다음 섹션에서는 LP 문제의 예를 보여주고 이를 해결하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 문제는 다음과 같습니다.
다음 제약 조건에 따라 3x + 4y를 최대화합니다.
x + 2y≤ 143x - y≥ 0x - y≤ 2
목표 함수 3x + 4y와 제약 조건은 모두 선형 표현식으로 주어지므로 선형 문제가 됩니다.
제약 조건은 가능한 영역, 즉 내부를 포함하여 아래에 표시된 삼각형을 정의합니다.
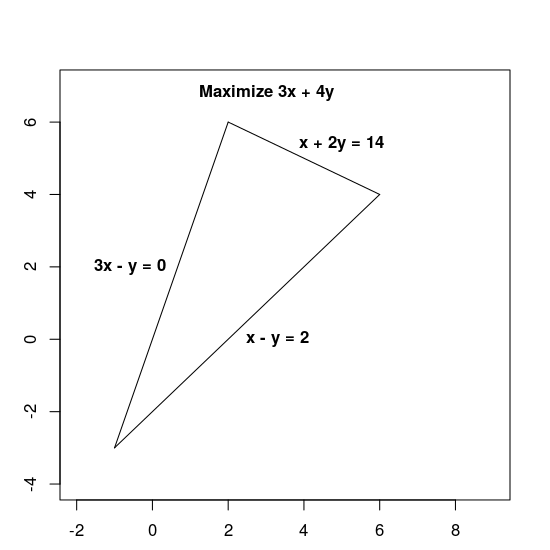
LP 문제 해결을 위한 기본 단계
LP 문제를 해결하려면 프로그램에 다음 단계가 포함되어야 합니다.
- 선형 솔버 래퍼를 가져옵니다.
- LP 솔버를 선언하고
- 변수를 정의하고
- 제약 조건을 정의하고
- 목표를 정의하고
- LP 솔버를 호출하고
- 솔루션 표시
MPSolver를 사용하는 솔루션
다음 섹션에서는 MPSolver 래퍼와 LP 솔버를 사용하여 문제를 해결하는 프로그램을 보여줍니다.
참고. 아래 프로그램을 실행하려면 OR-Tools를 설치해야 합니다.
기본 OR-Tools 선형 최적화 솔버는 Google의 사내 선형 프로그래밍 솔버인 Glop입니다. 빠르고 메모리 효율적이며 수치적으로 안정적입니다.
선형 솔버 래퍼 가져오기
아래와 같이 MIP 솔버 및 선형 솔버용 인터페이스인 OR-Tools 선형 솔버 래퍼를 가져오거나 포함합니다.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
C++
#include <iostream> #include <memory> #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
LP 솔버 선언
MPsolver는 Glop를 비롯한 여러 솔버의 래퍼입니다. 아래 코드는 GLOP 솔버를 선언합니다.
Python
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
if not solver:
return
C++
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
Java
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
C#
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
참고: 다른 LP 솔버를 사용하려면 GLOP를 PDLP로 바꾸세요. 솔버 선택에 대한 자세한 내용은 고급 LP 해결을 참조하고 서드 파티 솔버 설치에 대한 자세한 내용은 설치 가이드를 참고하세요.
변수 만들기
먼저 값이 0에서 무한대 사이의 값인 x와 y 변수를 만듭니다.
Python
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
C#
Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
제약조건 정의
다음으로 변수의 제약 조건을 정의합니다. 각 제약조건에 고유한 이름 (예: constraint0)을 지정한 다음 제약조건의 계수를 정의합니다.
Python
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
C++
// x + 2*y <= 14. MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 14.0); c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c0->SetCoefficient(y, 2); // 3*x - y >= 0. MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(0.0, infinity); c1->SetCoefficient(x, 3); c1->SetCoefficient(y, -1); // x - y <= 2. MPConstraint* const c2 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 2.0); c2->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c2->SetCoefficient(y, -1); LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
Java
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
C#
// x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0);
// 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0);
// x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
목표 함수 정의
다음 코드는 목표 함수 3x + 4y를 정의하고 이를 최대화 문제로 지정합니다.
