实时卡片显示在时间轴的该部分中,并且 显示当前的相关信息。
实时卡片非常适合用户处于活跃状态时 但希望定期查看 Google Glass 获取补充信息。例如,查看他们的时间 或在跑步时控制音乐播放器 想要跳过或暂停歌曲
如果这是您首次为 Glass 进行开发 阅读持续性任务指南 。该文档介绍了如何构建完整的 带有实时卡片的 Glassware,遵循我们的设计最佳实践。
运作方式
实时卡片让卡片能够保留当前状态 部分,只要这些内容相关即可。与静态卡片不同 已发布的卡片不会保留在时间轴上, 在使用完程序后将其移除。
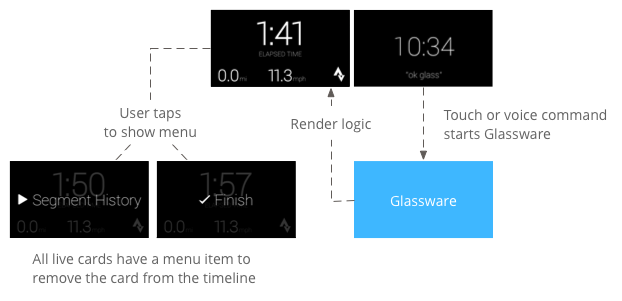
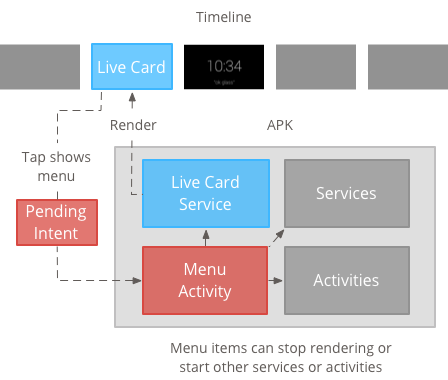
用户通常通过说出语音指令来启动实时卡片 在主菜单中,这会启动呈现卡片的后台服务。 然后,他们可以点按该卡片,以显示可执行操作的菜单项 例如,从时间轴将其关闭。
何时使用此类附加信息
实时卡片旨在处理用户可以参与的持续性任务 例如显示运行状态的显示屏 操作、导航期间的动画地图或音乐播放器。
实时卡片的另一个优势是 需要与用户实时互动的界面 以及对界面的实时更新
使用实时卡片时,时间轴仍可控制用户 因此,您可以在实际的卡片上向前或向后滑动 可在时间轴上导航,而不是对实际卡片本身执行操作。 此外,屏幕会根据系统的行为( 5 秒(无用户互动时或上移头部时)。
不过,实时卡片可以使用的 GPS 数据。这样你仍然可以打造引人入胜的体验 同时允许用户留在时间轴体验中执行其他操作 例如检查邮件
架构
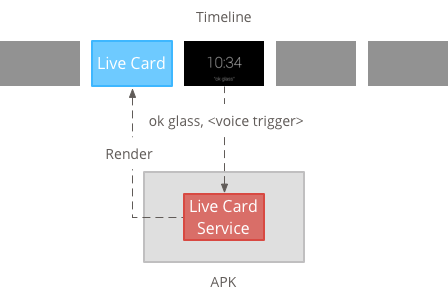
实时卡片需要一个长期运行的上下文,才能在该时间结束的整个 它们是可见的,因此请在后台服务中管理它们。
然后,您可以在服务完成后立即发布和呈现实际的卡片 启动或响应服务监控的其他事件。 您可以以较低的频率(每几秒一次)、 或高频率(最多以系统可刷新的频率进行刷新)。
当实际卡片不再相关时,销毁相应服务 停止渲染。
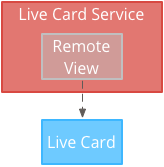
低频渲染
低频渲染仅限于一小部分 Android 且每显示一次 几秒。
您可以利用这一功能 无需不断呈现的简单内容 频繁更新。
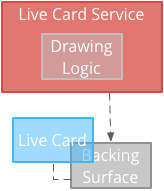
高频渲染
高频渲染让你可以使用更多 Android 图形框架中可用的自定义功能。
系统会为您提供 使用 2D 直接在上面绘制的实时卡片 甚至使用 OpenGL 绘制复杂的 3D 图形。
创建低频实时卡片
低频渲染需要由 RemoteViews 对象,该对象支持以下部分 Android 布局和视图:
在以下情况下使用低频率渲染:
- 您只需需要使用之前列出的标准 Android View API。
- 只需要相对不频繁的更新(在两个版本之间 刷新)。
注意事项:
- 有效卡片必须始终
PendingIntent声明为setAction()为卡片发布时间表提供 - 要在发布卡片后对其进行更改,请调用
setViews()在卡片上使用更新后的 RemoteViews 然后再次发布
如需创建低频实时卡片,请执行以下操作:
创建要呈现的布局或视图。以下示例 展示了虚构的篮球比赛的布局:
<TextView android:id="@+id/home_team_name_text_view" android:layout_width="249px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="40px" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/away_team_name_text_view" android:layout_width="249px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="40px" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/away_score_text_view" android:layout_width="249px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/away_team_name_text_view" android:layout_below="@+id/away_team_name_text_view" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="70px" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/home_score_text_view" android:layout_width="249px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/home_team_name_text_view" android:layout_below="@+id/home_team_name_text_view" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="70px" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/footer_text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_marginBottom="33px" android:textSize="26px" />创建一个服务来管理实时卡片并呈现布局或视图。 此示例服务每隔 1 次更新虚拟篮球比赛的得分 30 秒。
import java.util.Random; import com.google.android.glass.timeline.LiveCard; import com.google.android.glass.timeline.LiveCard.PublishMode; import android.app.PendingIntent; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.IBinder; import android.widget.RemoteViews; public class LiveCardService extends Service { private static final String LIVE_CARD_TAG = "LiveCardDemo"; private LiveCard mLiveCard; private RemoteViews mLiveCardView; private int homeScore, awayScore; private Random mPointsGenerator; private final Handler mHandler = new Handler(); private final UpdateLiveCardRunnable mUpdateLiveCardRunnable = new UpdateLiveCardRunnable(); private static final long DELAY_MILLIS = 30000; @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); mPointsGenerator = new Random(); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { if (mLiveCard == null) { // Get