Một vấn đề thường gặp liên quan đến việc lập lịch biểu là cửa hàng việc làm, trong đó có nhiều việc làm được xử lý trên nhiều máy.
Mỗi công việc bao gồm một chuỗi công việc và phải được thực hiện theo một chuỗi công việc nhất định
và mỗi công việc phải được xử lý trên một máy cụ thể.
Ví dụ: công việc có thể là sản xuất một mặt hàng tiêu dùng, chẳng hạn như
một chiếc ô tô.
Vấn đề là lên lịch cho các tác vụ trên máy sao cho giảm thiểu
length lịch biểu—thời gian cần để hoàn thành tất cả công việc.
Có một số hạn chế đối với vấn đề về cửa hàng việc làm:
- Không có tác vụ nào cho một công việc có thể được bắt đầu cho đến khi công việc trước đó của công việc đó được đã hoàn tất.
- Một máy chỉ có thể thực hiện một nhiệm vụ tại một thời điểm.
- Sau khi bắt đầu, một tác vụ phải chạy đến khi hoàn tất.
Ví dụ về bài toán
Dưới đây là một ví dụ đơn giản về một vấn đề tại cửa hàng việc làm, trong đó mỗi công việc đều được gắn nhãn bởi một cặp số (m, p), trong đó m là số máy thực hiện công việc phải được xử lý và p là thời gian xử lý của tác vụ — thời gian khoảng thời gian cần thiết. (Số công việc và máy bắt đầu từ 0.)
- công việc 0 = [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)]
- công việc 1 = [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)]
- công việc 2 = [(1, 4), (2, 3)]
Trong ví dụ, công việc 0 có 3 tác vụ. Đầu tiên, (0, 3), phải được xử lý trên máy 0 trong 3 đơn vị thời gian. Thứ hai, (1, 2), phải được xử lý trên máy 1 trong 2 đơn vị thời gian, v.v. Tổng cộng có 8 việc cần làm.
Giải pháp cho vấn đề
Giải pháp cho vấn đề cửa hàng việc làm là việc chỉ định thời gian bắt đầu cho mỗi
đáp ứng các ràng buộc được đưa ra ở trên.
Sơ đồ dưới đây trình bày một giải pháp khả thi cho vấn đề này:
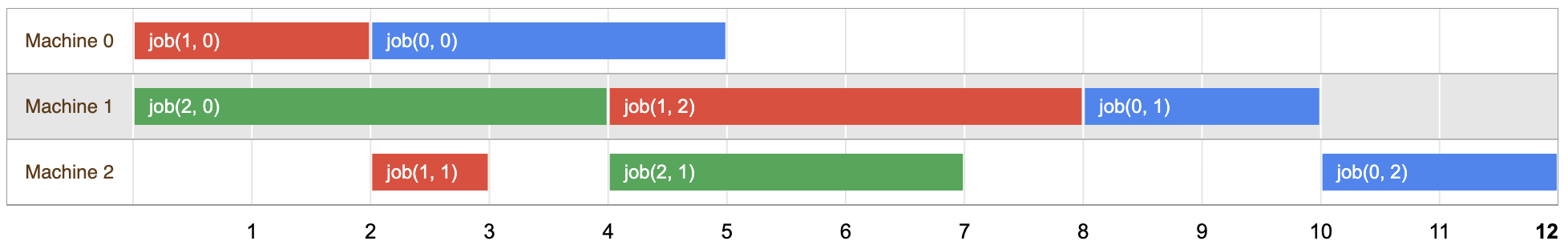
Bạn có thể kiểm tra để đảm bảo các tác vụ của từng công việc được lên lịch biểu ở thời gian không trùng lặp các khoảng thời gian, theo thứ tự được cung cấp bởi bài toán.
Độ dài của giải pháp này là 12, đây là lần đầu tiên khi cả 3 công việc đều đã hoàn tất. Tuy nhiên, như bạn sẽ thấy dưới đây, đây không phải là giải pháp tối ưu để sự cố.
Các biến và quy tắc ràng buộc của bài toán
Phần này mô tả cách thiết lập các biến và quy tắc ràng buộc cho
vấn đề.
