Gli utenti possono inviare messaggi agli agenti e gli agenti possono inviare messaggi agli utenti, ma non c'è altro. Per ogni messaggio possono esserci diverse parti coinvolte:
- L'utente inizia una conversazione con un agente tramite i punti di ingresso nella Ricerca, in Maps e nei link e nei siti web gestiti dal brand. Gli utenti devono aver eseguito l'accesso a un Account Google, ma solo il nome dell'utente viene condiviso con il partner. I messaggi degli utenti vengono criptati con TLS.
I messaggi aziendali funzionano come un livello tra l'utente e il partner per proteggere la privacy degli utenti. Questo livello assicura che le informazioni dell'Account Google dell'utente non vengono condivise con il partner o gli agenti in tempo reale decriptando e ricriptando ogni messaggio in entrata e in uscita e mappando l'Account Google dell'utente a un ID conversazione.
Google archivia i messaggi criptati per garantire la consegna e la sincronizzazione tra i dispositivi di un utente. Questi messaggi archiviati non possono essere condivisi con terze parti. L'accesso è disponibile solo con l'ID Google dell'utente.
L'agente è una rappresentazione di un brand, così come creata e gestita da un partner.
Il partner gestisce l'agente per conto di un brand. I partner ricevono i messaggi in entrata in un hook web specificato, instradano i messaggi in entrata all'automazione o agli agenti dal vivo per comporre risposte e inviano messaggi in uscita all'API Business Messages.
L'automazione gestisce i messaggi per gli utenti senza coinvolgimento umano.
Gli agenti dal vivo gestiscono i messaggi utente che richiedono il coinvolgimento di persone fisiche.
Ogni parte ha un ruolo nell'inviare e ricevere messaggi all'interno di una conversazione. Un flusso di messaggistica end-to-end inizia con un utente che invia un messaggio a un agente e termina quando l'utente riceve una risposta dall'agente.
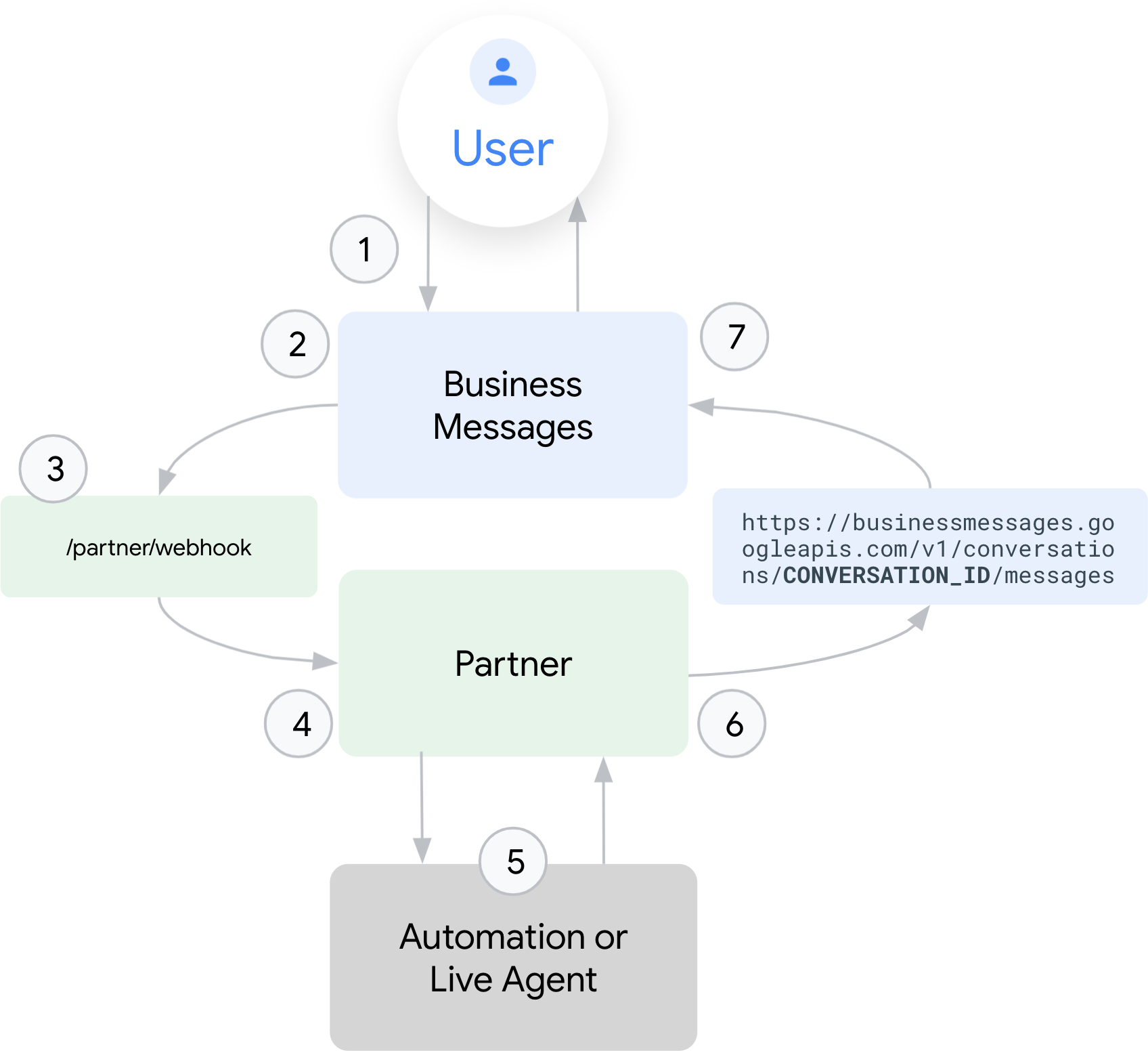
- Un utente avvia una conversazione e invia un messaggio a un agente di Business Messages.
- Business Messages assegna un ID alla conversazione. Gli ID conversazione sono permanenti e univoci per l'utente e l'agente. Se lo stesso utente ha contattato un agente diverso, quella conversazione avrà un ID conversazione diverso.
- Business Messages invia il messaggio criptato al webhook del partner. Il messaggio contiene l'ID conversazione univoco, l'ID agente, l'ID messaggio e le informazioni di contesto per l'origine della conversazione.
- Il partner riceve il messaggio e lo indirizza all'automazione o a un operatore.
- L'automazione crea automaticamente una risposta al messaggio dell'utente o un agente in tempo reale che ha accesso alla conversazione vede il messaggio dell'utente e crea una risposta di conseguenza.
- Il partner invia la risposta all'API Business Messages con l'ID conversazione come destinatario.
- Business Messages decripta e cripta di nuovo i messaggi, mappa l'ID conversazione con l'Account Google dell'utente e invia il messaggio all'utente.
