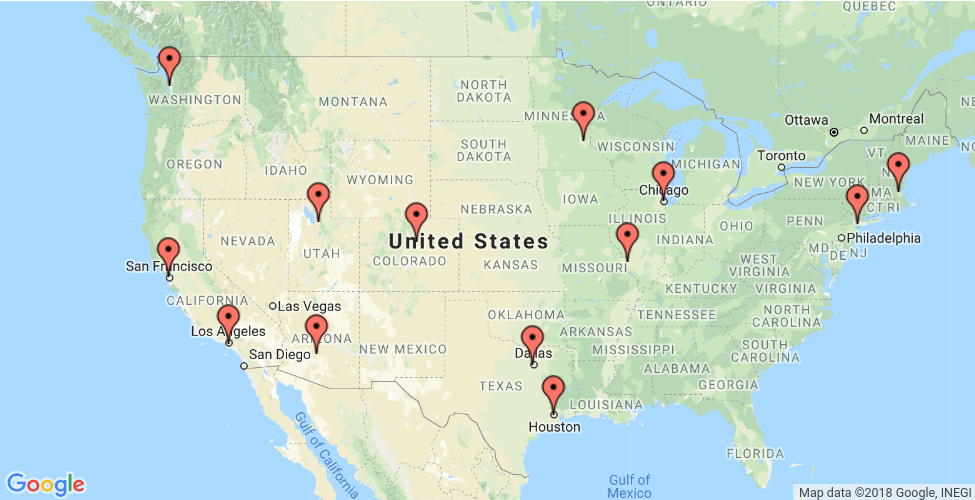
यह सेक्शन एक उदाहरण दिखाता है. इसमें, मैप पर बताई गई जगहों पर ट्रैवलिंग सेल्समैन प्रॉब्लम (टीएसपी) को हल करने का तरीका बताया गया है.
नीचे दिए सेक्शन में Python, C++, Java, और C# में प्रोग्राम दिखाए जाते हैं, जो OR-टूल का इस्तेमाल करके TSP का समाधान करते हैं
डेटा बनाएं
नीचे दिया गया कोड समस्या का डेटा बनाता है.
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
दूरी मैट्रिक्स एक ऐसी श्रेणी है जिसकी i, j एंट्री स्थान i से स्थान j और मील में दूरी है, जहां श्रेणी इंडेक्स इस क्रम में जगहों के मुताबिक हैं:
0. New York - 1. Los Angeles - 2. Chicago - 3. Minneapolis - 4. Denver - 5. Dallas
- 6. Seattle - 7. Boston - 8. San Francisco - 9. St. Louis - 10. Houston - 11. Phoenix - 12. Salt Lake City
डेटा में ये भी शामिल हैं:
- समस्या में वाहनों की संख्या, जो 1 है, क्योंकि यह TSP है. (वाहन की रूटिंग की समस्या (वीआरपी) के लिए, वाहनों की संख्या एक से ज़्यादा हो सकती है.)
- डिपो: रास्ते के लिए शुरू और खत्म होने की जगह. इस मामले में, डिपो 0 है, जो न्यूयॉर्क से मेल खाता है.
दूरी का मैट्रिक्स बनाने के दूसरे तरीके
इस उदाहरण में, दूरी के मैट्रिक्स को प्रोग्राम में साफ़ तौर पर दिखाया गया है. जगहों के बीच दूरियों का हिसाब लगाने के लिए भी फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है: उदाहरण के लिए, विमान में मौजूद पॉइंट के बीच यूक्लिडियन फ़ॉर्मूला. हालांकि, अभी भी लंबी दूरी की गणना करना और उन्हें मैट्रिक्स के तौर पर स्टोर करना ज़्यादा बेहतर होता है. हालांकि, रन टाइम के दौरान उनकी दूरियां कैलकुलेट करना आसान होता है. उदाहरण: एक सर्किट बोर्ड ड्रिल करने का एक उदाहरण देखें, जो इस तरह से दूरी की मैट्रिक्स बनाता है.
