简介
本教程介绍了如何使用 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 将带有标记的 Google 地图添加到网页中。此外,它还介绍了如何设置地图选项,以及如何使用控件插槽向地图添加标签。
下面便是您将在本教程的指导下创建的地图。标记位于乌鲁鲁卡塔丘塔国家公园中的乌鲁鲁(也称为“艾尔斯岩”)。
入门指南
在网页上创建带标记的 Google 地图需要执行以下三个步骤:
您需要一个网络浏览器。请根据所用平台从受支持的浏览器列表中选择一个常见的浏览器,例如 Google Chrome(推荐)、Firefox、Safari 或 Edge。
第 1 步:获取 API 密钥
本部分介绍如何使用您的 API 密钥对应用进行身份验证,以便使用 Maps JavaScript API。
请按照下列步骤获取 API 密钥:
前往 Google Cloud 控制台。
创建或选择一个项目。
点击继续,启用 API 和任何相关服务。
在凭据页面上,获取 API 密钥(并设置 API 密钥限制)。注意:如果您已有不受限的 API 密钥或存在浏览器限制的密钥,可以使用相应密钥。
如需防止配额盗用并保护 API 密钥,请参阅使用 API 密钥。
启用结算功能。如需了解详情,请参阅用量和结算。
获得 API 密钥后,点击“YOUR_API_KEY”将密钥添加到以下代码段中。复制并粘贴引导加载程序脚本标记,以便在自己的网页上使用。
<script> (g=>{var h,a,k,p="The Google Maps JavaScript API",c="google",l="importLibrary",q="__ib__",m=document,b=window;b=b[c]||(b[c]={});var d=b.maps||(b.maps={}),r=new Set,e=new URLSearchParams,u=()=>h||(h=new Promise(async(f,n)=>{await (a=m.createElement("script"));e.set("libraries",[...r]+"");for(k in g)e.set(k.replace(/[A-Z]/g,t=>"_"+t[0].toLowerCase()),g[k]);e.set("callback",c+".maps."+q);a.src=`https://maps.${c}apis.com/maps/api/js?`+e;d[q]=f;a.onerror=()=>h=n(Error(p+" could not load."));a.nonce=m.querySelector("script[nonce]")?.nonce||"";m.head.append(a)}));d[l]?console.warn(p+" only loads once. Ignoring:",g):d[l]=(f,...n)=>r.add(f)&&u().then(()=>d[l](f,...n))})({ key: "YOUR_API_KEY", v: "weekly", // Use the 'v' parameter to indicate the version to use (weekly, beta, alpha, etc.). // Add other bootstrap parameters as needed, using camel case. }); </script>
第 2 步:创建 HTML 网页
下方代码可创建一个基本的 HTML 网页:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--
@license
Copyright 2025 Google LLC. All Rights Reserved.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
-->
<html>
<head>
<title>Add a Map</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./style.css" />
<script type="module" src="./index.js"></script>
<!-- prettier-ignore -->
<script>(g=>{var h,a,k,p="The Google Maps JavaScript API",c="google",l="importLibrary",q="__ib__",m=document,b=window;b=b[c]||(b[c]={});var d=b.maps||(b.maps={}),r=new Set,e=new URLSearchParams,u=()=>h||(h=new Promise(async(f,n)=>{await (a=m.createElement("script"));e.set("libraries",[...r]+"");for(k in g)e.set(k.replace(/[A-Z]/g,t=>"_"+t[0].toLowerCase()),g[k]);e.set("callback",c+".maps."+q);a.src=`https://maps.${c}apis.com/maps/api/js?`+e;d[q]=f;a.onerror=()=>h=n(Error(p+" could not load."));a.nonce=m.querySelector("script[nonce]")?.nonce||"";m.head.append(a)}));d[l]?console.warn(p+" only loads once. Ignoring:",g):d[l]=(f,...n)=>r.add(f)&&u().then(()=>d[l](f,...n))})
({key: "YOUR_API_KEY", v: "weekly"});</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- The map, centered at Uluru, Australia. -->
<gmp-map center="-25.344,131.031" zoom="4" map-id="DEMO_MAP_ID">
</gmp-map>
</body>
</html>这是一个非常基本的 HTML 页面,它使用 gmp-map 元素在页面上显示地图。由于我们尚未添加任何 JavaScript 代码,因此地图将为空白。
