Earth Engine에서 벡터에서 래스터로 보간하면 FeatureCollection에서 Image이 생성됩니다. 특히 Earth Engine은 지형지물의 속성에 저장된 숫자 데이터를 사용하여 지형지물 외부의 새 위치에서 값을 보간합니다. 보간 결과 지정된 거리까지 보간된 값의 연속적인 Image가 생성됩니다.
역거리 가중치 보간
Earth Engine의 역거리 가중치 (IDW) 함수는 Basso et al. (1999)에 설명된 메서드를 기반으로 합니다. 역거리에 감쇠 계수 (gamma)의 형태로 추가 컨트롤 매개변수가 추가됩니다. 다른 매개변수로는 보간할 속성의 평균 및 표준 편차와 보간할 최대 범위 거리가 있습니다. 다음 예에서는 원래 래스터 데이터 세트의 공간 간격을 메우기 위해 보간된
메탄 농도 표면을 만듭니다. FeatureCollection는 2주간의 메탄 합성물을 샘플링하여 생성됩니다.
// Import two weeks of S5P methane and composite by mean. var ch4 = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S5P/OFFL/L3_CH4') .select('CH4_column_volume_mixing_ratio_dry_air') .filterDate('2019-08-01', '2019-08-15') .mean() .rename('ch4'); // Define an area to perform interpolation over. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Polygon( [[[-95.68487605978851, 43.09844605027055], [-95.68487605978851, 37.39358590079781], [-87.96148738791351, 37.39358590079781], [-87.96148738791351, 43.09844605027055]]], null, false); // Sample the methane composite to generate a FeatureCollection. var samples = ch4.addBands(ee.Image.pixelLonLat()) .sample({region: aoi, numPixels: 1500, scale:1000, projection: 'EPSG:4326'}) .map(function(sample) { var lat = sample.get('latitude'); var lon = sample.get('longitude'); var ch4 = sample.get('ch4'); return ee.Feature(ee.Geometry.Point([lon, lat]), {ch4: ch4}); }); // Combine mean and standard deviation reducers for efficiency. var combinedReducer = ee.Reducer.mean().combine({ reducer2: ee.Reducer.stdDev(), sharedInputs: true}); // Estimate global mean and standard deviation from the points. var stats = samples.reduceColumns({ reducer: combinedReducer, selectors: ['ch4']}); // Do the interpolation, valid to 70 kilometers. var interpolated = samples.inverseDistance({ range: 7e4, propertyName: 'ch4', mean: stats.get('mean'), stdDev: stats.get('stdDev'), gamma: 0.3}); // Define visualization arguments. var band_viz = { min: 1800, max: 1900, palette: ['0D0887', '5B02A3', '9A179B', 'CB4678', 'EB7852', 'FBB32F', 'F0F921']}; // Display to map. Map.centerObject(aoi, 7); Map.addLayer(ch4, band_viz, 'CH4'); Map.addLayer(interpolated, band_viz, 'CH4 Interpolated');
range 매개변수에 지정된 대로 가장 가까운 측정소에서 최대 70km까지만 보간이 적용됩니다.
크리깅
Kriging은 반변동의 모델링된 추정치를 사용하여 알려진 위치의 값을 최적으로 조합한 보간 값의 이미지를 만드는 보간 방법입니다. 크리깅 추정기에는 알려진 데이터 포인트에 맞는 반변동 그래프의 모양을 설명하는 매개변수가 필요합니다. 이러한 매개변수는 그림 1에 설명되어 있습니다.
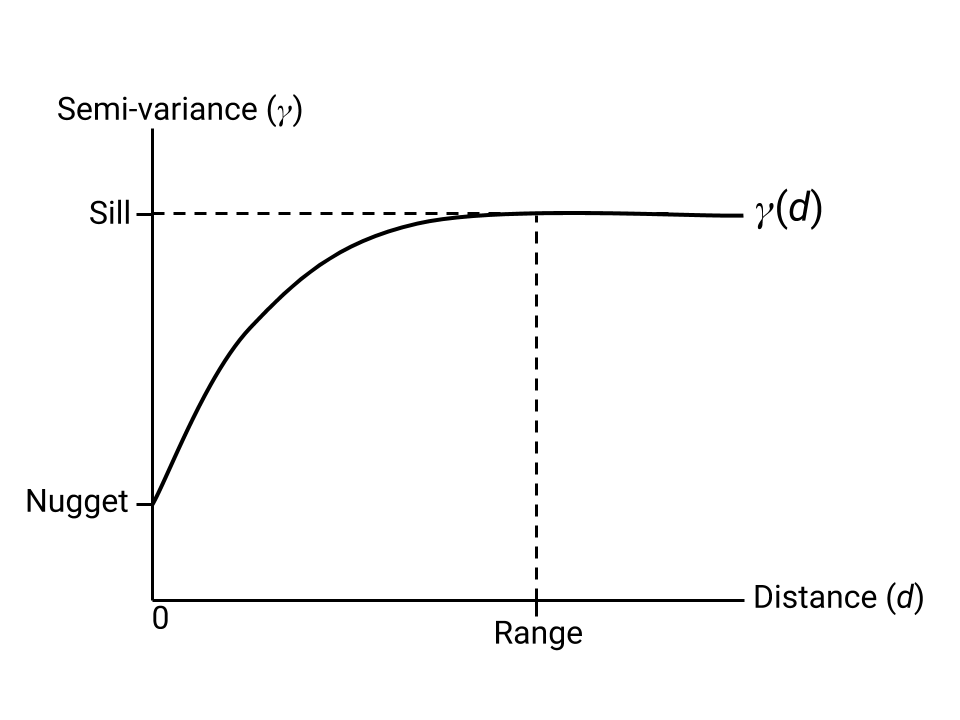
nugget, sill, range 매개변수
다음 예에서는 임의의 위치에서 해수면 온도 (SST) 이미지를 샘플링한 다음 Kriging을 사용하여 샘플에서 SST를 보간합니다.
// Load an image of sea surface temperature (SST). var sst = ee.Image('NOAA/AVHRR_Pathfinder_V52_L3/20120802025048') .select('sea_surface_temperature') .rename('sst') .divide(100); // Define a geometry in which to sample points var geometry = ee.Geometry.Rectangle([-65.60, 31.75, -52.18, 43.12]); // Sample the SST image at 1000 random locations. var samples = sst.addBands(ee.Image.pixelLonLat()) .sample({region: geometry, numPixels: 1000}) .map(function(sample) { var lat = sample.get('latitude'); var lon = sample.get('longitude'); var sst = sample.get('sst'); return ee.Feature(ee.Geometry.Point([lon, lat]), {sst: sst}); }); // Interpolate SST from the sampled points. var interpolated = samples.kriging({ propertyName: 'sst', shape: 'exponential', range: 100 * 1000, sill: 1.0, nugget: 0.1, maxDistance: 100 * 1000, reducer: 'mean', }); var colors = ['00007F', '0000FF', '0074FF', '0DFFEA', '8CFF41', 'FFDD00', 'FF3700', 'C30000', '790000']; var vis = {min:-3, max:40, palette: colors}; Map.setCenter(-60.029, 36.457, 5); Map.addLayer(interpolated, vis, 'Interpolated'); Map.addLayer(sst, vis, 'Raw SST'); Map.addLayer(samples, {}, 'Samples', false);
보간을 실행할 근방의 크기는 maxDistance 매개변수로 지정됩니다. 크기가 클수록 출력이 더 매끄러워지지만 계산 속도는 느려집니다.