दूसरा विकल्प यह है कि रूटिंग से जुड़ी समस्या के लिए, डाइनैमिक तरीके से दूरी या यात्रा के समय का मैट्रिक्स बनाने के लिए, Google Maps DISTANCE मैट्रिक्स एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करें.
रूटिंग मॉडल बनाएं
प्रोग्राम के मुख्य सेक्शन में मौजूद इस कोड से, इंडेक्स मैनेजर (manager) और रूटिंग मॉडल (routing) तैयार होता है. यह तरीका, सॉल्वर के इंंडेक्स इंडेक्स (जिसे आप अनदेखा कर सकते हैं) को जगहों की संख्या में बदल देता है. स्थान की संख्याएं, दूरी के मैट्रिक्स के इंडेक्स से मेल खाती हैं.
Python
data = create_data_model()
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
C++
DataModel data;
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
RoutingModel routing(manager);
Java
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
C#
DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
RoutingIndexManager को दिए गए इनपुट:
- दूरी के मैट्रिक्स की लाइनों की संख्या, जो डिपो के साथ-साथ जगहों की संख्या होती है.
- समस्या में मौजूद वाहनों की संख्या.
- डिपो से जुड़ा नोड.
दूरी का कॉलबैक बनाएं
रूटिंग सॉल्वर का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, आपको दूरी (या सार्वजनिक परिवहन) कॉलबैक बनाना होगा: यह एक ऐसा फ़ंक्शन है जो जगहों की किसी भी जोड़ी को लेता है और उनके बीच की दूरी लौटाता है. ऐसा करने का सबसे आसान तरीका दूरी के मैट्रिक्स का इस्तेमाल करना है.
नीचे दिया गया फ़ंक्शन, कॉलबैक बनाता है और उसे सॉल्वर के साथ
transit_callback_index के तौर पर रजिस्टर करता है.
Python
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
C++
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
Java
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
C#
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
The callback accepts two indices, from_index and to_index, and returns the
corresponding entry of the distance matrix.
Set the cost of travel
The arc cost evaluator tells the solver how to calculate the cost of travel between any two locations — in other words, the cost of the edge (or arc) joining them in the graph for the problem. The following code sets the arc cost evaluator.
Python
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
इस उदाहरण में, आर्क लागत का मूल्यांकन करने वाला transit_callback_index है, जो सॉल्वर का डिस्टेंस कॉलबैक के लिए अंदरूनी संदर्भ है. इसका मतलब है कि दो जगहों के बीच
यात्रा का शुल्क सिर्फ़ उनके बीच की दूरी है.
हालांकि, सामान्य रूप से लागत में अन्य कारण भी शामिल हो सकते हैं.
आप routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfVehicle() तरीकों का इस्तेमाल करके, आर्क की लागत के कई समीक्षक भी तय कर सकते हैं. यह वैल्यू इस बात पर निर्भर करती है कि कौनसी गाड़ी किन जगहों पर जा रही है.
उदाहरण के लिए, अगर दोनों वाहनों की स्पीड अलग है, तो जगहों के बीच की दूरी को कार की रफ़्तार से भाग देने पर मिलने वाली दूरी तय की जा सकती है. दूसरे शब्दों में, यात्रा में लगने वाला समय.
खोज पैरामीटर सेट करें
नीचे दिया गया कोड, पहला समाधान खोजने के लिए डिफ़ॉल्ट खोज पैरामीटर और अनुमान का तरीका सेट करता है:
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
Java
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
C#
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
इस कोड की मदद से, समाधान की पहली रणनीति PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC पर सेट की जाती है. यह सॉल्वर के लिए शुरुआती रास्ता बनाती है. यह रूट, किनारों को बार-बार जोड़कर, उन्हें सबसे कम वज़न वाली फ़ील्ड में ले जाता है. इससे, वे डिपो के अलावा किसी अन्य नोड पर नहीं जाते हैं. अन्य विकल्पों के लिए, समाधान की पहली रणनीति देखें.