an instance of a live card mLiveCard = new LiveCard(this, LIVE_CARD_TAG); // Inflate a layout into a remote view mLiveCardView = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), R.layout.main_layout); // Set up initial RemoteViews values homeScore = 0; awayScore = 0; mLiveCardView.setTextViewText(R.id.home_team_name_text_view, getString(R.string.home_team)); mLiveCardView.setTextViewText(R.id.away_team_name_text_view, getString(R.string.away_team)); mLiveCardView.setTextViewText(R.id.footer_text, getString(R.string.game_quarter)); // Set up the live card's action with a pending intent // to show a menu when tapped Intent menuIntent = new Intent(this, MenuActivity.class); menuIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK); mLiveCard.setAction(PendingIntent.getActivity( this, 0, menuIntent, 0)); // Publish the live card mLiveCard.publish(PublishMode.REVEAL); // Queue the update text runnable mHandler.post(mUpdateLiveCardRunnable); } return START_STICKY; } @Override public void onDestroy() { if (mLiveCard != null && mLiveCard.isPublished()) { //Stop the handler from queuing more Runnable jobs mUpdateLiveCardRunnable.setStop(true); mLiveCard.unpublish(); mLiveCard = null; } super.onDestroy(); } /** * Runnable that updates live card contents */ private class UpdateLiveCardRunnable implements Runnable{ private boolean mIsStopped = false; /* * Updates the card with a fake score every 30 seconds as a demonstration. * You also probably want to display something useful in your live card. * * If you are executing a long running task to get data to update a * live card(e.g, making a web call), do this in another thread or * AsyncTask. */ public void run(){ if(!isStopped()){ // Generate fake points. homeScore += mPointsGenerator.nextInt(3); awayScore += mPointsGenerator.nextInt(3); // Update the remote view with the new scores. mLiveCardView.setTextViewText(R.id.home_score_text_view, String.valueOf(homeScore)); mLiveCardView.setTextViewText(R.id.away_score_text_view, String.valueOf(awayScore)); // Always call setViews() to update the live card's RemoteViews. mLiveCard.setViews(mLiveCardView); // Queue another score update in 30 seconds. mHandler.postDelayed(mUpdateLiveCardRunnable, DELAY_MILLIS); } } public boolean isStopped() { return mIsStopped; } public void setStop(boolean isStopped) { this.mIsStopped = isStopped; } } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { /* * If you need to set up interprocess communication * (activity to a service, for instance), return a binder object * so that the client can receive and modify data in this service. * * A typical use is to give a menu activity access to a binder object * if it is trying to change a setting that is managed by the live card * service. The menu activity in this sample does not require any * of these capabilities, so this just returns null. */ return null; } }
创建高频实时卡片
通过高频渲染, 在后备 Surface 上 。
在以下情况下使用高频渲染:
- 您需要经常(每秒多次更新)实时卡片。
- 您需要灵活的渲染方式。借助高频渲染 使用 Android 视图和布局创建复杂的 OpenGL 图形。
注意事项:
- 您应始终创建后台服务,以在实时卡片的 Surface 上进行渲染。
- 有效卡片必须始终
PendingIntent声明为setAction()。 - 如果您满足以下条件,请使用
GLRenderer渲染 OpenGL 和DirectRenderingCallback所有其他情况。
使用 DirectRenderingCallback
如需使用标准 Android 视图和绘制逻辑创建实时卡片,请执行以下操作:
创建一个实现
DirectRenderingCallback、 通过在这些接口中实现回调,您可以在实时卡片 Surface 生命周期的重要事件期间执行操作。以下示例会创建一个后台线程以定期进行渲染,但您需要 可以更新卡片来响应外部事件(例如, 传感器或位置更新)。