Trước tiên, hãy cho phép task(i, j) biểu thị tác vụ thứ j trong trình tự cho công việc i. Cho
ví dụ: task(0, 2) biểu thị tác vụ thứ hai cho công việc 0, tương ứng với
cặp (1, 2) trong phần mô tả bài toán.
Tiếp theo, hãy xác định ti, j là thời gian bắt đầu cho task(i, j). Chiến lược phát hành đĩa đơn
ti, j là các biến trong vấn đề cửa hàng việc làm. Tìm một
bao gồm việc xác định giá trị cho các biến này, đáp ứng
theo yêu cầu của bài toán.
Có 2 loại quy tắc ràng buộc đối với vấn đề tại cửa hàng việc làm:
- Giới hạn đối với quy tắc ưu tiên – Những điều kiện này phát sinh từ các điều kiện mà đối với bất kỳ
hai nhiệm vụ liên tiếp trong cùng một công việc, thì nhiệm vụ đầu tiên phải được hoàn tất trước
thứ hai có thể bắt đầu. Ví dụ:
task(0, 2)vàtask(0, 3)là các tác vụ liên tiếp cho công việc 0. Vì thời gian xử lý củatask(0, 2)là 2, nên thời gian bắt đầu chotask(0, 3)phải sau thời gian bắt đầu nhiệm vụ 2 ít nhất là 2 đơn vị thời gian. (Có lẽ nhiệm vụ 2 là sơn cửa và phải mất 2 giờ để sơn dry.) Do đó, bạn sẽ gặp phải quy tắc ràng buộc sau:t0, 2 + 2 <=t0, 3
- Không có ràng buộc chồng chéo — Những hạn chế này phát sinh từ hạn chế mà
máy không thể làm việc đồng thời 2 tác vụ.
Ví dụ: tác vụ(0, 2) và tác vụ(2, 1) đều được xử lý trên máy 1.
Vì thời gian xử lý của họ lần lượt là 2 và 4, nên một trong những điều sau
các điều kiện ràng buộc phải có:
t0, 2 + 2 <=t2, 1 (nếutask(0, 2)được lên lịch trướctask(2, 1)) hoặct2, 1 + 4 <=t0, 2 (nếutask(2, 1)được lên lịch trướctask(0, 2)).
Mục tiêu của vấn đề
Mục tiêu của vấn đề tại cửa hàng việc làm là giảm thiểu makespan: khoảng thời gian từ thời điểm bắt đầu công việc sớm nhất đến thời điểm kết thúc muộn nhất.
Giải pháp chương trình
Các phần sau đây mô tả các yếu tố chính của một chương trình để giải quyết vấn đề của cửa hàng việc làm.
Nhập thư viện
Mã sau đây nhập thư viện bắt buộc.
Python
import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h"
Java
import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream;
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
Xác định dữ liệu
Tiếp theo, chương trình xác định dữ liệu cho bài toán.
Python
jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job)
C++
using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } }
Java
class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
C#
var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
Khai báo mô hình
Mã sau đây khai báo mô hình cho sự cố này.
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel();
Xác định các biến
Mã sau đây xác định các biến trong bài toán.
Python
# Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var)
C++
struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } }
Java
class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } }
C#
Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } }
Đối với mỗi công việc và công việc, chương trình sử dụng mã
Phương thức NewIntVar/new_int_var/newIntVar để tạo các biến:
start_var: Thời gian bắt đầu việc cần làm.end_var: Thời gian kết thúc việc cần làm.
Giới hạn trên của start_var và end_var là horizon, tổng của
thời gian xử lý cho tất cả các tác vụ trong tất cả các công việc.
horizon đủ lớn để hoàn tất tất cả các tác vụ vì lý do sau:
nếu bạn lên lịch các tác vụ trong khoảng thời gian không chồng chéo (không tối ưu
nghiệm), tổng thời lượng của lịch biểu chính xác là horizon. Vì vậy,
thời lượng của giải pháp tối ưu không được lớn hơn horizon.
Tiếp theo, chương trình sử dụng NewIntervalVar/new_interval_var/newIntervalVar
để tạo một biến khoảng thời gian – có giá trị là biến thời gian
khoảng thời gian – cho tác vụ. Dữ liệu đầu vào cho phương thức này là:
- Thời gian bắt đầu việc cần làm.
- Độ dài của khoảng thời gian cho tác vụ.
