Değişken alan, değer olarak bir dize, metin olarak da bir dize depolar. Değer, bir değişkenin kimliği, metin ise bir değişkenin adıdır.
Değişken alan
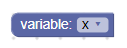
Düzenleyici açıkken değişken alanı

Daraltılmış bloktaki değişken alan
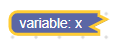
içerik üretimi
Untyped
JSON
{
"type": "example_variable_untyped",
"message0": "variable: %1",
"args0": [
{
"type": "field_variable",
"name": "FIELDNAME",
"variable": "x"
}
]
}
JavaScript
Blockly.Blocks['example_variable_untyped'] = {
init: function() {
this.appendDummyInput()
.appendField('variable:')
.appendField(new Blockly.FieldVariable('x'), 'FIELDNAME');
}
};
Yazılan
JSON
{
"type": "example_variable_typed",
"message0": "variable: %1",
"args0": [
{
"type": "field_variable",
"name": "FIELDNAME",
"variable": "x",
"variableTypes": ["Number", "String"],
"defaultType": "Number"
}
]
}
JavaScript
Blockly.Blocks['example_variable_typed'] = {
init: function() {
this.appendDummyInput()
.appendField('variable:')
.appendField(new Blockly.FieldVariable(
'X',
null,
['Number', 'String'],
'Number'
), 'FIELDNAME');
}
};
Değişken oluşturucu, isteğe bağlı bir değişken adı, isteğe bağlı bir doğrulayıcı, isteğe bağlı bir değişken türleri dizisi ve isteğe bağlı bir varsayılan tür alır.
- Değişken adı bir dize olmalıdır. Bu, alanın tuttuğu ilk değişkenin adı olacaktır. Değer boşsa veya tanımlanmamışsa benzersiz bir ad oluşturulur.
- Değişken türleri, dize dizisi olmalıdır. Bu, alana hangi tür değişkenlerin eklenebileceğini (ör. açılır listeye hangi tür değişkenlerin ekleneceğini) belirtir. Değer boş veya tanımlanmamışsa tüm değişken türleri kabul edilir (ve açılır listeye eklenir).
- Varsayılan tür bir dize olmalıdır. Bu, alanın ilk değişken modeli oluşturulurken kullanılır. Bu tanımlanmışsa değişken türleri dizisine dahil edilmelidir. Bu değer null veya tanımsızsa varsayılan olarak boş bir dize olur. Bu da başlangıç değişkeninin esnek bir şekilde yazılacağı anlamına gelir.
→ Katı tür oluşturma hakkında daha fazla bilgi için Tür Kontrolleri başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
Serileştirme
JSON
Değişken alanın JSON'u şu şekilde görünür:
{
"fields": {
"FIELDNAME": {
"id": "QJD^+@[RVIwbLSZoDb:V"
}
}
}
Burada FIELDNAME, değişken bir alana referans veren bir dizedir ve değer, alanın referans verdiği değişkenin kimliğidir.
Bu alanı araç kutusunda kullanıyorsanız referans verilebilecek bir değişken olmayacağından adı ve (isteğe bağlı) türü doğrudan da belirtebilirsiniz.
{
"fields": {
"FIELDNAME": {
"name": "my_variable",
"type": "string"
}
}
}
XML
Değişken bir alanın XML'si şu şekilde görünür:
<field name="VARIABLE" id="QJD^+@[RVIwbLSZoDb:V" variabletype="">name</field>
- Düğümün
nameözelliği, bir değişken alanına referans veren bir dize içeriyor. - Düğümün
idözelliği, alanın referans verdiği değişkenin kimliğini içerir. - Düğümün
variabletypeözelliği, değişkenin türünü içerir.variabletype, oluşturucunun varsayılan tür parametresiyle aynı kurallara uyar. - Düğümün iç metni, değişkenin adıdır. İç metin değeri, oluşturucunun değişken adı parametresiyle aynı kurallara uyar.
Değişken doğrulayıcı oluşturma
Değişken alanın değeri dizedir. Bu nedenle, tüm doğrulayıcılar dize kabul etmeli ve dize, null veya undefined döndürmelidir.
Aşağıda, yalnızca önceden tanımlanmış bazı değişkenleri seçenek olarak kabul eden bir doğrulayıcı örneği verilmiştir. Bu değişkenlerin, çalışma alanı yüklendiğinde Workspace.getVariableMap().createVariable işleviyle tanımlanması gerekir.
function(newValue) {
var validIds = ['Worf', 'Riker', 'Picard'];
if (validIds.indexOf(newValue) == -1) {
return null;
}
return newValue;
}

