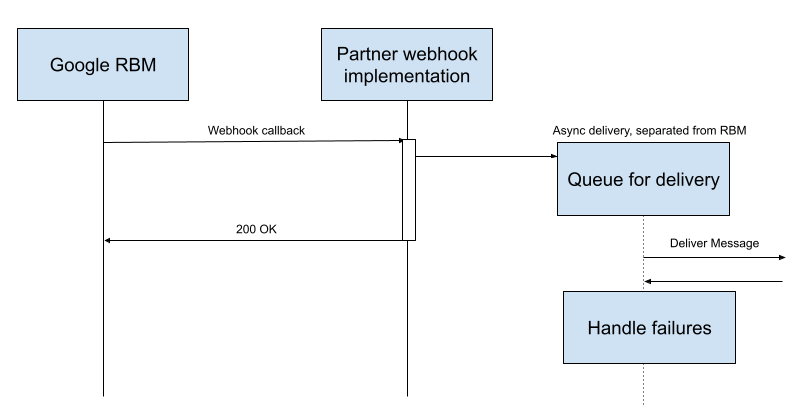
請務必不在 webhook 中處理 RBM 事件。處理期間發生的任何錯誤或延遲,都可能影響 webhook 傳回碼:
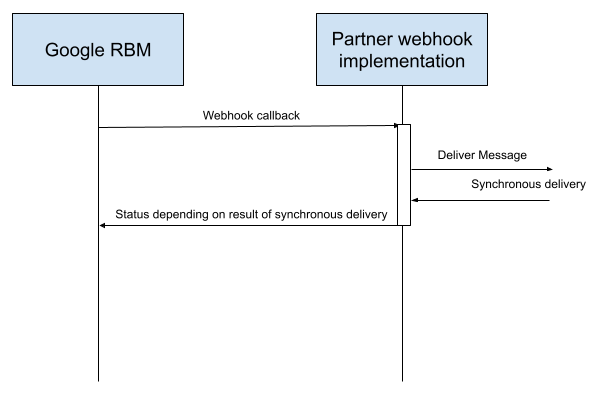
傳送失敗時的行為
當 RBM 收到 Webhook 呼叫傳回的回應時,如果回應不是 200 OK,就會使用延遲和重試機制。RBM 會增加每次重試之間的等待時間,最多可達 600 秒。重試作業會持續 7 天,之後就會捨棄訊息。
服務專員層級 Webhook 的影響
RBM 會將合作夥伴的訊息排入一個佇列。如果合作夥伴使用的是代理程式層級的 webhook,請務必記住,一個 webhook 發生錯誤,就會影響其他 webhook 的傳送作業。在失敗訊息的延遲期間,系統會呼叫屬於其他服務項目的 Webhook。不過,由於失敗的訊息會排入重試佇列,整體傳送率會下降,其他代理程式也會受到影響。
開發人員必須瞭解這個模型和程式碼,並盡可能接受訊息並將其排入處理佇列,以盡量減少傳回失敗的機會。