समाधान वाला प्रिंटर जोड़ें
यह फ़ंक्शन, सॉल्वर से मिला समाधान दिखाता है. फ़ंक्शन समाधान से रास्ता निकालता है और उसे कंसोल पर प्रिंट करता है.
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
फ़ंक्शन सबसे सही रास्ता और इसकी दूरी दिखाता है, जो ObjectiveValue() से मिलता है.
सॉल्यूशन को हल करें और प्रिंट करें
आखिर में, सॉल्वर को कॉल करें और सॉल्यूशन प्रिंट करें:
Python
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
C++
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
Java
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters); printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
C#
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
यह समाधान दिखाता है और सबसे अच्छा रास्ता दिखाता है.
प्रोग्राम चलाएं
इन प्रोग्राम को चलाने पर, ये आउटपुट दिखते हैं.
Objective: 7293 miles Route for vehicle 0: 0 -> 7 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 12 -> 6 -> 8 -> 1 -> 11 -> 10 -> 5 -> 9 -> 0
इस उदाहरण में, सिर्फ़ एक रास्ता है, क्योंकि यह टीएसपी है. हालांकि, वाहन की रूट करने से जुड़ी सामान्य समस्याओं में, समाधान में कई रास्ते शामिल हैं.
रास्तों को किसी सूची या अरे में सेव करें
समाधान को सीधे प्रिंट करने के विकल्प के रूप में, आप रास्ते (या वीआरपी के लिए रूट) को सूची या अरे में सेव कर सकते हैं. अगर आप बाद में इन रास्तों का इस्तेमाल करना चाहें, तो कर सकते हैं. उदाहरण के लिए, आप प्रोग्राम को अलग-अलग पैरामीटर के साथ कई बार चला सकते हैं. साथ ही, दिए गए सॉल्यूशन में फ़ाइल के रूट को तुलना के लिए सेव कर सकते हैं.
ये फ़ंक्शन समाधान में मौजूद रास्तों को किसी वीआरपी (शायद एक से ज़्यादा वाहनों के साथ) को सूची (Python) या श्रेणी (C++) के तौर पर सेव करते हैं.
Python
def get_routes(solution, routing, manager):
"""Get vehicle routes from a solution and store them in an array."""
# Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array whose
# i,j entry is the jth location visited by vehicle i along its route.
routes = []
for route_nbr in range(routing.vehicles()):
index = routing.Start(route_nbr)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
routes.append(route)
return routes
C++
std::vector<std::vector<int>> GetRoutes(const Assignment& solution,
const RoutingModel& routing,
const RoutingIndexManager& manager) {
// Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array, whose
// i, j entry is the node for the jth visit of vehicle i.
std::vector<std::vector<int>> routes(manager.num_vehicles());
// Get routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < manager.num_vehicles(); ++vehicle_id) {
int64_t index = routing.Start(vehicle_id);
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
}
}
return routes;
}
आप रूटिंग सेक्शन में किसी भी VRP उदाहरण में रूट पाने के लिए इन फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं.
यह कोड रास्तों को दिखाता है.
Python
routes = get_routes(solution, routing, manager)
# Display the routes.
for i, route in enumerate(routes):
print('Route', i, route)
C++
const std::vector⟨std::vector⟨int⟩⟩
routes = GetRoutes(*solution,
routing,
manager);
// Display the routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < routes.size(); ++vehicle_id) {
LOG(INFO) << "Route " << vehicle_id;
for (int j = 1; j < routes[vehicle_id].size(); ++j) {
LOG(INFO) << routes[vehicle_id][j];
}
}
मौजूदा उदाहरण के लिए, यह कोड नीचे दिए गए रास्ते को दिखाता है:
Route 0 [0, 7, 2, 3, 4, 12, 6, 8, 1, 11, 10, 5, 9, 0]
व्यायाम के तौर पर, आउटपुट को फ़ॉर्मैट करने के लिए ऊपर दिए गए कोड में उसी तरह से बदलाव करें जिस तरह आप प्रोग्राम के लिए सॉल्यूशन प्रिंटर डालते हैं.