public class LiveCardRenderer implements DirectRenderingCallback { // About 30 FPS. private static final long FRAME_TIME_MILLIS = 33; private SurfaceHolder mHolder; private boolean mPaused; private RenderThread mRenderThread; @Override public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) { // Update your views accordingly. } @Override public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) { mPaused = false; mHolder = holder; updateRendering(); } @Override public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) { mHolder = null; updateRendering(); } @Override public void renderingPaused(SurfaceHolder holder, boolean paused) { mPaused = paused; updateRendering(); } /** * Start or stop rendering according to the timeline state. */ private void updateRendering() { boolean shouldRender = (mHolder != null) && !mPaused; boolean rendering = mRenderThread != null; if (shouldRender != rendering) { if (shouldRender) { mRenderThread = new RenderThread(); mRenderThread.start(); } else { mRenderThread.quit(); mRenderThread = null; } } } /** * Draws the view in the SurfaceHolder's canvas. */ private void draw() { Canvas canvas; try { canvas = mHolder.lockCanvas(); } catch (Exception e) { return; } if (canvas != null) { // Draw on the canvas. mHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas); } } /** * Redraws in the background. */ private class RenderThread extends Thread { private boolean mShouldRun; /** * Initializes the background rendering thread. */ public RenderThread() { mShouldRun = true; } /** * Returns true if the rendering thread should continue to run. * * @return true if the rendering thread should continue to run */ private synchronized boolean shouldRun() { return mShouldRun; } /** * Requests that the rendering thread exit at the next opportunity. */ public synchronized void quit() { mShouldRun = false; } @Override public void run() { while (shouldRun()) { draw(); SystemClock.sleep(FRAME_TIME_MILLIS); } } } }设置
DirectRenderingCallback的实例 作为LiveCardSurfaceHolder的回调。这个 让实时卡片知道使用什么逻辑来呈现自身。// Tag used to identify the LiveCard in debugging logs. private static final String LIVE_CARD_TAG = "my_card"; // Cached instance of the LiveCard created by the publishCard() method. private LiveCard mLiveCard; private void publishCard(Context context) { if (mLiveCard == null) { mLiveCard = new LiveCard(this, LIVE_CARD_TAG); // Enable direct rendering. mLiveCard.setDirectRenderingEnabled(true); mLiveCard.getSurfaceHolder().addCallback( new LiveCardRenderer()); Intent intent = new Intent(context, MenuActivity.class); mLiveCard.setAction(PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0, intent, 0)); mLiveCard.publish(LiveCard.PublishMode.SILENT); } else { // Card is already published. return; } } private void unpublishCard(Context context) { if (mLiveCard != null) { mLiveCard.unpublish(); mLiveCard = null; } }
使用 OpenGL
创建一个实现
GlRenderer。 通过此接口实现回调,可让您在发生重要事件时执行操作 。此示例绘制了一个旋转的彩色立方体。import com.google.android.glass.timeline.GlRenderer; import android.opengl.GLES20; import android.opengl.Matrix; import android.os.SystemClock; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig; /** * Renders a 3D OpenGL Cube on a {@link LiveCard}. */ public class CubeRenderer implements GlRenderer { /** Rotation increment per frame. */ private static final float CUBE_ROTATION_INCREMENT = 0.6f; /** The refresh rate, in frames per second. */ private static final int REFRESH_RATE_FPS = 60; /** The duration, in