了解代码
在此示例的这个阶段,我们有:
- 使用
!DOCTYPE html声明以 HTML5 形式声明应用。 - 使用引导加载程序加载了 Maps JavaScript API。
- 创建了一个
gmp-map元素来保存地图。
以 HTML5 形式声明您的应用
我们建议您在自己的 Web 应用内声明真正的 DOCTYPE。在本文的示例中,我们使用 HTML5 DOCTYPE 以 HTML5 形式声明了应用,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
目前大多数浏览器都会在“标准模式”下呈现使用此 DOCTYPE 声明的内容,这意味着您的应用应该具有更高的跨浏览器兼容性。此外,DOCTYPE 还旨在以适当方式降级;无法理解该声明的浏览器会将其忽略,并使用“怪异模式”显示其内容。
请注意,某些 CSS 在怪异模式下可正常运作,在标准模式下则是无效的。具体而言,所有百分比形式的尺寸都必须从父级块元素继承,并且如果其中任一祖先元素未能指定尺寸,则假定其尺寸为 0 x 0 像素。因此,我们添加了以下 style 声明:
<style>
gmp-map {
height: 100%;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>加载 Maps JavaScript API
引导程序加载器会准备 Maps JavaScript API 以进行加载(在调用 importLibrary() 之前不会加载任何库)。
<script> (g=>{var h,a,k,p="The Google Maps JavaScript API",c="google",l="importLibrary",q="__ib__",m=document,b=window;b=b[c]||(b[c]={});var d=b.maps||(b.maps={}),r=new Set,e=new URLSearchParams,u=()=>h||(h=new Promise(async(f,n)=>{await (a=m.createElement("script"));e.set("libraries",[...r]+"");for(k in g)e.set(k.replace(/[A-Z]/g,t=>"_"+t[0].toLowerCase()),g[k]);e.set("callback",c+".maps."+q);a.src=`https://maps.${c}apis.com/maps/api/js?`+e;d[q]=f;a.onerror=()=>h=n(Error(p+" could not load."));a.nonce=m.querySelector("script[nonce]")?.nonce||"";m.head.append(a)}));d[l]?console.warn(p+" only loads once. Ignoring:",g):d[l]=(f,...n)=>r.add(f)&&u().then(()=>d[l](f,...n))})({ key: "YOUR_API_KEY", v: "weekly", // Use the 'v' parameter to indicate the version to use (weekly, beta, alpha, etc.). // Add other bootstrap parameters as needed, using camel case. }); </script>
如需了解如何获取自己的 API 密钥,请参阅第 3 步:获取 API 密钥。
在教程的这一阶段,系统会显示一个空白窗口,其中仅显示未设置格式的标签文本。这是因为我们尚未添加任何 JavaScript 代码。
创建 gmp-map 元素
要在网页上显示地图,我们必须为其留出一个位置。为此,我们通常会创建一个 gmp-map 元素,然后在浏览器的文档对象模型 (DOM) 中获取对该元素的引用。您也可以使用 div 元素来执行此操作(了解详情),但建议使用 gmp-map 元素。
以下代码定义了 gmp-map 元素,并设置了 center、zoom 和 map-id 参数。
<gmp-map center="-25.344,131.031" zoom="4" map-id="DEMO_MAP_ID"> </gmp-map>
您必须始终提供 center 和 zoom 选项。在以上代码中,center 属性用于向 API 指示地图的中心位置,而 zoom 属性用于指定地图的缩放级别。0 是最低缩放级别,会显示整个地球。调高缩放级别值,就能以更高的分辨率放大地球。
缩放级别
以单幅图像形式提供整个地球的地图需要巨幅尺寸的地图,或者分辨率极低的小幅地图。因此,Google 地图和 Maps JavaScript API 中的地图图像分成了地图“图块”和“缩放级别”。在较低的缩放级别,一小部分地图图块便可涵盖大片区域;在较高的缩放级别,图块分辨率更高,涵盖的区域较小。以下列表显示了您在每个缩放级别看到的地图的大致详细程度:
- 1:世界
- 5:大陆/洲
- 10:城市
- 15:街道
- 20:建筑物
以下三幅图像反映了东京同一位置在缩放级别分别为 0、7 和 18 时的情况。
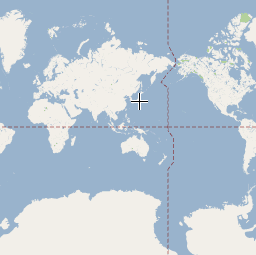
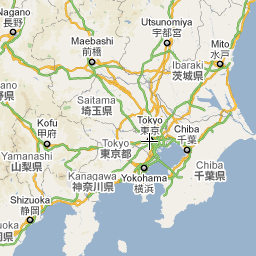
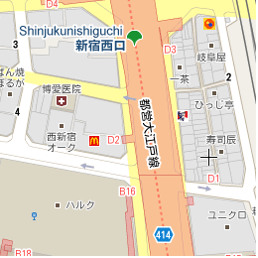
以下代码描述了用于设置 gmp-map 元素大小的 CSS。
/* Set the size of the gmp-map element that contains the map */ gmp-map { height: 400px; /* The height is 400 pixels */ width: 100%; /* The width is the width of the web page */ }
在以上代码中,style 元素用于设置 gmp-map 的大小。将宽度和高度设置为大于 0px 的值,才能让地图显示出来。在本例中,gmp-map 的高度设置为 400 像素,宽度设置为 100%,即按网页的完整宽度显示地图。建议始终明确设置高度和宽度样式。
控制广告资源配置
您可以使用控件插槽将 HTML 表单控件添加到地图中。位置是地图上预定义的位置;使用 slot 属性可为元素设置所需的位置,并将元素嵌套在 gmp-map 元素中。以下代码段展示了如何向地图的左上角添加 HTML 标签。
