ส่วนต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างปัญหา LP และแสดงวิธีแก้โจทย์ ปัญหามีดังนี้
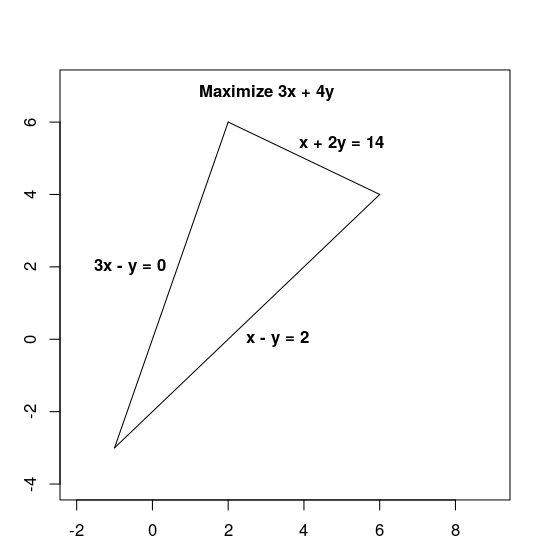
เพิ่ม 3x + 4y ให้มากที่สุดภายใต้ข้อจำกัดต่อไปนี้
x + 2y≤ 143x - y≥ 0x - y≤ 2
ทั้งฟังก์ชันวัตถุประสงค์ 3x + 4y และข้อจํากัดจะกำหนดด้วยนิพจน์เชิงเส้น ซึ่งทำให้เป็นปัญหาเชิงเส้น
ข้อจำกัดจะกำหนดภูมิภาคที่เป็นไปได้ ซึ่งก็คือสามเหลี่ยมที่แสดงด้านล่าง รวมถึงพื้นที่ภายในด้วย
ขั้นตอนพื้นฐานสำหรับการแก้ปัญหาหน้า Landing Page
หากต้องการแก้ปัญหา LP โปรแกรมของคุณควรมีขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้
- นำเข้า Wrapper ของตัวแก้วิดีโอเชิงเส้น
- ประกาศโปรแกรมแก้ LP
- กำหนดตัวแปร
- กำหนดข้อจำกัด
- กำหนดวัตถุประสงค์
- เรียกใช้โปรแกรมแก้ LP และ
- แสดงโซลูชัน
โซลูชันที่ใช้ MPSolver
ส่วนต่อไปนี้จะแสดงโปรแกรมที่แก้ปัญหาโดยใช้ Wrapper ของ MPSolver และโปรแกรมแก้โจทย์ LP
หมายเหตุ คุณต้องติดตั้ง OR-Tools เพื่อเรียกใช้โปรแกรมด้านล่าง
เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเชิงเส้น "หรือ" เครื่องมือหลักคือ Glop ซึ่งเป็นโปรแกรมแก้ปัญหาโปรแกรมเชิงเส้นภายในของ Google ซึ่งทำงานเร็ว ประหยัดหน่วยความจำ และเสถียรตัวเลข
นำเข้า Wrapper เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์เชิงเส้น
นำเข้า (หรือรวม) Wrapper เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์เชิงเส้น "หรือ" ซึ่งเป็นอินเทอร์เฟซสำหรับเครื่องมือแก้ปัญหา MIP และเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์เชิงเส้นดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
C++
#include <iostream> #include <memory> #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
ประกาศเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์ LP
MPsolver คือ Wrapper สำหรับเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์ที่หลากหลาย รวมถึง Glop โค้ดด้านล่างนี้ประกาศเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์ GLOP
Python
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
if not solver:
return
C++
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
Java
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
C#
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
หมายเหตุ: แทนที่ PDLP ด้วย GLOP เพื่อใช้เครื่องมือแก้ LP อื่น โปรดดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการเลือกเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิตที่การแก้ LP ขั้นสูง และสำหรับการติดตั้งเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์คณิตของบุคคลที่สาม โปรดดูคู่มือการติดตั้ง
สร้างตัวแปร
ก่อนอื่น ให้สร้างตัวแปร x และ y ซึ่งค่าอยู่ในช่วงตั้งแต่ 0 ถึงค่าอนันต์
Python
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
C#
Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
กําหนดข้อจํากัด
ต่อไป ให้กำหนดข้อจำกัดของตัวแปร ตั้งชื่อที่ไม่ซ้ำกันให้แต่ละจุด (เช่น constraint0) จากนั้นกำหนดค่าสัมประสิทธิ์สำหรับข้อจำกัด
Python
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
C++
// x + 2*y <= 14. MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 14.0); c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c0->SetCoefficient(y, 2); // 3*x - y >= 0. MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(0.0, infinity); c1->SetCoefficient(x, 3); c1->SetCoefficient(y, -1); // x - y <= 2. MPConstraint* const c2 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 2.0); c2->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c2->SetCoefficient(y, -1); LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
Java
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
C#
// x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0);
// 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0);
// x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
กำหนดฟังก์ชันวัตถุประสงค์
โค้ดต่อไปนี้กำหนดฟังก์ชันวัตถุประสงค์ 3x + 4y และระบุว่านี่คือปัญหาการเพิ่มสูงสุด
Python
# Objective function: 3x + 4y. solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
C++
// Objective function: 3x + 4y. MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 3); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 4); objective->SetMaximization();
Java
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y. MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(x, 3); objective.setCoefficient(y, 4); objective.setMaximization();
C#
// Objective function: 3x + 4y. solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y);
เรียกใช้เครื่องมือแก้โจทย์
โค้ดต่อไปนี้จะเรียกเครื่องมือแก้โจทย์
Python
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
C++
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
Java
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
C#
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
แสดงคำตอบ
โค้ดต่อไปนี้จะแสดงโซลูชัน
Python
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print(f"Objective value = {solver.Objective().Value():0.1f}")
print(f"x = {x.solution_value():0.1f}")
print(f"y = {y.solution_value():0.1f}")
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
C++
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; LOG(INFO) << "Optimal objective value = " << objective->Value(); LOG(INFO) << x->name() << " = " << x->solution_value(); LOG(INFO) << y->name() << " = " << y->solution_value();
Java
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
C#
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
โปรแกรมทั้งหมด
โปรดดูรายการโปรแกรมทั้งหมดด้านล่าง
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def LinearProgrammingExample():
"""Linear programming sample."""