milliseconds, of one frame. */ private static final float FRAME_TIME_MILLIS = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(1) / REFRESH_RATE_FPS; private final float[] mMVPMatrix; private final float[] mProjectionMatrix; private final float[] mViewMatrix; private final float[] mRotationMatrix; private final float[] mFinalMVPMatrix; private Cube mCube; private float mCubeRotation; private long mLastUpdateMillis; public CubeRenderer() { mMVPMatrix = new float[16]; mProjectionMatrix = new float[16]; mViewMatrix = new float[16]; mRotationMatrix = new float[16]; mFinalMVPMatrix = new float[16]; // Set the fixed camera position (View matrix). Matrix.setLookAtM(mViewMatrix, 0, 0.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); } @Override public void onSurfaceCreated(EGLConfig config) { // Set the background frame color GLES20.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); GLES20.glClearDepthf(1.0f); GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST); GLES20.glDepthFunc(GLES20.GL_LEQUAL); mCube = new Cube(); } @Override public void onSurfaceChanged(int width, int height) { float ratio = (float) width / height; GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height); // This projection matrix is applied to object coordinates in the onDrawFrame() method. Matrix.frustumM(mProjectionMatrix, 0, -ratio, ratio, -1.0f, 1.0f, 3.0f, 7.0f); // modelView = projection x view Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix, 0, mProjectionMatrix, 0, mViewMatrix, 0); } @Override public void onDrawFrame() { GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Apply the rotation. Matrix.setRotateM(mRotationMatrix, 0, mCubeRotation, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view Matrix.multiplyMM(mFinalMVPMatrix, 0, mMVPMatrix, 0, mRotationMatrix, 0); // Draw cube. mCube.draw(mFinalMVPMatrix); updateCubeRotation(); } /** Updates the cube rotation. */ private void updateCubeRotation() { if (mLastUpdateMillis != 0) { float factor = (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - mLastUpdateMillis) / FRAME_TIME_MILLIS; mCubeRotation += CUBE_ROTATION_INCREMENT * factor; } mLastUpdateMillis = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); } }创建一项服务来管理活动卡片并设置 将
CubeRenderer类用作实时卡片的渲染程序。import com.google.android.glass.timeline.LiveCard; import com.google.android.glass.timeline.LiveCard.PublishMode; import android.app.PendingIntent; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.IBinder; /** * Creates a {@link LiveCard} rendering a rotating 3D cube with OpenGL. */ public class OpenGlService extends Service { private static final String LIVE_CARD_TAG = "opengl"; private LiveCard mLiveCard; @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return null; } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { if (mLiveCard == null) { mLiveCard = new LiveCard(this, LIVE_CARD_TAG); mLiveCard.setRenderer(new CubeRenderer()); mLiveCard.setAction( PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, new Intent(this, MenuActivity.class), 0)); mLiveCard.publish(PublishMode.REVEAL); } else { mLiveCard.navigate(); } return START_STICKY; } @Override public void onDestroy() { if (mLiveCard != null && mLiveCard.isPublished()) { mLiveCard.unpublish(); mLiveCard = null; } super.onDestroy(); } }
import android.opengl.GLES20;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
/**
* Renders a 3D Cube using OpenGL ES 2.0.
