Поле переменной хранит строку в качестве своего значения и строку в качестве своего текста. Значение — это идентификатор переменной, а текст — имя переменной.
Переменное поле
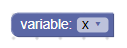
Переменное поле с открытым редактором
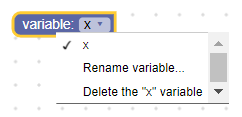
Переменное поле в свернутом блоке
Создание
Нетипизированный
JSON
{
"type": "example_variable_untyped",
"message0": "variable: %1",
"args0": [
{
"type": "field_variable",
"name": "FIELDNAME",
"variable": "x"
}
]
}
JavaScript
Blockly.Blocks['example_variable_untyped'] = {
init: function() {
this.appendDummyInput()
.appendField('variable:')
.appendField(new Blockly.FieldVariable('x'), 'FIELDNAME');
}
};
Напечатано
JSON
{
"type": "example_variable_typed",
"message0": "variable: %1",
"args0": [
{
"type": "field_variable",
"name": "FIELDNAME",
"variable": "x",
"variableTypes": ["Number", "String"],
"defaultType": "Number"
}
]
}
JavaScript
Blockly.Blocks['example_variable_typed'] = {
init: function() {
this.appendDummyInput()
.appendField('variable:')
.appendField(new Blockly.FieldVariable(
'X',
null,
['Number', 'String'],
'Number'
), 'FIELDNAME');
}
};
Конструктор переменных принимает необязательное имя переменной, необязательный валидатор , необязательный массив типов переменных и необязательный тип по умолчанию.
- Имя переменной должно быть строкой. Это будет имя исходной переменной, хранящейся в поле. Если значение равно null или не определено, будет сгенерировано уникальное имя.
- Типы переменных должны быть массивом строк. Это указывает полю, какие типы переменных оно может содержать (т.е. какие типы переменных добавлять в раскрывающийся список). Если значение равно null или не определено, будут приняты (и добавлены в раскрывающийся список) все типы переменных.
- Тип по умолчанию должен быть строковым. Он будет использоваться при создании исходной модели переменной поля. Если он определён, он должен быть включён в массив типов переменных. Если он равен null или не определён, это значение по умолчанию — пустая строка, то есть исходная переменная будет иметь гибкую типизацию.
→ Дополнительную информацию о строгой типизации см. в разделе Проверка типов .
Сериализация
JSON
JSON для переменного поля выглядит так:
{
"fields": {
"FIELDNAME": {
"id": "QJD^+@[RVIwbLSZoDb:V"
}
}
}
Где FIELDNAME — строка, ссылающаяся на поле переменной, а значение — идентификатор переменной, на которую ссылается поле.
Если вы используете это поле на панели инструментов, вы также можете напрямую указать имя и (необязательно) тип, поскольку не будет доступной для ссылки переменной.
{
"fields": {
"FIELDNAME": {
"name": "my_variable",
"type": "string"
}
}
}
XML
XML для переменного поля выглядит так:
<field name="VARIABLE" id="QJD^+@[RVIwbLSZoDb:V" variabletype="">name</field>
- Атрибут
nameузла содержит строку, ссылающуюся на переменное поле. - Атрибут
idузла содержит идентификатор переменной, на которую ссылается поле. - Атрибут
variabletypeузла содержит тип переменной. Этотvariabletypeподчиняется тем же правилам, что и параметр типа по умолчанию конструктора. - Внутренний текст узла — это имя переменной. Значение внутреннего текста подчиняется тем же правилам, что и параметр имени переменной конструктора.
Создание валидатора переменных
Значение поля переменной — строка, поэтому любые валидаторы должны принимать строку и возвращать строку, null или undefined .
Вот пример валидатора, который принимает в качестве параметров только некоторые предопределённые переменные. Эти переменные необходимо определить с помощью функции Workspace.getVariableMap().createVariable при загрузке рабочей области.
function(newValue) {
var validIds = ['Worf', 'Riker', 'Picard'];
if (validIds.indexOf(newValue) == -1) {
return null;
}
return newValue;
}