<!-- The map, centered at Uluru, Australia. -->
<gmp-map center="-25.344,131.031" zoom="4" map-id="DEMO_MAP_ID">
<div id="controls" slot="control-inline-start-block-start">
<h3>My Google Maps Demo</h3>
</div>
</gmp-map>第 3 步:添加 JavaScript 代码
本部分介绍如何将 Maps JavaScript API 加载到网页中,以及如何自行编写 JavaScript,以利用 API 添加带标记的地图。
TypeScript
async function initMap(): Promise<void> { // Request the needed libraries. const [{ Map }, { AdvancedMarkerElement }] = await Promise.all([ google.maps.importLibrary('maps') as Promise<google.maps.MapsLibrary>, google.maps.importLibrary( 'marker' ) as Promise<google.maps.MarkerLibrary>, ]); // Get the gmp-map element. const mapElement = document.querySelector( 'gmp-map' ) as google.maps.MapElement; // Get the inner map. const innerMap = mapElement.innerMap; // Set map options. innerMap.setOptions({ mapTypeControl: false, }); // Add a marker positioned at the map center (Uluru). const marker = new AdvancedMarkerElement({ map: innerMap, position: mapElement.center, title: 'Uluru/Ayers Rock', }); } initMap();
JavaScript
async function initMap() { // Request the needed libraries. const [{ Map }, { AdvancedMarkerElement }] = await Promise.all([ google.maps.importLibrary('maps'), google.maps.importLibrary('marker'), ]); // Get the gmp-map element. const mapElement = document.querySelector('gmp-map'); // Get the inner map. const innerMap = mapElement.innerMap; // Set map options. innerMap.setOptions({ mapTypeControl: false, }); // Add a marker positioned at the map center (Uluru). const marker = new AdvancedMarkerElement({ map: innerMap, position: mapElement.center, title: 'Uluru/Ayers Rock', }); } initMap();
当调用 initMap() 时,上述代码会执行以下操作:
- 加载
maps和marker库。 - 从 DOM 中获取地图元素。
- 在内部地图上设置其他地图选项。
- 向地图添加标记。
获取地图对象并设置选项
innerMap 表示 Map 类的实例。如需设置地图选项,请从地图元素中获取 innerMap 实例,然后调用 setOptions。以下代码段展示了如何从 DOM 获取 innerMap 实例,然后调用 setOptions:
// Get the gmp-map element. const mapElement = document.querySelector( "gmp-map" ) as google.maps.MapElement; // Get the inner map. const innerMap = mapElement.innerMap; // Set map options. innerMap.setOptions({ mapTypeControl: false, });
等待地图加载
使用 gmp-map 元素时,地图会异步加载。如果在初始化时发出其他请求(例如地理定位或地点详情请求),可能会导致竞态条件。为确保代码仅在地图完全加载后运行,请在初始化函数中使用 addListenerOnce 空闲事件处理程序,如下所示:
// Do things once the map has loaded. google.maps.event.addListenerOnce(innerMap, 'idle', () => { // Run this code only after the map has loaded. console.log("The map is now ready!"); });
这样做可确保您的代码仅在地图加载后运行;在应用的生命周期内,处理程序仅触发一次。
完整示例代码
如需查看完整的示例代码,请点击此处:
TypeScript