*
* For more information on how to use OpenGL ES 2.0 on Android, see the
* <a href="//developer.android.com/training/graphics/opengl/index.html">
* Displaying Graphics with OpenGL ES</a> developer guide.
*/
public class Cube {
/** Cube vertices */
private static final float VERTICES[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f
};
/** Vertex colors. */
private static final float COLORS[] = {
0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
};
/** Order to draw vertices as triangles. */
private static final byte INDICES[] = {
0, 1, 3, 3, 1, 2, // Front face.
0, 1, 4, 4, 5, 1, // Bottom face.
1, 2, 5, 5, 6, 2, // Right face.
2, 3, 6, 6, 7, 3, // Top face.
3, 7, 4, 4, 3, 0, // Left face.
4, 5, 7, 7, 6, 5, // Rear face.
};
/** Number of coordinates per vertex in {@link VERTICES}. */
private static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3;
/** Number of values per colors in {@link COLORS}. */
private static final int VALUES_PER_COLOR = 4;
/** Vertex size in bytes. */
private final int VERTEX_STRIDE = COORDS_PER_VERTEX * 4;
/** Color size in bytes. */
private final int COLOR_STRIDE = VALUES_PER_COLOR * 4;
/** Shader code for the vertex. */
private static final String VERTEX_SHADER_CODE =
"uniform mat4 uMVPMatrix;" +
"attribute vec4 vPosition;" +
"attribute vec4 vColor;" +
"varying vec4 _vColor;" +
"void main() {" +
" _vColor = vColor;" +
" gl_Position = uMVPMatrix * vPosition;" +
"}";
/** Shader code for the fragment. */
private static final String FRAGMENT_SHADER_CODE =
"precision mediump float;" +
"varying vec4 _vColor;" +
"void main() {" +
" gl_FragColor = _vColor;" +
"}";
private final FloatBuffer mVertexBuffer;
private final FloatBuffer mColorBuffer;
private final ByteBuffer mIndexBuffer;
private final int mProgram;
private final int mPositionHandle;
private final int mColorHandle;
private final int mMVPMatrixHandle;
public Cube() {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(VERTICES.length * 4);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
mVertexBuffer = byteBuffer.asFloatBuffer();
mVertexBuffer.put(VERTICES);
mVertexBuffer.position(0);
byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(COLORS.length * 4);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
mColorBuffer = byteBuffer.asFloatBuffer();
mColorBuffer.put(COLORS);
mColorBuffer.position(0);
mIndexBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(INDICES.length);
mIndexBuffer.put(INDICES);
mIndexBuffer.position(0);
mProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(mProgram, loadShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, VERTEX_SHADER_CODE));
GLES20.glAttachShader(
mProgram, loadShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, FRAGMENT_SHADER_CODE));
GLES20.glLinkProgram(mProgram);
mPositionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgram, "vPosition");
mColorHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgram, "vColor");
mMVPMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgram, "uMVPMatrix");
}
/**
* Encapsulates the OpenGL ES instructions for drawing this shape.