प्रोग्राम पूरे करें
सभी टीएसपी प्रोग्राम नीचे दिखाए गए हैं.
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) between cities."""
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP using distance matrix. */
public class TspCities {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCities.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP using distance matrix.
/// </summary>
public class TspCities
{
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
उदाहरण: सर्किट बोर्ड ड्रिल करना
अगले उदाहरण में, एक ऑटोमेटेड बोर्ड के साथ सर्किट बोर्ड में ड्रिलिंग छेद शामिल हैं. समस्या यह है कि बोर्ड पर ड्रिल करने के लिए सबसे छोटा रास्ता ढूंढना होता है, ताकि सभी ज़रूरी छेद किए जा सकें. यह उदाहरण TSPLIB से लिया गया है. यह TSP से जुड़ी समस्याओं की एक लाइब्रेरी है.
यहां गड्ढों की जगहों का स्कैटर चार्ट दिया गया है:
ये सेक्शन ऐसे प्रोग्राम दिखाते हैं जो सॉल्वर के डिफ़ॉल्ट खोज पैरामीटर का इस्तेमाल करके, सर्किट बोर्ड से जुड़ी समस्या का अच्छा हल ढूंढते हैं. इसके बाद, हम खोज की रणनीति बदलकर बेहतर समाधान ढूंढने का तरीका दिखाएंगे.
डेटा बनाएं
इस समस्या के डेटा में, विमान में 280 बिंदु शामिल हैं, जो ऊपर दिए गए स्कैटर चार्ट में दिखाए गए हैं. प्रोग्राम, हवाई जहाज़ के बिंदुओं से मेल खाने वाले क्रम में जोड़े गए क्रम में डेटा बनाता है, जैसा कि नीचे दिखाया गया है.
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
दूरी के मैट्रिक्स की गणना करें
नीचे दिया गया फ़ंक्शन डेटा में किसी भी दो बिंदु के बीच इयूक्लिडीन दूरी की गणना करता है और उसे एक अरे में संग्रहित करता है. क्योंकि रूटिंग सॉल्वर पूर्णांकों पर काम करता है, फ़ंक्शन परिकलित दूरी को पूर्णांकों में बदल देता है. इस संख्या से सराउंडिंग पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ता है, लेकिन दूसरे मामलों में ऐसा हो सकता है. राउंडिंग में लगने वाली समस्याओं से बचने के लिए, दूरी के मैट्रिक्स को बढ़ाना देखें.
Python
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
C++
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
Java
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
दूरी का कॉलबैक जोड़ें
दूरी कॉलबैक बनाने वाला कोड पिछले उदाहरण के जैसा ही है. हालांकि, इस मामले में यह प्रोग्राम, फ़ंक्शन को कॉल करता है. यह फ़ंक्शन कॉलबैक को जोड़ने से पहले, डिस्टेंस मैट्रिक्स की गणना करता है.
Python
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
सॉल्यूशन प्रिंटर
ये फ़ंक्शन, कंसोल में समाधान को प्रिंट करते हैं. आउटपुट को और छोटा बनाने के लिए, फ़ंक्शन रूट में स्थानों के केवल इंडेक्स दिखाता है.
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
मुख्य फ़ंक्शन
मुख्य फ़ंक्शन और पिछले उदाहरण में मुख्य फ़ंक्शन एक जैसा है, लेकिन इसमें फ़ंक्शन का एक कॉल भी शामिल है, जो दूरी का मैट्रिक्स बनाता है.