Python
# Objective function: 3x + 4y. solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
C++
// Objective function: 3x + 4y. MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 3); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 4); objective->SetMaximization();
Java
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y. MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(x, 3); objective.setCoefficient(y, 4); objective.setMaximization();
C#
// Objective function: 3x + 4y. solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y);
솔버 호출
다음 코드는 솔버를 호출합니다.
Python
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
C++
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
Java
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
C#
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
솔루션 표시
다음 코드는 솔루션을 보여줍니다.
Python
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print(f"Objective value = {solver.Objective().Value():0.1f}")
print(f"x = {x.solution_value():0.1f}")
print(f"y = {y.solution_value():0.1f}")
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
C++
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; LOG(INFO) << "Optimal objective value = " << objective->Value(); LOG(INFO) << x->name() << " = " << x->solution_value(); LOG(INFO) << y->name() << " = " << y->solution_value();
Java
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
C#
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
전체 프로그램
전체 프로그램은 다음과 같습니다.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def LinearProgrammingExample():
"""Linear programming sample."""
# Instantiate a Glop solver, naming it LinearExample.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
if not solver:
return
# Create the two variables and let them take on any non-negative value.
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
# Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
# Solve the system.
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print(f"Objective value = {solver.Objective().Value():0.1f}")
print(f"x = {x.solution_value():0.1f}")
print(f"y = {y.solution_value():0.1f}")
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
print("\nAdvanced usage:")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.wall_time():d} milliseconds")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.iterations():d} iterations")
LinearProgrammingExample()
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void LinearProgrammingExample() {
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
const double infinity = solver->infinity();
// x and y are non-negative variables.
MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 14.0);
c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c0->SetCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(0.0, infinity);
c1->SetCoefficient(x, 3);
c1->SetCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint* const c2 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 2.0);
c2->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c2->SetCoefficient(y, -1);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
// Objective function: 3x + 4y.
MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective();
objective->SetCoefficient(x, 3);
objective->SetCoefficient(y, 4);
objective->SetMaximization();
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:";
LOG(INFO) << "Optimal objective value = " << objective->Value();
LOG(INFO) << x->name() << " = " << x->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << y->name() << " = " << y->solution_value();
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
operations_research::LinearProgrammingExample();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.linearsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/** Simple linear programming example. */
public final class LinearProgrammingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 3);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 4);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");
}
private LinearProgrammingExample() {}
}
C#
using System;
using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
public class LinearProgrammingExample
{
static void Main()
{
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
// x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0);
// 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0);
// x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
// Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y);
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("\nAdvanced usage:");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.WallTime() + " milliseconds");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Iterations() + " iterations");
}
}
최적의 솔루션
프로그램은 아래와 같이 문제에 대한 최적의 해결책을 반환합니다.
Number of variables = 2
Number of constraints = 3
Solution:
x = 6.0
y = 4.0
Optimal objective value = 34.0
다음은 솔루션을 보여주는 그래프입니다.
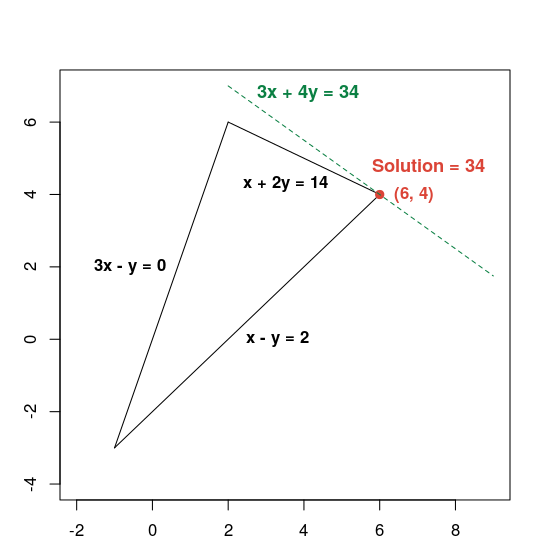
녹색 파선은 목표 함수를 최적 값 34와 같게 설정하여 정의됩니다. 방정식의 형태가 3x + 4y = c인 모든 선은 점선과 평행하며 34는 선이 가능한 영역을 교차하는 가장 큰 c 값입니다.
선형 최적화 문제 해결에 관한 자세한 내용은 고급 LP 해결을 참고하세요.