async function initMap(): Promise<void> { // Request the needed libraries. const [{ Map }, { AdvancedMarkerElement }] = await Promise.all([ google.maps.importLibrary('maps') as Promise<google.maps.MapsLibrary>, google.maps.importLibrary( 'marker' ) as Promise<google.maps.MarkerLibrary>, ]); // Get the gmp-map element. const mapElement = document.querySelector( 'gmp-map' ) as google.maps.MapElement; // Get the inner map. const innerMap = mapElement.innerMap; // Set map options. innerMap.setOptions({ mapTypeControl: false, }); // Add a marker positioned at the map center (Uluru). const marker = new AdvancedMarkerElement({ map: innerMap, position: mapElement.center, title: 'Uluru/Ayers Rock', }); } initMap();
JavaScript
async function initMap() { // Request the needed libraries. const [{ Map }, { AdvancedMarkerElement }] = await Promise.all([ google.maps.importLibrary('maps'), google.maps.importLibrary('marker'), ]); // Get the gmp-map element. const mapElement = document.querySelector('gmp-map'); // Get the inner map. const innerMap = mapElement.innerMap; // Set map options. innerMap.setOptions({ mapTypeControl: false, }); // Add a marker positioned at the map center (Uluru). const marker = new AdvancedMarkerElement({ map: innerMap, position: mapElement.center, title: 'Uluru/Ayers Rock', }); } initMap();
CSS
/* * Always set the map height explicitly to define the size of the div element * that contains the map. */ gmp-map { height: 100%; } /* * Optional: Makes the sample page fill the window. */ html, body { height: 100%; margin: 0; padding: 0; }
HTML
<html>
<head>
<title>Add a Map</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./style.css" />
<script type="module" src="./index.js"></script>
<!-- prettier-ignore -->
<script>(g=>{var h,a,k,p="The Google Maps JavaScript API",c="google",l="importLibrary",q="__ib__",m=document,b=window;b=b[c]||(b[c]={});var d=b.maps||(b.maps={}),r=new Set,e=new URLSearchParams,u=()=>h||(h=new Promise(async(f,n)=>{await (a=m.createElement("script"));e.set("libraries",[...r]+"");for(k in g)e.set(k.replace(/[A-Z]/g,t=>"_"+t[0].toLowerCase()),g[k]);e.set("callback",c+".maps."+q);a.src=`https://maps.${c}apis.com/maps/api/js?`+e;d[q]=f;a.onerror=()=>h=n(Error(p+" could not load."));a.nonce=m.querySelector("script[nonce]")?.nonce||"";m.head.append(a)}));d[l]?console.warn(p+" only loads once. Ignoring:",g):d[l]=(f,...n)=>r.add(f)&&u().then(()=>d[l](f,...n))})
({key: "AIzaSyA6myHzS10YXdcazAFalmXvDkrYCp5cLc8", v: "weekly"});</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- The map, centered at Uluru, Australia. -->
<gmp-map center="-25.344,131.031" zoom="4" map-id="DEMO_MAP_ID">
<div id="controls" slot="control-inline-start-block-start">
<h3>My Google Maps Demo</h3>
</div>
</gmp-map>
</body>
</html>试用示例
详细了解标记:
提示和问题排查
- 详细了解如何获取纬度/经度坐标,或如何将地址转换为地理坐标。
- 您可以通过调整样式和属性等选项来自定义地图。如需详细了解如何自定义地图,请参阅有关样式设置和在地图上绘制的指南。
- 在网络浏览器中使用开发者工具控制台来测试和运行代码、阅读错误报告并解决代码存在的问题。
- 使用以下键盘快捷键在 Chrome 中打开控制台:
Command+Option+J(在 Mac 上)或 Ctrl+Shift+J(在 Windows 上)。 按照以下步骤操作,获取 Google 地图上某个位置的纬度和经度坐标。
- 在浏览器中打开 Google 地图。
- 在地图上右键点击需要坐标的确切位置。
- 从菜单中选择纬度和经度坐标。
您可以使用地理编码服务将地址转换为纬度和经度坐标。开发者指南详细介绍了如何开始使用地理编码服务。