प्रोग्राम को चलाना
सारे प्रोग्राम अगले सेक्शन में दिखाए जाते हैं. इस प्रोग्राम को चलाने पर, यह इस रूट को दिखाता है:
Total distance: 2790 Route of vehicle 0: 0 -> 1 -> 279 -> 2 -> 278 -> 277 -> 247 -> 248 -> 249 -> 246 -> 244 -> 243 -> 242 -> 241 -> 240 -> 239 -> 238 -> 237 -> 236 -> 235 -> 234 -> 233 -> 232 -> 231 -> 230 -> 245 -> 250 -> 229 -> 228 -> 227 -> 226 -> 225 -> 224 -> 223 -> 222 -> 221 -> 220 -> 219 -> 218 -> 217 -> 216 -> 215 -> 214 -> 213 -> 212 -> 211 -> 210 -> 209 -> 208 -> 251 -> 254 -> 255 -> 257 -> 256 -> 253 -> 252 -> 207 -> 206 -> 205 -> 204 -> 203 -> 202 -> 142 -> 141 -> 146 -> 147 -> 140 -> 139 -> 265 -> 136 -> 137 -> 138 -> 148 -> 149 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 178 -> 179 -> 180 -> 181 -> 182 -> 183 -> 184 -> 186 -> 185 -> 192 -> 196 -> 197 -> 198 -> 144 -> 145 -> 143 -> 199 -> 201 -> 200 -> 195 -> 194 -> 193 -> 191 -> 190 -> 189 -> 188 -> 187 -> 163 -> 164 -> 165 -> 166 -> 167 -> 168 -> 169 -> 171 -> 170 -> 172 -> 105 -> 106 -> 104 -> 103 -> 107 -> 109 -> 110 -> 113 -> 114 -> 116 -> 117 -> 61 -> 62 -> 63 -> 65 -> 64 -> 84 -> 85 -> 115 -> 112 -> 86 -> 83 -> 82 -> 87 -> 111 -> 108 -> 89 -> 90 -> 91 -> 102 -> 101 -> 100 -> 99 -> 98 -> 97 -> 96 -> 95 -> 94 -> 93 -> 92 -> 79 -> 88 -> 81 -> 80 -> 78 -> 77 -> 76 -> 74 -> 75 -> 73 -> 72 -> 71 -> 70 -> 69 -> 66 -> 68 -> 67 -> 57 -> 56 -> 55 -> 54 -> 53 -> 52 -> 51 -> 50 -> 49 -> 48 -> 47 -> 46 -> 45 -> 44 -> 43 -> 58 -> 60 -> 59 -> 42 -> 41 -> 40 -> 39 -> 38 -> 37 -> 36 -> 35 -> 34 -> 33 -> 32 -> 31 -> 30 -> 29 -> 124 -> 123 -> 122 -> 121 -> 120 -> 119 -> 118 -> 156 -> 157 -> 158 -> 173 -> 162 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 150 -> 151 -> 155 -> 152 -> 154 -> 153 -> 128 -> 129 -> 130 -> 131 -> 18 -> 19 -> 20 -> 127 -> 126 -> 125 -> 28 -> 27 -> 26 -> 25 -> 21 -> 24 -> 22 -> 23 -> 13 -> 12 -> 14 -> 11 -> 10 -> 9 -> 7 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 275 -> 274 -> 273 -> 272 -> 271 -> 270 -> 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 132 -> 133 -> 269 -> 268 -> 134 -> 135 -> 267 -> 266 -> 264 -> 263 -> 262 -> 261 -> 260 -> 258 -> 259 -> 276 -> 3 -> 4 -> 0
यहां इससे जुड़े रास्ते का ग्राफ़ दिया गया है:
OR-टूल लाइब्रेरी सामान्य कंप्यूटर पर एक सेकंड से भी कम समय में ऊपर दी गई जानकारी को बहुत जल्दी ढूंढ लेती है. ऊपर की यात्रा की कुल अवधि 2790 है.
प्रोग्राम पूरे करें
यहां सर्किट बोर्ड के उदाहरण दिए गए हैं.
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) on a circuit board."""
import math
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["locations"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.locations.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP. */
public class TspCircuitBoard {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCircuitBoard.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.locations.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP.
/// A description of the problem can be found here:
/// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesperson_problem.
/// </summary>
public class TspCircuitBoard
{
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.Locations.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Define cost of each arc.