# Instantiate a Glop solver, naming it LinearExample.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
if not solver:
return
# Create the two variables and let them take on any non-negative value.
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
# Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
# Solve the system.
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print(f"Objective value = {solver.Objective().Value():0.1f}")
print(f"x = {x.solution_value():0.1f}")
print(f"y = {y.solution_value():0.1f}")
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
print("\nAdvanced usage:")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.wall_time():d} milliseconds")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.iterations():d} iterations")
LinearProgrammingExample()
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void LinearProgrammingExample() {
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
const double infinity = solver->infinity();
// x and y are non-negative variables.
MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 14.0);
c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c0->SetCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(0.0, infinity);
c1->SetCoefficient(x, 3);
c1->SetCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint* const c2 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 2.0);
c2->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c2->SetCoefficient(y, -1);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
// Objective function: 3x + 4y.
MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective();
objective->SetCoefficient(x, 3);
objective->SetCoefficient(y, 4);
objective->SetMaximization();
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:";
LOG(INFO) << "Optimal objective value = " << objective->Value();
LOG(INFO) << x->name() << " = " << x->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << y->name() << " = " << y->solution_value();
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
operations_research::LinearProgrammingExample();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.linearsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/** Simple linear programming example. */
public final class LinearProgrammingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 3);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 4);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");
}
private LinearProgrammingExample() {}
}
C#
using System;
using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
public class LinearProgrammingExample
{
static void Main()
{
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
// x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0);
// 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0);
// x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
// Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y);
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("\nAdvanced usage:");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.WallTime() + " milliseconds");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Iterations() + " iterations");
}
}
โซลูชันที่ดีที่สุด
โปรแกรมจะแสดงวิธีแก้ปัญหาที่เหมาะสมที่สุดตามที่แสดงด้านล่าง
Number of variables = 2
Number of constraints = 3
Solution:
x = 6.0
y = 4.0
Optimal objective value = 34.0
นี่คือกราฟแสดงเฉลย
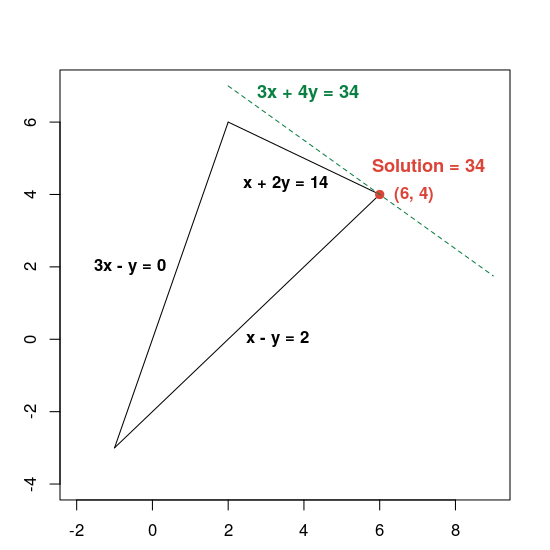
เส้นประสีเขียวจะกำหนดโดยการตั้งค่าฟังก์ชันวัตถุประสงค์ให้เท่ากับค่าที่เหมาะสมที่สุดที่ 34 ทุกบรรทัดที่มีสมการอยู่ในรูปแบบ 3x + 4y = c ขนานกับเส้นประ และ 34 คือค่า c ที่มากที่สุดซึ่งเส้นตัดกับพื้นที่ที่เป็นไปได้
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการแก้ปัญหาการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเชิงเส้นได้ที่การแก้ปัญหา LP ขั้นสูง
