يخزّن حقل المتغيّر سلسلة كنص وقيمة. القيمة هي رقم تعريف لمتغير، بينما النص هو اسم المتغير.
الحقل المتغيّر
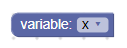
حقل متغيّر مع فتح المحرّر

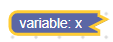
حقل متغير في مربّع مصغّر
الإنشاء
غير محدّد النوع
JSON
{
"type": "example_variable_untyped",
"message0": "variable: %1",
"args0": [
{
"type": "field_variable",
"name": "FIELDNAME",
"variable": "x"
}
]
}
JavaScript
Blockly.Blocks['example_variable_untyped'] = {
init: function() {
this.appendDummyInput()
.appendField('variable:')
.appendField(new Blockly.FieldVariable('x'), 'FIELDNAME');
}
};
مكتوب
JSON
{
"type": "example_variable_typed",
"message0": "variable: %1",
"args0": [
{
"type": "field_variable",
"name": "FIELDNAME",
"variable": "x",
"variableTypes": ["Number", "String"],
"defaultType": "Number"
}
]
}
JavaScript
Blockly.Blocks['example_variable_typed'] = {
init: function() {
this.appendDummyInput()
.appendField('variable:')
.appendField(new Blockly.FieldVariable(
'X',
null,
['Number', 'String'],
'Number'
), 'FIELDNAME');
}
};
يأخذ منشئ المتغير اسم متغير اختياري ومدقّقًا اختياريًا ومصفوفة اختيارية من أنواع المتغيرات ونوعًا تلقائيًا اختياريًا.
- يجب أن يكون اسم المتغيّر سلسلة. سيكون هذا هو اسم المتغير الأوّلي الذي يحتوي عليه الحقل. إذا كانت القيمة فارغة أو غير محدّدة، سيتم إنشاء اسم فريد.
- يجب أن تكون أنواع المتغيرات مصفوفة من السلاسل. يحدّد هذا الحقل أنواع المتغيّرات التي يمكن أن يتضمّنها الحقل (أي أنواع المتغيّرات التي يجب إضافتها إلى القائمة المنسدلة). إذا كانت القيمة فارغة أو غير محدّدة، سيتم قبول جميع أنواع المتغيرات (وستتم إضافتها إلى القائمة المنسدلة).
- يجب أن يكون النوع التلقائي سلسلة. سيتم استخدام هذا الخيار عند إنشاء نموذج المتغيّر الأوّلي للحقل. في حال تحديد هذا الحقل، يجب تضمينه في مصفوفة أنواع المتغيرات. إذا كانت القيمة فارغة أو غير محدّدة، ستكون القيمة التلقائية لهذا المتغيّر سلسلة فارغة، ما يعني أنّ المتغيّر الأوّلي سيكون من النوع المرن.
→ لمزيد من المعلومات حول الكتابة الصارمة، راجِع عمليات التحقّق من النوع.
نشر الحلقات على نحو متسلسِل
JSON
يبدو ملف JSON الخاص بحقل متغيّر على النحو التالي:
{
"fields": {
"FIELDNAME": {
"id": "QJD^+@[RVIwbLSZoDb:V"
}
}
}
حيث FIELDNAME هي سلسلة تشير إلى حقل متغير، والقيمة هي رقم تعريف المتغير الذي يشير إليه الحقل.
إذا كنت تستخدم هذا الحقل في مجموعة الأدوات، يمكنك أيضًا تحديد الاسم والنوع (اختياري) مباشرةً، لأنّه لن يتوفّر أي متغير يمكن الرجوع إليه.
{
"fields": {
"FIELDNAME": {
"name": "my_variable",
"type": "string"
}
}
}
XML
يبدو رمز XML الخاص بحقل متغيّر على النحو التالي:
<field name="VARIABLE" id="QJD^+@[RVIwbLSZoDb:V" variabletype="">name</field>
- تحتوي السمة
nameللعقدة على سلسلة تشير إلى حقل متغير. - تحتوي السمة
idللعقدة على معرّف المتغيّر الذي يشير إليه الحقل. - تحتوي السمة
variabletypeللعقدة على نوع المتغير. تتّبعvariabletypeالقواعد نفسها المتّبعة في مَعلمة النوع التلقائية للدالة الإنشائية. - النص الداخلي للعقدة هو اسم المتغيّر. تخضع قيمة النص الداخلي للقواعد نفسها التي تخضع لها مَعلمة اسم المتغيّر في الدالة الإنشائية.
إنشاء أداة التحقّق من صحة المتغيّرات
قيمة حقل المتغيّر هي سلسلة، لذا يجب أن تقبل أي أدوات التحقّق سلسلة وأن تعرض سلسلة أو null أو undefined.
في ما يلي مثال على أداة التحقّق التي تقبل بعض المتغيّرات المحدّدة مسبقًا فقط كخيارات. يجب تحديد هذه المتغيرات باستخدام الدالة
Workspace.getVariableMap().createVariable
عند تحميل مساحة العمل.
function(newValue) {
var validIds = ['Worf', 'Riker', 'Picard'];
if (validIds.indexOf(newValue) == -1) {
return null;
}
return newValue;
}