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
खोज की रणनीति बदलना
रूटिंग सॉल्वर हमेशा TSP के लिए सबसे बेहतर समाधान नहीं देता है, क्योंकि रूटिंग से जुड़ी समस्याएं हल होने में ज़्यादा मुश्किल होती हैं. उदाहरण के लिए, पिछले उदाहरण में दिया गया समाधान सबसे अच्छा रास्ता नहीं है.
एक बेहतर समाधान खोजने के लिए, आप गाइडेड स्थानीय खोज नाम की एक ज़्यादा बेहतर खोज रणनीति का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं, जो एक समाधान है जो समाधान को स्थानीय कम से कम से बचता है. यह ऐसा समाधान है जो आस-पास के सभी रास्तों से छोटा होता है, लेकिन ग्लोबल कम से कम नहीं. स्थानीय मिनिमम से दूर जाने के बाद, सॉल्वर खोज जारी रखता है.
नीचे दिए गए उदाहरणों में दिखाया गया है कि सर्किट बोर्ड के उदाहरण के लिए स्थानीय गाइड वाली खोज कैसे सेट की जाती है.
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
search_parameters.log_search = True
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_local_search_metaheuristic(
LocalSearchMetaheuristic::GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH);
searchParameters.mutable_time_limit()->set_seconds(30);
search_parameters.set_log_search(true);
Java
प्रोग्राम की शुरुआत में, यह `इंपोर्ट` स्टेटमेंट जोड़ें:import com.google.protobuf.Duration;इसके बाद, खोज पैरामीटर इस तरह सेट करें:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.setLocalSearchMetaheuristic(LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Value.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
.setTimeLimit(Duration.newBuilder().setSeconds(30).build())
.setLogSearch(true)
.build();
C#
प्रोग्राम की शुरुआत में यह लाइन जोड़ें:using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes; // Durationइसके बाद, खोज पैरामीटर इस तरह सेट करें:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
searchParameters.LocalSearchMetaheuristic = LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Types.Value.GuidedLocalSearch;
searchParameters.TimeLimit = new Duration { Seconds = 30 };
searchParameters.LogSearch = true;
दूसरी स्थानीय खोज रणनीतियों के लिए, स्थानीय खोज विकल्प देखें.
ऊपर दिए गए उदाहरण, खोज के लिए लॉग इन करने की सुविधा भी चालू करते हैं. हालांकि, लॉग इन करना ज़रूरी नहीं है, लेकिन डीबग करने में यह मददगार साबित हो सकता है.
ऊपर बताए गए बदलाव करने के बाद, जब आप इस प्रोग्राम को चलाएंगे, तब आपको नीचे दिया गया तरीका दिखेगा. यह समाधान पिछले सेक्शन में दिखाए गए समाधान से छोटा है.
Objective: 2672 Route: 0 -> 3 -> 276 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 -> 14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 23 -> 22 -> 24 -> 21 -> 25 -> 26 -> 27 -> 28 -> 125 -> 126 -> 127 -> 20 -> 19 -> 130 -> 129 -> 128 -> 153 -> 154 -> 152 -> 155 -> 151 -> 150 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 180 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 158 -> 157 -> 156 -> 118 -> 119 -> 120 -> 121 -> 122 -> 123 -> 124 -> 29 -> 30 -> 31 -> 32 -> 33 -> 34 -> 35 -> 36 -> 37 -> 38 -> 39 -> 40 -> 41 -> 42 -> 59 -> 60 -> 58 -> 43 -> 44 -> 45 -> 46 -> 47 -> 48 -> 49 -> 50 -> 51 -> 52 -> 53 -> 54 -> 55 -> 56 -> 57 -> 67 -> 68 -> 66 -> 69 -> 70 -> 71 -> 72 -> 73 -> 75 -> 74 -> 76 -> 77 -> 78 -> 80 -> 81 -> 88 -> 79 -> 92 -> 93 -> 94 -> 95 -> 96 -> 97 -> 98 -> 99 -> 100 -> 101 -> 102 -> 91 -> 90 -> 89 -> 108 -> 111 -> 87 -> 82 -> 83 -> 86 -> 112 -> 115 -> 85 -> 84 -> 64 -> 65 -> 63 -> 62 -> 61 -> 117 -> 116 -> 114 -> 113 -> 110 -> 109 -> 107 -> 103 -> 104 -> 105 -> 106 -> 173 -> 172 -> 171 -> 170 -> 169 -> 168 -> 167 -> 166 -> 165 -> 164 -> 163 -> 162 -> 187 -> 188 -> 189 -> 190 -> 191 -> 192 -> 185 -> 186 -> 184 -> 183 -> 182 -> 181 -> 179 -> 178 -> 149 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 266 -> 267 -> 135 -> 134 -> 268 -> 269 -> 133 -> 132 -> 131 -> 18 -> 17 -> 16 -> 15 -> 270 -> 271 -> 272 -> 273 -> 274 -> 275 -> 259 -> 258 -> 260 -> 261 -> 262 -> 263 -> 264 -> 265 -> 139 -> 140 -> 147 -> 146 -> 141 -> 142 -> 145 -> 144 -> 198 -> 197 -> 196 -> 193 -> 194 -> 195 -> 200 -> 201 -> 199 -> 143 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 206 -> 207 -> 252 -> 253 -> 256 -> 257 -> 255 -> 254 -> 251 -> 208 -> 209 -> 210 -> 211 -> 212 -> 213 -> 214 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 218 -> 219 -> 220 -> 221 -> 222 -> 223 -> 224 -> 225 -> 226 -> 227 -> 232 -> 233 -> 234 -> 235 -> 236 -> 237 -> 230 -> 231 -> 228 -> 229 -> 250 -> 245 -> 238 -> 239 -> 240 -> 241 -> 242 -> 243 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 248 -> 247 -> 277 -> 278 -> 2 -> 279 -> 1 -> 0
खोज के ज़्यादा विकल्पों के लिए, रूटिंग के विकल्प देखें.
सबसे अच्छे एल्गोरिदम अब नियमित रूप से हज़ारों नोड के साथ टीएसपी इंस्टेंस को हल कर सकते हैं. {0}लेखन के समय रिकॉर्ड pla85900TSPLIB, 85,900 नोड वाला VLSI ऐप्लिकेशन होता है. लाखों नोड वाले कुछ मामलों में, समाधानों को इष्टतम टूर से 1% कम मिलने की गारंटी है.)
दूरी के मैट्रिक्स को बढ़ाना
क्योंकि रूटिंग सॉल्वर पूर्णांकों पर काम करता है, अगर आपके दूरी के मैट्रिक्स में गैर-पूर्णांक प्रविष्टियां हैं, तो आपको दूरियों को पूर्णांक में बदलना होगा. अगर कुछ दूरियां छोटी होती हैं, तो राउंडिंग उस समाधान को प्रभावित कर सकती है.
राउंडिंग में किसी भी समस्या से बचने के लिए, scale दूरी के मैट्रिक्स किए जा सकते हैं: मैट्रिक्स की सभी प्रविष्टियों को एक बड़ी संख्या से गुणा करें — जैसे 100. यह किसी भी रास्ते की लंबाई को 100 के फ़ैक्टर से गुणा कर देता है, लेकिन हल नहीं बदलता. इसका
इसका लाभ यह है कि अब मैट्रिक्स की एंट्री को राउंड ऑफ़ करने पर, राउंडिंग में
दूरी के मुकाबले बहुत कम (जो कि 0.5 से ज़्यादा नहीं हो सकती) है. इसलिए, सॉल्यूशन पर इसका कोई असर नहीं पड़ेगा.
दूरी के मैट्रिक्स को स्केल करने पर, आपको समाधान प्रिंटर को बदलना होगा. इसके लिए, आपको लंबाई की स्केलिंग के फ़ैक्टर को स्केलिंग फ़ैक्टर से भाग देना होगा. इससे, आपको मापी गई दूरी दिखेगी.