*
* @param mvpMatrix The Model View Project matrix in which to draw this shape
*/
public void draw(float[] mvpMatrix) {
// Add program to OpenGL environment.
GLES20.glUseProgram(mProgram);
// Prepare the cube coordinate data.
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
mPositionHandle, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, VERTEX_STRIDE, mVertexBuffer);
// Prepare the cube color data.
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mColorHandle);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
mColorHandle, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, COLOR_STRIDE, mColorBuffer);
// Apply the projection and view transformation.
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mMVPMatrixHandle, 1, false, mvpMatrix, 0);
// Draw the cube.
GLES20.glDrawElements(
GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, INDICES.length, GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, mIndexBuffer);
// Disable vertex arrays.
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(mColorHandle);
}
/** Loads the provided shader in the program. */
private static int loadShader(int type, String shaderCode){
int shader = GLES20.glCreateShader(type);
GLES20.glShaderSource(shader, shaderCode);
GLES20.glCompileShader(shader);
return shader;
}
}
让实时卡片聚焦
使用 LiveCard.publish() 发布已发布的卡片时,您需要向其传递一个参数
来控制它是否立即获得焦点。
要让时间轴在发布后立即跳转到卡片,请使用
LiveCard.PublishMode.REVEAL。
如需以静默方式发布卡片并让用户自行导航到该卡片,请使用
LiveCard.PublishMode.SILENT。
此外,LiveCard.navigate()
方法,您可以在卡片发布后跳转到卡片。例如,如果用户尝试启动
已启动,则可以跳转到直播卡片
卡片。
创建和显示菜单
实时卡片无法显示自己的菜单系统,因此您需要创建一个 activity 来显示菜单 。
然后,菜单 activity 可以包含用于停止实时卡片的项,从 沉浸模式,或您想执行的任何其他操作。您还可以添加 系统设置 activity(例如音量控制)显示为菜单项。有关 请参阅 启动设置。
创建菜单资源
创建菜单资源的方法与在 Android 平台上创建菜单资源相同,但请遵循以下规则: Glass 准则:
- 为每个菜单项提供一个 50 × 50 像素的菜单项图标。菜单 图标必须为白色,背景为透明。请参阅 玻璃菜单项图标 或下载下来供自己使用。
- 使用能够描述该操作且采用标题大小写的简短名称。祈使动词起作用 (例如“分享”或“全部回复”)。
- Glass 不会显示没有菜单项的实时卡片。至少, 提供 Stop 菜单项,以便用户从 时间轴。
通过 CheckBox 微件 不受支持。
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:id="@+id/menu_item_1" android:title="@string/Menu_Item_1" <!-- must have "Stop" menu item --> android:icon="@drawable/menu_item_1_icon" /> <!-- white on transparent icon --> </menu>
创建 Activity 来处理菜单回调
您必须定义一个菜单 activity,以供用户点按实时卡片时调用。
替换以下内容
Activity 回调方法
在菜单 activity 中正确创建、显示和关闭菜单:
onCreateOptionsMenu()扩充 XML 菜单资源。onAttachedToWindow()当 activity 获得焦点时显示菜单。onPrepareOptionsMenu()用于根据需要显示或隐藏菜单项。例如,您可以 根据用户执行的操作调整搜索范围。例如,您可以根据视频内容 某些情境数据。onOptionsItemSelected()会处理用户选择。onOptionsMenuClosed()以完成 activity,使其不再显示在实际卡片上。
您必须在此处结束 activity,这样当菜单通过选择或向下滑动关闭时,此 activity 正确完成。
/**
* Activity showing the options menu.
*/
public class MenuActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
openOptionsMenu();
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
MenuInflater inflater = getMenuInflater();
inflater.inflate(R.menu.stopwatch, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle item selection.