- Thời gian kết thúc việc cần làm.
- Tên cho biến khoảng thời gian.
Trong mọi giải pháp, end_var trừ start_var phải bằng duration.
Xác định các điều kiện ràng buộc
Mã sau đây xác định các quy tắc ràng buộc cho bài toán này.
Python
# Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end )
C++
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } }
Java
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } }
C#
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } }
Chương trình này sử dụng phương thức AddNoOverlap/add_no_overlap/addNoOverlap của mô hình
để tạo ra những ràng buộc không chồng chéo, giúp ngăn chặn việc cần làm
cùng một máy không bị chồng chéo về thời gian.
Tiếp theo, chương trình sẽ thêm các điều kiện ràng buộc về mức độ ưu tiên để ngăn chặn các nhiệm vụ liên tiếp cho cùng một công việc không bị trùng lặp về thời gian. Đối với mỗi công việc và mỗi tác vụ trong công việc đó, một quy tắc ràng buộc tuyến tính sẽ được thêm vào để chỉ định rằng điểm cuối thời gian của một tác vụ xảy ra trước thời gian bắt đầu của tác vụ tiếp theo trong công việc đó.
Xác định mục tiêu
Mã sau đây xác định mục tiêu của bài toán.
Python
# Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var)
C++
// Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var);
Java
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar);
C#
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar);
Mã này tạo một biến mục tiêu và ràng buộc biến đó phải là giá trị lớn nhất của kết thúc tất cả công việc.
Gọi trình giải
Mã sau đây gọi trình giải.
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model)
C++
const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build());
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model);
C#
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}");
Hiển thị kết quả
Đoạn mã sau đây cho thấy kết quả, bao gồm cả lịch biểu và công việc tối ưu ngắt quãng.
Python
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.")
C++
if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; }
Java
if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); }
C#
if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); }
Lịch biểu tối ưu như sau:
Optimal Schedule Length: 11
Machine 0: job_0_0 job_1_0
[0,3] [3,5]
Machine 1: job_2_0 job_0_1 job_1_2
[0,4] [4,6] [7,11]
Machine 2: job_1_1 job_0_2 job_2_1
[5,6] [6,8] [8,11]

Độc giả mắt đại bàng kiểm tra máy 1 có thể thắc mắc tại sao công việc_1_2 được lên lịch vào lúc thời gian 7 thay vì thời gian 6. Cả hai đều là giải pháp hợp lệ, nhưng hãy nhớ: mục tiêu là giảm thiểu khoảng thời gian tạo. Việc di chuyển công việc_1_2 sớm hơn sẽ không làm giảm khoảng thời gian tạo , vì vậy hai nghiệm bằng nhau từ góc độ của người giải.
Toàn bộ chương trình
Cuối cùng, sau đây là toàn bộ chương trình cho vấn đề về cửa hàng việc làm.
Python
"""Minimal jobshop example.""" import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model def main() -> None: """Minimal jobshop problem.""" # Data. jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job) # Create the model. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var) # Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end ) # Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var) # Creates the solver and solve. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model) if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.") # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" - conflicts: {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" - branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" - wall time: {solver.wall_time}s") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
C++
// Nurse scheduling problem with shift requests. #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void MinimalJobshopSat() { using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } } // Creates the model. CpModelBuilder cp_model; struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var); const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build()); if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; } // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main() { operations_research::sat::MinimalJobshopSat(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** Minimal Jobshop problem. */ public class MinimalJobshopSat { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model); if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); } // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.printf(" conflicts: %d%n", solver.numConflicts()); System.out.printf(" branches : %d%n", solver.numBranches()); System.out.printf(" wall time: %f s%n", solver.wallTime()); } private MinimalJobshopSat() {} }
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class ScheduleRequestsSat { private class AssignedTask : IComparable { public int jobID; public int taskID; public int start; public int duration; public AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } public int CompareTo(object obj) { if (obj == null) return 1; AssignedTask otherTask = obj as AssignedTask; if (otherTask != null) { if (this.start != otherTask.start) return this.start.CompareTo(otherTask.start); else return this.duration.CompareTo(otherTask.duration); } else throw new ArgumentException("Object is not a Temperature"); } } public static void Main(String[] args) { var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar); // Solve CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}"); if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); } Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts: {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()}s"); } }