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.stop:
stopService(new Intent(this, StopwatchService.class));
return true;
default:
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
@Override
public void onOptionsMenuClosed(Menu menu) {
// Nothing else to do, closing the activity.
finish();
}
}
将菜单 activity 设为透明
为了与 Glass 样式保持一致,请将菜单 activity 因此该实时卡片仍会显示在下方 菜单:
创建
res/values/styles.xml文件并声明样式 使 activity 的背景变为透明:<resources> <style name="MenuTheme" parent="@android:style/Theme.DeviceDefault"> <item name="android:windowBackground">@android:color/transparent</item> <item name="android:colorBackgroundCacheHint">@null</item> <item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true</item> <item name="android:windowAnimationStyle">@null</item> </style> </resources>在
AndroidManifest.xml文件中,将主题分配给菜单 activity:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest ... > ... <application ... > ... <activity android:name=".MenuActivity" android:theme="@style/MenuTheme" ...> </activity> </application> </manifest>
显示菜单
提供
PendingIntent
使用 setAction() 实现卡片操作。待处理 intent 用于启动
在用户点按卡片时的菜单 activity:
Intent menuIntent = new Intent(this, MenuActivity.class);
mLiveCard.setAction(PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, menuIntent, 0));
mLiveCard.publish(LiveCard.PublishMode.REVEAL); // or SILENT
支持上下文语音指令
表明您的
MenuActivity支持 上下文相关语音指令:// Initialize your LiveCard as usual. mLiveCard.setVoiceActionEnabled(true); mLiveCard.publish(LiveCard.PublishMode.REVEAL); // or SILENT修改
MenuActivity以支持通过语音流程进行调用:/** * Activity showing the options menu. */ public class MenuActivity extends Activity { private boolean mFromLiveCardVoice; private boolean mIsFinishing; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); mFromLiveCardVoice = getIntent().getBooleanExtra(LiveCard.EXTRA_FROM_LIVECARD_VOICE, false); if (mFromLiveCardVoice) { // When activated by voice from a live card, enable voice commands. The menu // will automatically "jump" ahead to the items (skipping the guard phrase // that was already said at the live card). getWindow().requestFeature(WindowUtils.FEATURE_VOICE_COMMANDS); } } @Override public void onAttachedToWindow() { super.onAttachedToWindow(); if (!mFromLiveCardVoice) { openOptionsMenu(); } } @Override public boolean onCreatePanelMenu(int featureId, Menu menu) { if (isMyMenu(featureId)) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.stopwatch, menu); return true; } return super.onCreatePanelMenu(featureId, menu); } @Override public boolean onPreparePanel(int featureId, View view, Menu menu) { if (isMyMenu(featureId)) { // Don't reopen menu once we are finishing. This is necessary // since voice menus reopen themselves while in focus. return !mIsFinishing; } return super.onPreparePanel(featureId, view, menu); } @Override public boolean onMenuItemSelected(int featureId, MenuItem item) { if (isMyMenu(featureId)) { // Handle item selection. switch (item.getItemId()) { case R.id.stop_this: stopService(new Intent(this, StopwatchService.class)); return true; } } return super.onMenuItemSelected(featureId, item); } @Override public void onPanelClosed(int featureId, Menu menu) { super.onPanelClosed(featureId, menu); if (isMyMenu(featureId)) { // When the menu panel closes, either an item is selected from the menu or the // menu is dismissed by swiping down. Either way, we end the activity. isFinishing = true; finish(); } } /** * Returns {@code true} when the {@code featureId} belongs to the options menu or voice * menu that are controlled by this menu activity. */ private boolean isMyMenu(int featureId) { return featureId == Window.FEATURE_OPTIONS_PANEL || featureId == WindowUtils.FEATURE_VOICE_COMMANDS; } }
请查看 情境语音指令 指南。
菜单实用程序
有几个辅助方法可用于修改菜单的外观和行为。如需了解详情,请参阅 MenuUtils。
